List of Astronomical Events for 2016 - Science
... Planetary events Oppositions (outer planets only) – Alignments between the Sun, Earth and an outer planet such as Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus or Neptune. During this time the planet is near its closest position to Earth and is seen at its brightest and fullest. The planets will mainly be visible ...
... Planetary events Oppositions (outer planets only) – Alignments between the Sun, Earth and an outer planet such as Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus or Neptune. During this time the planet is near its closest position to Earth and is seen at its brightest and fullest. The planets will mainly be visible ...
Chap 11 Characterizing Stars v2
... The H-R diagram reveals the existence of four major groupings of stars: main-sequence stars, giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs. The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between a main-sequence star’s mass and the total energy it emits. Distances to stars can be determined usin ...
... The H-R diagram reveals the existence of four major groupings of stars: main-sequence stars, giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs. The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between a main-sequence star’s mass and the total energy it emits. Distances to stars can be determined usin ...
26A Phases of the Moon
... Notice whether or not the black sticker remains in the dark throughout the cycle. 7. Switch roles within your group until everyone has observed the lunar cycle again. ...
... Notice whether or not the black sticker remains in the dark throughout the cycle. 7. Switch roles within your group until everyone has observed the lunar cycle again. ...
Opportunity Approaching Mountain Climbing Goal and Signs of
... brightest stars of summer, Vega and Arcturus, are high overhead toward the east and southwest, respectively. Far below Arcturus are the planet Saturn and, to its lower right, Spica. Nearly that high in the southeast is the orange-red supergiant Antares, amid fainter stars of upper Scorpius. Friday, ...
... brightest stars of summer, Vega and Arcturus, are high overhead toward the east and southwest, respectively. Far below Arcturus are the planet Saturn and, to its lower right, Spica. Nearly that high in the southeast is the orange-red supergiant Antares, amid fainter stars of upper Scorpius. Friday, ...
reach for the stars
... older Pop II stars formed when there was little in the Universe but H and He. After these stars had fused H and He into heavier elements, they often scattered material back into space (through supernovae and planetary nebula). The younger Pop I stars then formed out of gaseous clouds of H, He, and t ...
... older Pop II stars formed when there was little in the Universe but H and He. After these stars had fused H and He into heavier elements, they often scattered material back into space (through supernovae and planetary nebula). The younger Pop I stars then formed out of gaseous clouds of H, He, and t ...
Formation of the Solar System Section 28.1
... Scientific theories on the origin of the solar system must explain observed facts, such as the shape of the solar system, differences among the planets, and the nature of the oldest planetary surfaces—asteroids, meteorites, and comets. ...
... Scientific theories on the origin of the solar system must explain observed facts, such as the shape of the solar system, differences among the planets, and the nature of the oldest planetary surfaces—asteroids, meteorites, and comets. ...
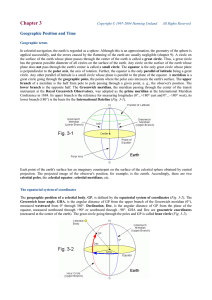
The Geographic Position of a Celestial Body
... Declinations of the planets and the moon are also influenced by the inclinations of their own orbits to the ecliptic. The plane of the moon's orbit, for example, is inclined to the ecliptic by approx. 5° and makes a tumbling movement (precession, see below) with a cycle of 18.6 years (Saros cycle). ...
... Declinations of the planets and the moon are also influenced by the inclinations of their own orbits to the ecliptic. The plane of the moon's orbit, for example, is inclined to the ecliptic by approx. 5° and makes a tumbling movement (precession, see below) with a cycle of 18.6 years (Saros cycle). ...
Sky & Astronomy - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... • The 4 moons of Jupiter are Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto • They are called Galilean satellites in Galileo’s honor • Jupiter and its moons form a mini-model of the heliocentric system • The moons are not moving around the Earth, but are centered on Jupiter • He concluded that perhaps other obj ...
... • The 4 moons of Jupiter are Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto • They are called Galilean satellites in Galileo’s honor • Jupiter and its moons form a mini-model of the heliocentric system • The moons are not moving around the Earth, but are centered on Jupiter • He concluded that perhaps other obj ...
