04jan20.ppt
... 2. Earth does not orbit Sun; it is the center of the universe Unfortunately, with notable exceptions like Aristarchus, the Greeks did not think the stars could be that far away, and therefore rejected the correct explanation (1)… Thus setting the stage for the long, historical showdown between Earth ...
... 2. Earth does not orbit Sun; it is the center of the universe Unfortunately, with notable exceptions like Aristarchus, the Greeks did not think the stars could be that far away, and therefore rejected the correct explanation (1)… Thus setting the stage for the long, historical showdown between Earth ...
ASTR 1010 Homework Solutions
... proportional to the masses of the two objects and inversely proportional to the square of their separation. So, if the mass of the hypothetical planet is 4 times greater than the mass of the Earth, then that would increase the gravitational force by a factor of 4. But the diameter of this hypothetic ...
... proportional to the masses of the two objects and inversely proportional to the square of their separation. So, if the mass of the hypothetical planet is 4 times greater than the mass of the Earth, then that would increase the gravitational force by a factor of 4. But the diameter of this hypothetic ...
Advanced AMG EOC Review 2014-2015
... How does the Coriolis effect deflect wind in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres? How and where does friction affect wind speed and direction? What are jet streams? At what altitude and latitude are they located? What direction do they flow? How do winds blow around high and low pressure centers i ...
... How does the Coriolis effect deflect wind in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres? How and where does friction affect wind speed and direction? What are jet streams? At what altitude and latitude are they located? What direction do they flow? How do winds blow around high and low pressure centers i ...
a MS Word version.
... 10. What does conservation of angular momentum have to do with the distribution of planets around a newborn star? How are planets' orbits predicted to be distributed in a "solar system" and does this prediction describe our solar system correctly? How come the Sun is not spinning extremely rapidly c ...
... 10. What does conservation of angular momentum have to do with the distribution of planets around a newborn star? How are planets' orbits predicted to be distributed in a "solar system" and does this prediction describe our solar system correctly? How come the Sun is not spinning extremely rapidly c ...
solar system notes
... down for each of the planets. How do these values compare to the orbital period of each planet (Table 2)? Better still type [xx,yy]=ginput on the MATLAB command line and using the mouse, click on each of the peaks. Once you’ve clicked on all 9, press enter and the values will be saved in the xx arra ...
... down for each of the planets. How do these values compare to the orbital period of each planet (Table 2)? Better still type [xx,yy]=ginput on the MATLAB command line and using the mouse, click on each of the peaks. Once you’ve clicked on all 9, press enter and the values will be saved in the xx arra ...
Mapping the Stars
... A Tool for Studying Stars • The combination of research done between Danish astronomer (Hertzsprung) and American astronomer (Henry Norris Russell) on the brightness and temperature of stars resulted in a graph called what? • H-R diagram • What does the diagram show? • It shows the relationship bet ...
... A Tool for Studying Stars • The combination of research done between Danish astronomer (Hertzsprung) and American astronomer (Henry Norris Russell) on the brightness and temperature of stars resulted in a graph called what? • H-R diagram • What does the diagram show? • It shows the relationship bet ...
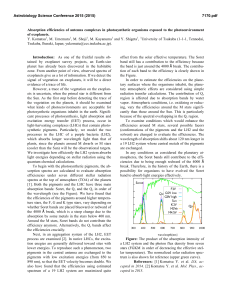
Absorption efficiencies of antenna complexes in photosynthetic
... 890 nm), so that the EET velocity becomes double. We also have found that the efficiencies using estimated spectrum of a 19 LH2 system are maximized quite ...
... 890 nm), so that the EET velocity becomes double. We also have found that the efficiencies using estimated spectrum of a 19 LH2 system are maximized quite ...
The Milky Way * A Classic Galaxy
... must be one too • Star formation happening in disk right through today • 10 million solar mass Giant black hole in nucleus of our Galaxy, evidence by rapid orbital motion of stars and gas light years away. • Dust disk is dense and vertically thin, sun lives in this layer, near outskirts of Milky Way ...
... must be one too • Star formation happening in disk right through today • 10 million solar mass Giant black hole in nucleus of our Galaxy, evidence by rapid orbital motion of stars and gas light years away. • Dust disk is dense and vertically thin, sun lives in this layer, near outskirts of Milky Way ...
The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation
... pebbles, then rocks, then boulders, then planetesimals, then planets. Some planets become massive enough to also accumulate Hydrogen and Helium gas. • However, during and after formation, it seems that some planets are able to migrate in their disks, drifting inwards to settle close to the star. We ...
... pebbles, then rocks, then boulders, then planetesimals, then planets. Some planets become massive enough to also accumulate Hydrogen and Helium gas. • However, during and after formation, it seems that some planets are able to migrate in their disks, drifting inwards to settle close to the star. We ...
Eclipse of the Sun 1 September 2016
... By taking pictures of stars near the Sun during totality, scientists were able to show that gravity can bend light from stars, also called gravitational refraction. ...
... By taking pictures of stars near the Sun during totality, scientists were able to show that gravity can bend light from stars, also called gravitational refraction. ...
Astronomy Exam Notes.docx
... 7. A black hole and a normal star have the same mass. They each have an Earth-sized planet orbiting them at the same distance as the Earth is from the Sun. a) the black hole pulls harder on its planet than the normal star does b) the two planets feel identical pulls c) the normal star pulls harder o ...
