* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geologic Time and Origins of the Earth
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Gaia hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
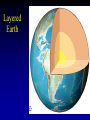
Earth Origins • AFTER “Big Bang” • Earth Origins are described by the Nebular Hypothesis Nebular Hypothesis 1 • Solar system did not exist 5 billion years ago • A giant cloud of dust and gas occupied this area of space – Many times larger than the present solar system – A lot of space between individual atoms of gas, metal and ions Nebular Hypothesis 2 • Something caused this cloud to condense • Maybe a nearby star exploded, sending its mass out into space • This mass collided with our dust cloud N.H. 2, continued • Nearby supernova caused cloud to condense • Accretion began Nebular Hypothesis 3 • • • • Cloud continues to condense Center of cloud attracts the most matter Cloud flattens into a disk and begins to rotate Incredible amount of heat generated in the center – So much heat that atoms are fused together, and the sun “turns on” As the nebula collapses, it heats up, spins faster, and flattens. Nebular Hypothesis 4 • A new sun in the center of a disk of dust • More volatile elements move away from the sun – H, He, Methane, Ammonia • Accretion continues in the disk – Planets form by collision Nebular Hypothesis 5 • Accretion continued until most of the matter accreted into planets • Accretion occurred in stages, with the “Late Heavy Bombardment” happening ~3 b.y.a. Why is the N.H. a hypothesis and not a theory? • Observations are indirect • We were not there to see it • What we can see is very slow Making the Earth 1 • Accretion acts over an extended area (the disk) and for a extended period of time • Solid grains condense out of the nebula’s gas – This is a chemistry process • Grains accrete into larger bodies (planetesimals) – This is a dynamic, collisional process • Planetesimals collide to produce protoplanets • Protoplanets accrete more material and become genuine planets Making the Earth 2 • Earth cools a bit: – Elements, minerals condense/crystallize • Iron, nickel, then rocky material • Layered Earth forms: – Stays molten due to heat of radioactive elements and L.H.B. • Iron and nickel sink to center, rocky material floats outward (density sort). • This is called differentiation Layered Earth