Practice Midterm 1
... 20. How would the passengers on the spaceship view our clocks? A) Time is the same for everyone. B) Our clocks are going fast. C) Our clocks are going slow. D) Our clocks are going at the same rate as theirs. E) They can’t see our clocks, but we can see theirs. 21. Kepler’s second law, which states ...
... 20. How would the passengers on the spaceship view our clocks? A) Time is the same for everyone. B) Our clocks are going fast. C) Our clocks are going slow. D) Our clocks are going at the same rate as theirs. E) They can’t see our clocks, but we can see theirs. 21. Kepler’s second law, which states ...
Regents Review
... the sun (Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars). They are all rocky and similar to Earth in size, composition and density. • Jovian Planets: further away (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune), gaseous with a small solid core. Massive but less dense! ...
... the sun (Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars). They are all rocky and similar to Earth in size, composition and density. • Jovian Planets: further away (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune), gaseous with a small solid core. Massive but less dense! ...
The Celestial E-Sphere
... The first outing for the Celestial E-Sphere was at Astrofest in February 2007. Scores of attendees asked about the program making very admiring comments. Several of followed up since and asked for copies. In all cases where there has been feedback it has been very positive. Some of the lecturers and ...
... The first outing for the Celestial E-Sphere was at Astrofest in February 2007. Scores of attendees asked about the program making very admiring comments. Several of followed up since and asked for copies. In all cases where there has been feedback it has been very positive. Some of the lecturers and ...
Celestial Objects
... Precession 6 – The Earth behaves somewhat like a spinning top, causing the axis of rotation to trace out a circle. This slow conical motion of the Earth’s axis of rotation is called precession, and is due to the gravitational effects of the Sun and Moon on the Earth’s equatorial bulge. Precession sl ...
... Precession 6 – The Earth behaves somewhat like a spinning top, causing the axis of rotation to trace out a circle. This slow conical motion of the Earth’s axis of rotation is called precession, and is due to the gravitational effects of the Sun and Moon on the Earth’s equatorial bulge. Precession sl ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Measuring distances to stars • Measure parallax – the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. • Knowing the angle that the star’s position changes and the size of Earth’s orbit, astronomers can calculate the distance of the star from earth. ...
... Measuring distances to stars • Measure parallax – the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. • Knowing the angle that the star’s position changes and the size of Earth’s orbit, astronomers can calculate the distance of the star from earth. ...
The Solar System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Satellites to Venus • 1970’s Russia/Soviet Union sent the Venera probes that photographed and mapped the surface • In 1995 the United States probe Magellan also mapped the surface in ...
... Satellites to Venus • 1970’s Russia/Soviet Union sent the Venera probes that photographed and mapped the surface • In 1995 the United States probe Magellan also mapped the surface in ...
1 month - Otterbein
... – Using a ruler marked in mm, we round to the nearest marking – at most off by half a division, or 0.5 mm – Cite a measurement of 15 mm as 15 0.5 mm to indicate that the real value of the length is likely to be anywhere between 14.5 mm and 15.5 mm – If a theory predicts a value of 15.2 mm, then a ...
... – Using a ruler marked in mm, we round to the nearest marking – at most off by half a division, or 0.5 mm – Cite a measurement of 15 mm as 15 0.5 mm to indicate that the real value of the length is likely to be anywhere between 14.5 mm and 15.5 mm – If a theory predicts a value of 15.2 mm, then a ...
Astronomy Study Guide and Key Astronomy Study Guide
... line (in that order). This is the alignment that creates a full moon…when the side of the Moon that faces the Earth is also the side that is lit up by the Sun. If a Solar Eclipse is happening, what phase must the Moon be in? Why? A Solar Eclipse is when the Moon’s shadow falls on the Earth. For that ...
... line (in that order). This is the alignment that creates a full moon…when the side of the Moon that faces the Earth is also the side that is lit up by the Sun. If a Solar Eclipse is happening, what phase must the Moon be in? Why? A Solar Eclipse is when the Moon’s shadow falls on the Earth. For that ...