... 7. A black hole and a normal star have the same mass. They each have an Earth-sized planet orbiting them at the same distance as the Earth is from the Sun. a) the black hole pulls harder on its planet than the normal star does b) the two planets feel identical pulls c) the normal star pulls harder o ...
Closest ever exoplanet is potentially habitable
... discovered by an international team of researchers, is very probably rocky like our own planet, while its minimum mass is 1.3 times that of the Earth. It is located seven million kilometers from Proxima Centauri, which is 20 times closer than the distance of the Earth from the Sun. However, Proxima ...
... discovered by an international team of researchers, is very probably rocky like our own planet, while its minimum mass is 1.3 times that of the Earth. It is located seven million kilometers from Proxima Centauri, which is 20 times closer than the distance of the Earth from the Sun. However, Proxima ...
HR Diagram
... __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. If star Large and star Small were the same temperature, explain why Large would appear brighter. __________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. If star Large and star Small were the same temperature, explain why Large would appear brighter. __________________ ...
Chapter 2
... Complete the following concept map by correctly adding the connecting phrases or terms provided to the appropriate locations. Some items may be used more than once; others may not be applicable to this diagram. 1. converts simple elements such as 2. present in 3. for example 4. extrasolar planets su ...
... Complete the following concept map by correctly adding the connecting phrases or terms provided to the appropriate locations. Some items may be used more than once; others may not be applicable to this diagram. 1. converts simple elements such as 2. present in 3. for example 4. extrasolar planets su ...
11.2b The Solar System Asteroids and Gas Giants
... would have clumped together into another terrestrial planet but the planet Jupiter was too close and its large gravity force prevented the asteroids from clumping together and instead made them collide and break into more pieces. ...
... would have clumped together into another terrestrial planet but the planet Jupiter was too close and its large gravity force prevented the asteroids from clumping together and instead made them collide and break into more pieces. ...
Wide-eyed Telescope Finds its First Transiting
... 2000 times greater than a conventional astronomical telescope. The instruments run under robotic control and are housed in their own customised building. The eight individual cameras on each mount are small by telescope standards – the lenses are just 11cm in diameter – but coupled with state-of-the ...
... 2000 times greater than a conventional astronomical telescope. The instruments run under robotic control and are housed in their own customised building. The eight individual cameras on each mount are small by telescope standards – the lenses are just 11cm in diameter – but coupled with state-of-the ...
Wide-eyed Telescope Finds its First Transiting
... 2000 times greater than a conventional astronomical telescope. The instruments run under robotic control and are housed in their own customised building. The eight individual cameras on each mount are small by telescope standards – the lenses are just 11cm in diameter – but coupled with state-of-the ...
... 2000 times greater than a conventional astronomical telescope. The instruments run under robotic control and are housed in their own customised building. The eight individual cameras on each mount are small by telescope standards – the lenses are just 11cm in diameter – but coupled with state-of-the ...
old_exam_questions - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and
... Which kind of Main Sequence star burns longer, a small red star or a big blue star (circle one)? How do main sequence stars form? Be sure to include all of the important processes. ...
... Which kind of Main Sequence star burns longer, a small red star or a big blue star (circle one)? How do main sequence stars form? Be sure to include all of the important processes. ...
Document
... Use the ecliptic and the celestial sphere to explain the positions that lead to lunar and solar eclipses. Match cycles of the moon to corresponding positions of Earth, moon, and sun. Explain why the constellations visible in the night sky change throughout the year. As.1.2 Use scientific not ...
... Use the ecliptic and the celestial sphere to explain the positions that lead to lunar and solar eclipses. Match cycles of the moon to corresponding positions of Earth, moon, and sun. Explain why the constellations visible in the night sky change throughout the year. As.1.2 Use scientific not ...
Lecture 10
... Precession of the equinoxes • If the position of the celestial poles and equators are changing on the celestial sphere, this means that the celestial coordinates of objects, which are defined by reference to the celestial equator and celestial poles, must also be constantly changing. • Because of t ...
... Precession of the equinoxes • If the position of the celestial poles and equators are changing on the celestial sphere, this means that the celestial coordinates of objects, which are defined by reference to the celestial equator and celestial poles, must also be constantly changing. • Because of t ...
Motion of the Moon Phases of the Moon
... against the stars (half a degree per hour) • The motion of the Moon relative to the stars causes it to rise 50 minutes later every day • The Moon returns to the same position amongst the stars every 27.3 days (its orbital period or sidereal period) ...
... against the stars (half a degree per hour) • The motion of the Moon relative to the stars causes it to rise 50 minutes later every day • The Moon returns to the same position amongst the stars every 27.3 days (its orbital period or sidereal period) ...
Evening Planets in School Year 2016-17
... school year, while Saturn is still fairly high. By early in November, Saturn will set before twilight ends, and around Thanksgiving, it departs. Saturn passes conjunction with the Sun on December 10, and by New Year’s Day 2017, it emerges low in the southeastern morning twilight. The ringed planet t ...
... school year, while Saturn is still fairly high. By early in November, Saturn will set before twilight ends, and around Thanksgiving, it departs. Saturn passes conjunction with the Sun on December 10, and by New Year’s Day 2017, it emerges low in the southeastern morning twilight. The ringed planet t ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.