AUST – HORIZON AND BEYOND part 1
... Nebulae are gigantic clouds in space they are made up of dust and gas, often the remains of exploded stars. Nebulae gather due to the effect of gravity. Nebulaes are the beginning of stars. Nebulae some times glow red as they are warmed by radiation from nearby stars. ...
... Nebulae are gigantic clouds in space they are made up of dust and gas, often the remains of exploded stars. Nebulae gather due to the effect of gravity. Nebulaes are the beginning of stars. Nebulae some times glow red as they are warmed by radiation from nearby stars. ...
File - Mrs. Andrews` CBA classes
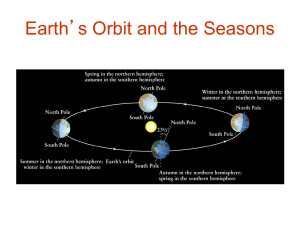
... Three reasons why summer is warmer: Day is longer so heat is absorbed longer Sun rays are more concentrated; absorb more energy per square kilometer Higher angle sun rays lose less energy to the atmosphere as the travel a shorter ...
... Three reasons why summer is warmer: Day is longer so heat is absorbed longer Sun rays are more concentrated; absorb more energy per square kilometer Higher angle sun rays lose less energy to the atmosphere as the travel a shorter ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... Star Clusters • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... Star Clusters • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
Name TEST Date ______ Space Test Review Write the sentence to
... My Very Excellent Mother Just Served Us Nachos. ...
... My Very Excellent Mother Just Served Us Nachos. ...
Practice Quiz Gravitation
... 3) The moons of Mars, Phobos (Fear) and Deimos (Terror), are very close to the planet compared to Earth's Moon. Their orbital radii are 9,378 km and 23,459 km respectively. What is the ratio of the orbital speed of Phobos to that of Deimos? A) 0.2528 B) 0.3998 C) 1.582 D) 3.956 Answer: C 4) Two bodi ...
... 3) The moons of Mars, Phobos (Fear) and Deimos (Terror), are very close to the planet compared to Earth's Moon. Their orbital radii are 9,378 km and 23,459 km respectively. What is the ratio of the orbital speed of Phobos to that of Deimos? A) 0.2528 B) 0.3998 C) 1.582 D) 3.956 Answer: C 4) Two bodi ...
Study Guide: Chapters 32-‐34 FROSH CHAPTER 32 1. What is
... e. Extreme temperatures due to no atmosphere and location to the sun _________________________ f. Seen as blue due to frozen methane in atmosphere and rotates top to bottom __________________ g. Largest pl ...
... e. Extreme temperatures due to no atmosphere and location to the sun _________________________ f. Seen as blue due to frozen methane in atmosphere and rotates top to bottom __________________ g. Largest pl ...
Magnetic traces in meteorites
... This image of the interacting galaxy pair Arp 147 was taken by the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 after the Hubble Space Telescope came back online after an equipment failure in September this year. The fault was managed by transferring processing tasks to a part of the HST unused and untested since ...
... This image of the interacting galaxy pair Arp 147 was taken by the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 after the Hubble Space Telescope came back online after an equipment failure in September this year. The fault was managed by transferring processing tasks to a part of the HST unused and untested since ...
9-Unit 1Chapter 11 Workbook
... 16. _______________________: the orbit of a satellite that is moving at the same speed and direction as Earth’s rotation, with the result that the satellite stays stationary above a fixed point on Earth. 17. _______________________: one of many small rocky bodies in our solar system, most of which o ...
... 16. _______________________: the orbit of a satellite that is moving at the same speed and direction as Earth’s rotation, with the result that the satellite stays stationary above a fixed point on Earth. 17. _______________________: one of many small rocky bodies in our solar system, most of which o ...
AstronomyQuotes
... In the early 1600s Galileo used the telescope to show that the milky way is composed of individual stars. We are a spiral galaxy with many spiral arms that revolve around a bulge on a relatively flat disk, surrounded by a dimmer halo. The Halo contains about 200 globular clusters of stars. Our galax ...
... In the early 1600s Galileo used the telescope to show that the milky way is composed of individual stars. We are a spiral galaxy with many spiral arms that revolve around a bulge on a relatively flat disk, surrounded by a dimmer halo. The Halo contains about 200 globular clusters of stars. Our galax ...
