DTU 8e Chap 5 Formation of the Solar System
... Jupiter and Saturn were initially worlds of rock and metal that pulled onto themselves large amounts of hydrogen and helium, along with some water. Uranus and Neptune were also initially worlds of rock and metal, but they attracted more water and less hydrogen and helium than the other giant planets ...
... Jupiter and Saturn were initially worlds of rock and metal that pulled onto themselves large amounts of hydrogen and helium, along with some water. Uranus and Neptune were also initially worlds of rock and metal, but they attracted more water and less hydrogen and helium than the other giant planets ...
AST1001.ch2
... The Greeks knew that the lack of observable parallax could mean one of two things: 1. Stars are so far away that stellar parallax is too small to notice with the naked eye. 2. Earth does not orbit Sun; it is the center of the universe. With rare exceptions, such as Aristarchus, the Greeks rejected ...
... The Greeks knew that the lack of observable parallax could mean one of two things: 1. Stars are so far away that stellar parallax is too small to notice with the naked eye. 2. Earth does not orbit Sun; it is the center of the universe. With rare exceptions, such as Aristarchus, the Greeks rejected ...
The Planets
... Our solar system consists of the sun, eight planets, moons, dwarf planets, an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, the asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas all orbit the sun. The nine planets that orbit the sun are (in ...
... Our solar system consists of the sun, eight planets, moons, dwarf planets, an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, the asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas all orbit the sun. The nine planets that orbit the sun are (in ...
ppt
... If star wobbles with amplitude of 1 arc-second (1/3600th of a degree), then it is at distance of 1 parsec (definition of parsec). 1 pc = 3.26 light years. In general, ...
... If star wobbles with amplitude of 1 arc-second (1/3600th of a degree), then it is at distance of 1 parsec (definition of parsec). 1 pc = 3.26 light years. In general, ...
CP CircularGravityReview
... Choose the best answer to each question and write the appropriate letter in the space provided. 6. \Mhy did Newton think there was a force acting on the moon? A) Becausethe moon alwayskeepsone side toward the earth B) Becausethe moon movesin a curved path C) Becausethere is no air on the moon D) Bec ...
... Choose the best answer to each question and write the appropriate letter in the space provided. 6. \Mhy did Newton think there was a force acting on the moon? A) Becausethe moon alwayskeepsone side toward the earth B) Becausethe moon movesin a curved path C) Becausethere is no air on the moon D) Bec ...
PHYSICS 1500 - ASTRONOMY TOTAL: 100 marks Section A Please
... (c) Halley formed in the inner solar system and was ejected by Jupiter to the Kuiper belt. (d) Halley is really an S-type asteroid. (e) Halley was once a moon of Neptune and was ripped away by a large impact. ...
... (c) Halley formed in the inner solar system and was ejected by Jupiter to the Kuiper belt. (d) Halley is really an S-type asteroid. (e) Halley was once a moon of Neptune and was ripped away by a large impact. ...
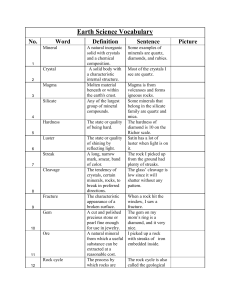
Earth Science Vocabulary No. Word Definition Sentence Picture 1
... usually because it is denser. A type of strike-slip fault that accommodates the relative horizontal slip between other tectonic elements. The lateral displacement along transform faults often ends or changes form abruptly. States that, for all linear systems, the net response of two or more stimuli ...
... usually because it is denser. A type of strike-slip fault that accommodates the relative horizontal slip between other tectonic elements. The lateral displacement along transform faults often ends or changes form abruptly. States that, for all linear systems, the net response of two or more stimuli ...
Announcements
... We can’t see below the horizon (we can’t see through the Earth!). So, we need to have telescopes in different locations, and we have to think about the timing of the Earth’s rotation when planning observations. The Earth is constantly rotating, so a telescope has to constantly move to follow a star ...