In your own words explain what the following terms
... 3. Describe and sketch the set-up of and annotate one projection method and one filtered method for safely viewing the sun. 4. Convert 80.0 km/hr to ft/s, record your answer using significant figures. 5. The Earth is approximately 12 600km in diameter, the Moon is approximately 3 600km in diameter, ...
... 3. Describe and sketch the set-up of and annotate one projection method and one filtered method for safely viewing the sun. 4. Convert 80.0 km/hr to ft/s, record your answer using significant figures. 5. The Earth is approximately 12 600km in diameter, the Moon is approximately 3 600km in diameter, ...
Celestial Motions - Georgia State University
... • Why do we see phases of the Moon? – Half the Moon is lit by the Sun; half is in shadow, and its appearance to us is determined by the relative positions of Sun, Moon, and Earth ...
... • Why do we see phases of the Moon? – Half the Moon is lit by the Sun; half is in shadow, and its appearance to us is determined by the relative positions of Sun, Moon, and Earth ...
Our local neighbourhood – The Solar System (PPT file, 6.12 MB)
... Many Kuiper Belt objects, exist in what is believed to be a vast shell of icy and rocky objects that live at the very edge of our solar system. ...
... Many Kuiper Belt objects, exist in what is believed to be a vast shell of icy and rocky objects that live at the very edge of our solar system. ...
Ch 8.3 - The Solar System
... - Without the use of an optical aid, we can see Venus, Mars, and Jupiter at night. - The inner solar system consists of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, Terrestrial Planets. - The giant planets, beyond Mars are; Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, make up the outer Solar System. These are gaseous ...
... - Without the use of an optical aid, we can see Venus, Mars, and Jupiter at night. - The inner solar system consists of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, Terrestrial Planets. - The giant planets, beyond Mars are; Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, make up the outer Solar System. These are gaseous ...
Link to Notes - Coweta County Schools
... moon’s gravity on different sides of the Earth Moon matters more because it’s closer, so the difference in pull is more Sun does help though, since it’s mass is so large Larger tides occur when sun and moon line up (spring tides), smaller ones occur when they are in opposition (neap tides) ...
... moon’s gravity on different sides of the Earth Moon matters more because it’s closer, so the difference in pull is more Sun does help though, since it’s mass is so large Larger tides occur when sun and moon line up (spring tides), smaller ones occur when they are in opposition (neap tides) ...
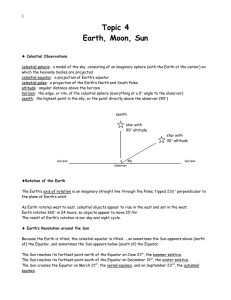
Topic 4: Sun, Earth, Moon and the Solar System
... Essential Questions: How does space exploration involve scientists from many different fields? How does classifying stars help scientists to understand the universe? Why is scientific argumentation necessary in scientific inquiry and what role does it play in the generation and validation of scienti ...
... Essential Questions: How does space exploration involve scientists from many different fields? How does classifying stars help scientists to understand the universe? Why is scientific argumentation necessary in scientific inquiry and what role does it play in the generation and validation of scienti ...
Final Exam Space Unit Review
... Azimuth: angle clockwise from North, the direction we must face to see the star (i.e. 180oS or “at an azimuth of 180oS). Azimuth coordinates MUST have degrees PLUS direction. Do the 3 practice problems on pg. 359 and the Alt-Azimuth Coordinates Practice Sheet (BLM 5Draw and label “altitude” and “a ...
... Azimuth: angle clockwise from North, the direction we must face to see the star (i.e. 180oS or “at an azimuth of 180oS). Azimuth coordinates MUST have degrees PLUS direction. Do the 3 practice problems on pg. 359 and the Alt-Azimuth Coordinates Practice Sheet (BLM 5Draw and label “altitude” and “a ...
Lecture - UMass Amherst
... 1. The Sun would hold 1.3 million Earths. i.e. the radius of the Sun is about 100 times that of the Earth. 2. There are ~100 billion "Suns" in a galaxy like our ...
... 1. The Sun would hold 1.3 million Earths. i.e. the radius of the Sun is about 100 times that of the Earth. 2. There are ~100 billion "Suns" in a galaxy like our ...