Venus - Uplift Education
... have completely reconstructed 300 to 500 million years ago. Volcano activities, deformation of the crust have shaped the surface. At least 85% of the Venusian surface is covered with volcanic rock with huge lava flows flooded the plains. The flows have also produced channels that extend for hundreds ...
... have completely reconstructed 300 to 500 million years ago. Volcano activities, deformation of the crust have shaped the surface. At least 85% of the Venusian surface is covered with volcanic rock with huge lava flows flooded the plains. The flows have also produced channels that extend for hundreds ...
My Moon: Moon Phases - University of Louisville
... ● Kepler’s laws describe common features of the motions of orbiting objects, including their elliptical paths around the sun. Orbits ...
... ● Kepler’s laws describe common features of the motions of orbiting objects, including their elliptical paths around the sun. Orbits ...
friends of the planetarium newsletter - june 2010
... South Equatorial Belt (SEB), the brown cloudy band is twice as wide as Earth and more than twenty times as long. The loss of such an enormous "stripe" can be seen with ease halfway across the solar system. "In any size telescope, or even in large binoculars, Jupiter's signature appearance has always ...
... South Equatorial Belt (SEB), the brown cloudy band is twice as wide as Earth and more than twenty times as long. The loss of such an enormous "stripe" can be seen with ease halfway across the solar system. "In any size telescope, or even in large binoculars, Jupiter's signature appearance has always ...
Glossary
... aeronautical—anything related to the science, design, or operation of aircraft. (p. 199) aft—the rear of a spacecraft or any other ship. (p. 309) air lock—an airtight chamber, usually located between two regions of unequal pressure, in which air pressure can be regulated. (p. 274) albedo—a celestial ...
... aeronautical—anything related to the science, design, or operation of aircraft. (p. 199) aft—the rear of a spacecraft or any other ship. (p. 309) air lock—an airtight chamber, usually located between two regions of unequal pressure, in which air pressure can be regulated. (p. 274) albedo—a celestial ...
Comet: Small body of ice, rock, and cosmic dust loosely packed
... However, the Moon's orbit is inclined about 5 degrees to the Earth's orbit. The Moon passes through the ecliptic only twice a month at a pair of points called the nodes. The rest of the time the Moon is either above or below the plane of the Earth's orbit and does not pass directly through the Earth ...
... However, the Moon's orbit is inclined about 5 degrees to the Earth's orbit. The Moon passes through the ecliptic only twice a month at a pair of points called the nodes. The rest of the time the Moon is either above or below the plane of the Earth's orbit and does not pass directly through the Earth ...
SYLLABUS Spring 2012 SCIE 3304, SECTION 001 ASTRONOMY
... This is a one semester course on astronomy with an emphasis on celestial motions, phases of moon, eclipses, history of astronomy, gravity, electromagnetic radiation, telescopes, and physical properties of the planets, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and the discovery of extrasolar planets, study of t ...
... This is a one semester course on astronomy with an emphasis on celestial motions, phases of moon, eclipses, history of astronomy, gravity, electromagnetic radiation, telescopes, and physical properties of the planets, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and the discovery of extrasolar planets, study of t ...
here - Immersive Theatres
... A tiny singlecelled organism, similar to today’s bacteria. It lived on certain substances in the water, and did not require any oxygen. ...
... A tiny singlecelled organism, similar to today’s bacteria. It lived on certain substances in the water, and did not require any oxygen. ...
Earth Dimensions
... earth. Approximately 100 km thick, the lithosphere is the portion of the crust and mantle that contain the plates which move around forming earth's features. ...
... earth. Approximately 100 km thick, the lithosphere is the portion of the crust and mantle that contain the plates which move around forming earth's features. ...
Name: Pd: _____ Ast: _____ Solar System Study Guide Vocabulary
... 1) Solar System - A star together with the group of planets and other celestial bodies that are held by its gravitational attraction and revolve around it 2) Celestial Objects - Objects such as planets, moons, and stars that are located in the sky or in space 3) Star - A ball of gas in space that pr ...
... 1) Solar System - A star together with the group of planets and other celestial bodies that are held by its gravitational attraction and revolve around it 2) Celestial Objects - Objects such as planets, moons, and stars that are located in the sky or in space 3) Star - A ball of gas in space that pr ...
Our Solar System
... Earth, and Mars) are small and rocky with iron cores The four outer planets – (Jupiter, Saturn, ...
... Earth, and Mars) are small and rocky with iron cores The four outer planets – (Jupiter, Saturn, ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.