04_Home_Science3 (04_Home_Science3)
... D. roll each ball down a hill and see which ball rolls the fastest 18. The day during the year when the Northern Hemisphere receives the greatest amount of sunlight is called the A. fall equinox. B. spring equinox. C. winter solstice. D. summer solstice. 19. If you are on a seesaw and want your frie ...
... D. roll each ball down a hill and see which ball rolls the fastest 18. The day during the year when the Northern Hemisphere receives the greatest amount of sunlight is called the A. fall equinox. B. spring equinox. C. winter solstice. D. summer solstice. 19. If you are on a seesaw and want your frie ...
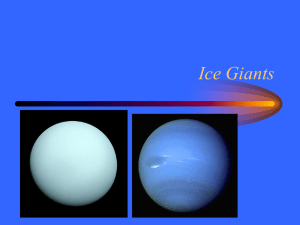
Team 1:The Outer Planets and Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors
... • The sun’s interior consists of the core, the radiation zone, and the convection zone. • The core is where the suns energy is produced. • The radiation Zone is region of very tightly packed gas where energy is transferred mainly in the form of electromagnetic radiation. • The convection zone is the ...
... • The sun’s interior consists of the core, the radiation zone, and the convection zone. • The core is where the suns energy is produced. • The radiation Zone is region of very tightly packed gas where energy is transferred mainly in the form of electromagnetic radiation. • The convection zone is the ...
A Relative-Scaled Model of the Solar System
... driving from Fremont almost all the way to Yosemite or Lake Tahoe! The distances to stars are so great that even with our fastest rocket ships it would take about 150,000 years just to arrive at the nearest star. And most stars that we see in the sky are hundreds or thousands of light years away. Im ...
... driving from Fremont almost all the way to Yosemite or Lake Tahoe! The distances to stars are so great that even with our fastest rocket ships it would take about 150,000 years just to arrive at the nearest star. And most stars that we see in the sky are hundreds or thousands of light years away. Im ...
Why use these sites
... Students know the Sun is a typical star and is powered by nuclear reactions, primarily the fusion of hydrogen to form helium. ...
... Students know the Sun is a typical star and is powered by nuclear reactions, primarily the fusion of hydrogen to form helium. ...
The Earth in Orbit - School
... To measure really BIG distances we need really BIG units. We have seen that the distance between the Sun and the Earth actual varies between about 147 and 152 million km. The average value is about 150 million km (actually 149597870.691 kilometres). We call this distance 1 astronomical unit or AU. I ...
... To measure really BIG distances we need really BIG units. We have seen that the distance between the Sun and the Earth actual varies between about 147 and 152 million km. The average value is about 150 million km (actually 149597870.691 kilometres). We call this distance 1 astronomical unit or AU. I ...
Movement around the sun - E
... time. Earth also rotates, or spins, on its axis. It takes one day to spin around itself one complete time. Earth’s axis is not straight up and down, but tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees. The rotation is what causes the change from day to night. This tilt is responsible for having seasons. If Earth ...
... time. Earth also rotates, or spins, on its axis. It takes one day to spin around itself one complete time. Earth’s axis is not straight up and down, but tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees. The rotation is what causes the change from day to night. This tilt is responsible for having seasons. If Earth ...
Precession
... a spot near the star Polaris. • Due to its rotation, Earth has a slight bulge around its middle – gravity from the sun and moon pull on the bulge twisting Earth on its axis. • The result is that the twisting of the axis of rotation combines with the rotation of the Earth causing precession. • Earth’ ...
... a spot near the star Polaris. • Due to its rotation, Earth has a slight bulge around its middle – gravity from the sun and moon pull on the bulge twisting Earth on its axis. • The result is that the twisting of the axis of rotation combines with the rotation of the Earth causing precession. • Earth’ ...
view powerpoint
... • A solid rocky mantle surrounds the core with a thin crust of about 100 kilometers. ...
... • A solid rocky mantle surrounds the core with a thin crust of about 100 kilometers. ...
Lecture 36: Strange New Worlds
... Orbital Periods < 10 days Inside the orbit of Mercury Densities like Jupiter and Saturn, so they are gas giants. Selection effect? How does a Jupiter-size gas planet get so close to its parent star? ...
... Orbital Periods < 10 days Inside the orbit of Mercury Densities like Jupiter and Saturn, so they are gas giants. Selection effect? How does a Jupiter-size gas planet get so close to its parent star? ...