H-R Diagram
... (3) 6. Our sun has a temperature of 6000 K and an absolute magnitude of + 4.7. Use an asterisk (*) to show the location of the sun on your diagram. To what group does the sun belong? (4) 7. Betelgeuse is 150 parsecs away and has a surface temperature of only 3200 K. Yet Betelgeuse is one of the brig ...
... (3) 6. Our sun has a temperature of 6000 K and an absolute magnitude of + 4.7. Use an asterisk (*) to show the location of the sun on your diagram. To what group does the sun belong? (4) 7. Betelgeuse is 150 parsecs away and has a surface temperature of only 3200 K. Yet Betelgeuse is one of the brig ...
ILÍDIO LOPES ()
... The study of magnetic activity in solartype stars is of fundamental importance for stellar structure and evolution. It is ...
... The study of magnetic activity in solartype stars is of fundamental importance for stellar structure and evolution. It is ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... 3) supernovae destroy the less massive stars in the spiral arms 4) there is too high a density in the spiral arms to create low-mass stars ...
... 3) supernovae destroy the less massive stars in the spiral arms 4) there is too high a density in the spiral arms to create low-mass stars ...
15-3 Notes: Galaxies
... Irregular galaxies are galaxies that have no definite shape. The smallest irregular galaxies have only about 10 million stars. The largest irregular galaxies can contain several billion stars. Galaxies contain not only stars and planetary systems. Large features, such as gas clouds and star clusters ...
... Irregular galaxies are galaxies that have no definite shape. The smallest irregular galaxies have only about 10 million stars. The largest irregular galaxies can contain several billion stars. Galaxies contain not only stars and planetary systems. Large features, such as gas clouds and star clusters ...
the life cycles of stars (5) - U3A Bendigo Courses / Activities
... HEAVY WEIGHT STARS with zero age mass more than 8 M O The main sequence life burning hydrogen lasts only 100 million years instead of 10 billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressu ...
... HEAVY WEIGHT STARS with zero age mass more than 8 M O The main sequence life burning hydrogen lasts only 100 million years instead of 10 billion for the sun. These are O and B type stars. Even before leaving the main sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressu ...
2010-02 LAAS Bulletin I - Los Angeles Astronomical Society
... from ours. And as you can see from figure 1 at left, we can look forward to far warmer temperatures than that. Figure 2 below left expands the temperature scale around the age of 12 billion years, showing planetary temperature, as the sun becomes first a red giant star, and then an asymptotic giant ...
... from ours. And as you can see from figure 1 at left, we can look forward to far warmer temperatures than that. Figure 2 below left expands the temperature scale around the age of 12 billion years, showing planetary temperature, as the sun becomes first a red giant star, and then an asymptotic giant ...
File
... parallax method of distance measurement only works for “near” stars. A special type of pulsating stars, Cepheid variables, has an absolute brightness correlated to its pulsation period, which can be used to determine distance. Much of the analysis of Cepheid variable stars was performed by American ...
... parallax method of distance measurement only works for “near” stars. A special type of pulsating stars, Cepheid variables, has an absolute brightness correlated to its pulsation period, which can be used to determine distance. Much of the analysis of Cepheid variable stars was performed by American ...
Astr604-Ch1
... 1.2.3 Masses and radii of stars The mass of a star can be measured only by its gravitational effect. Under certain conditions, the mass of star that is member of a binary system can calculate based on spectral line shifts. The radii of a number of stars have been found directly from measurement of t ...
... 1.2.3 Masses and radii of stars The mass of a star can be measured only by its gravitational effect. Under certain conditions, the mass of star that is member of a binary system can calculate based on spectral line shifts. The radii of a number of stars have been found directly from measurement of t ...
Solutions to End-of-Chapter Problems (Chapter 2)
... The Think About It and See It For Yourself questions are not numbered in the book, so we list them in the order in which they appear, keyed by section number. ...
... The Think About It and See It For Yourself questions are not numbered in the book, so we list them in the order in which they appear, keyed by section number. ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.