Everything from Velocity, Seasons, Tides
... Sun, it can never appear to be far away from the Sun in the sky. We can’t see it in the day because Sunlight blocks it out, but we can see it as the Sun either sets or rises Mercury behaves the same way, but Venus is much brighter ...
... Sun, it can never appear to be far away from the Sun in the sky. We can’t see it in the day because Sunlight blocks it out, but we can see it as the Sun either sets or rises Mercury behaves the same way, but Venus is much brighter ...
The Seasons
... moving faster during the winter, it takes a shorter time to travel ¼ the way around the sun. Most people would expect that the earth is closer to the sun during the summer and farther from the sun in the winter. As you have seen this is not true. What factor is responsible for the degree of heating ...
... moving faster during the winter, it takes a shorter time to travel ¼ the way around the sun. Most people would expect that the earth is closer to the sun during the summer and farther from the sun in the winter. As you have seen this is not true. What factor is responsible for the degree of heating ...
Chapter 2: The Copernican Revolution
... Copernicus published his great work, De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium) and the early 17th century. Many astronomers used Copernicus’s system, but under the assumption that the earth’s motion was a mathematical fiction rather than physically real. No books supporting the Copernican view were ...
... Copernicus published his great work, De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium) and the early 17th century. Many astronomers used Copernicus’s system, but under the assumption that the earth’s motion was a mathematical fiction rather than physically real. No books supporting the Copernican view were ...
File - Earth and Environmental Science and Biology
... to explain aspects of a person's personality and predict future events in their life based on the positions of the sun, moon, and other planetary objects at the time of their birth. ...
... to explain aspects of a person's personality and predict future events in their life based on the positions of the sun, moon, and other planetary objects at the time of their birth. ...
Astronomical Constants
... 27) Circle the seven planets of the ancient world from the alphabetic list presented below. Earth Jupiter Mars ...
... 27) Circle the seven planets of the ancient world from the alphabetic list presented below. Earth Jupiter Mars ...
doc - Discover Earth Science
... 1. Tides - the rhythmic rise and fall of sea level 2. There are 2 high tides and 2 low tides every 24 hours -roughly a. one high tide (direct high tide) is caused by the Moon’s gravitational pull on the ocean on the side of the Earth facing the Moon b. one high tide (indirect high tide) is caused by ...
... 1. Tides - the rhythmic rise and fall of sea level 2. There are 2 high tides and 2 low tides every 24 hours -roughly a. one high tide (direct high tide) is caused by the Moon’s gravitational pull on the ocean on the side of the Earth facing the Moon b. one high tide (indirect high tide) is caused by ...
2b. Which of Kepler`s laws did this illustrate? (State the law – don`t
... Follow all the procedures described below. Write answers on a separate sheet or enter your descriptions and answers directly below the questions using italics or bold. Descriptions and answers must be in complete sentences. ...
... Follow all the procedures described below. Write answers on a separate sheet or enter your descriptions and answers directly below the questions using italics or bold. Descriptions and answers must be in complete sentences. ...
To learn how the shape and period of... To learn how the shape of the orbit... Gravity, Orbits and Kepler’s Laws
... Follow all the procedures described below. Write answers on a separate sheet or enter your descriptions and answers directly below the questions using italics or bold. Descriptions and answers must be in complete sentences. ...
... Follow all the procedures described below. Write answers on a separate sheet or enter your descriptions and answers directly below the questions using italics or bold. Descriptions and answers must be in complete sentences. ...
Topic 4: Earth-Moon-Sun
... “catch up” with the Moon’s orbit, the Moon rises 50 minutes later each day. Moon’s period of rotation = 27 days Moon’s period of revolution = 27 days Because its period of rotation equals its period of revolution, there is only one side of the Moon always seen from Earth. Moon phases are the chang ...
... “catch up” with the Moon’s orbit, the Moon rises 50 minutes later each day. Moon’s period of rotation = 27 days Moon’s period of revolution = 27 days Because its period of rotation equals its period of revolution, there is only one side of the Moon always seen from Earth. Moon phases are the chang ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.