... We can’t see below the horizon (we can’t see through the Earth!). So, we need to have telescopes in different locations, and we have to think about the timing of the Earth’s rotation when planning observations. The Earth is constantly rotating, so a telescope has to constantly move to follow a star ...
Document
... Explaining the Characteristics of the Solar System 1. The orbits of the planets lie in the same plane because the rotating solar nebula collapsed into a disk, and the planets formed in that disk. Objects are co-eval (4.) 2. The division into small inner and giant outer planets rests upon the amoun ...
... Explaining the Characteristics of the Solar System 1. The orbits of the planets lie in the same plane because the rotating solar nebula collapsed into a disk, and the planets formed in that disk. Objects are co-eval (4.) 2. The division into small inner and giant outer planets rests upon the amoun ...
PowerPoint
... Formation of OUR Solar System? • Looks like a supernova explosion nearby may have done the job… Probably a type II high-mass star supernova, from the relative abundances of elements in meteorites. • Blast wave compresses interstellar cloud, and the debris of that explosion is contained in the first ...
... Formation of OUR Solar System? • Looks like a supernova explosion nearby may have done the job… Probably a type II high-mass star supernova, from the relative abundances of elements in meteorites. • Blast wave compresses interstellar cloud, and the debris of that explosion is contained in the first ...
Light-years
... to form a dense object with gravity so strong that light cannot escape it. a. b. c. d. ...
... to form a dense object with gravity so strong that light cannot escape it. a. b. c. d. ...
File
... more than a few millions could have been saved. Perhaps it was better thus. Even if they had not been so disturbingly human as their sculpture shows, we could not have helped admiring them and grieving for their fate. They left thousands of visual records and the machines for projecting them, togeth ...
... more than a few millions could have been saved. Perhaps it was better thus. Even if they had not been so disturbingly human as their sculpture shows, we could not have helped admiring them and grieving for their fate. They left thousands of visual records and the machines for projecting them, togeth ...
Lecture 3, PPT version
... of the North pole with respect to the sky. This “minor motion” is very slow (takes 26,000 years to complete), but is important to navigation by the stars! Right now, the North Star is “Polaris” (the tail star of the Little Dipper). Five thousand years ago the North Star was Thuban, and in 14,000 it ...
... of the North pole with respect to the sky. This “minor motion” is very slow (takes 26,000 years to complete), but is important to navigation by the stars! Right now, the North Star is “Polaris” (the tail star of the Little Dipper). Five thousand years ago the North Star was Thuban, and in 14,000 it ...
Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System
... © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. ...
... © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. ...
Third Grade Astronomy
... Objects in the Sky have patterns of movement. The Sun, for example, appears to move across the sky in the same way everyday, but its path changes slowly over the seasons. The moon moves across the sky on a daily basis much like the Sun. The Sun, Moon and stars all have properties, locations and move ...
... Objects in the Sky have patterns of movement. The Sun, for example, appears to move across the sky in the same way everyday, but its path changes slowly over the seasons. The moon moves across the sky on a daily basis much like the Sun. The Sun, Moon and stars all have properties, locations and move ...
Welcome to Our Universe!
... • Closest planet to the size of Earth • Has a thick mantle and iron core • Much drier than Earth and atmosphere is 90% more dense • Hottest planet Over 400⁰C • No moons • Terrestrial Planet • 7,521 miles in diameter ...
... • Closest planet to the size of Earth • Has a thick mantle and iron core • Much drier than Earth and atmosphere is 90% more dense • Hottest planet Over 400⁰C • No moons • Terrestrial Planet • 7,521 miles in diameter ...
Earth
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
How Telescopes Changed our Universe
... In our own solar system, telescopes found planets our eyes could not see. Are there other planets outside of our solar system? ...
... In our own solar system, telescopes found planets our eyes could not see. Are there other planets outside of our solar system? ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.