The Milky Way
... The preceding chapters gave you a modern view of Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow ...
... The preceding chapters gave you a modern view of Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow ...
1 Chapter 1 1-1. How long does it take the Earth to orbit the Sun? a
... 1-13. What type of motion leads to the Sun rising and setting? a.) Earth’s rotation X b.) Earth’s revolution c.) The Sun’s revolution d.) The Sun’s rotation 1-14. What type of motion leads to stars rising approximately 4 minutes earlier each day than it did the day before? a.) Earth’s rotation b.) E ...
... 1-13. What type of motion leads to the Sun rising and setting? a.) Earth’s rotation X b.) Earth’s revolution c.) The Sun’s revolution d.) The Sun’s rotation 1-14. What type of motion leads to stars rising approximately 4 minutes earlier each day than it did the day before? a.) Earth’s rotation b.) E ...
4QA Jeopardy
... One piece of evidence used to back up the Big Bang was the Doppler Effect. What does the Doppler Affect show us? a.) Stars and Galaxies are moving away ...
... One piece of evidence used to back up the Big Bang was the Doppler Effect. What does the Doppler Affect show us? a.) Stars and Galaxies are moving away ...
Geologic Time and Origins of the Earth
... • More volatile elements move away from the sun – H, He, Methane, Ammonia ...
... • More volatile elements move away from the sun – H, He, Methane, Ammonia ...
Grade 8 Science Astronomy Benchmark DO NOT WRITE ON THIS
... 4. Comet 13. A __________ Is a space rock thai hits the earth’s surface. 1. Meteor 2. Meteorite 3. Crater 4. Comet ...
... 4. Comet 13. A __________ Is a space rock thai hits the earth’s surface. 1. Meteor 2. Meteorite 3. Crater 4. Comet ...
planet - Groups
... When did we prove that Copernicus was right, that the Earth really does orbit the Sun? A.1543, when his book was published B.1610, when Galileo first observed with a telescope C.1687, when Newton published the Law of Gravity D.1830’s, when astronomers measured the first trigonometric parallaxes ...
... When did we prove that Copernicus was right, that the Earth really does orbit the Sun? A.1543, when his book was published B.1610, when Galileo first observed with a telescope C.1687, when Newton published the Law of Gravity D.1830’s, when astronomers measured the first trigonometric parallaxes ...
Review
... D) The orbits of Pluto and the other distant dwarf planets are tilted in different directions. 30) Planets orbiting other stars are hard to detect because they A) only reflect light, are very small B) are far away, are very small C) are far away, only reflect light D) all three 31) Planets orbiting ...
... D) The orbits of Pluto and the other distant dwarf planets are tilted in different directions. 30) Planets orbiting other stars are hard to detect because they A) only reflect light, are very small B) are far away, are very small C) are far away, only reflect light D) all three 31) Planets orbiting ...
A Changing Planet - Illinois State University
... The Earth has a large iron core, but the moon does not. The moon has exactly the same oxygen isotope composition as the Earth, items from other parts of the solar system have different oxygen isotope compositions. ...
... The Earth has a large iron core, but the moon does not. The moon has exactly the same oxygen isotope composition as the Earth, items from other parts of the solar system have different oxygen isotope compositions. ...
Chapter 4: The Origin of Modern Astronomy - Otto
... The preceding chapters gave you a modern view of Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow ...
... The preceding chapters gave you a modern view of Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow ...
Middle School Curriculum Standards: Earth Science
... 3.1b Solubility can be affected by the nature of the solute and solvent, temperature, and pressure. The rate of solution can be affected by the size of the particles, stirring, temperature, and the amount of solute already dissolved. 3.1c The motion of particles helps to explain the phases (states) ...
... 3.1b Solubility can be affected by the nature of the solute and solvent, temperature, and pressure. The rate of solution can be affected by the size of the particles, stirring, temperature, and the amount of solute already dissolved. 3.1c The motion of particles helps to explain the phases (states) ...
Learning Tracker for Space Unit with ANSWERS
... The closer they are together, the greater the gravity between them. It’s kind of like with magnets. The closer together they are, the harder they pull. ...
... The closer they are together, the greater the gravity between them. It’s kind of like with magnets. The closer together they are, the harder they pull. ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.