Large and small planets Journey through the Solar System
... Organise the children into groups of three. Give each group a sheet of coloured paper and a drawing compass. The size of the piece of paper needed to draw the planet is shown in the fifth column. Each group makes a different planet. The children complete Task 2 on the worksheet and adjust the compa ...
... Organise the children into groups of three. Give each group a sheet of coloured paper and a drawing compass. The size of the piece of paper needed to draw the planet is shown in the fifth column. Each group makes a different planet. The children complete Task 2 on the worksheet and adjust the compa ...
Pluto
... cloud” (a sphere of perhaps 1012 comets, about 50,000 AU from the Sun) • Sometimes perturbed by a passing star and deflected into the Solar System • Made of primitive material that is important for understanding the early Solar System • So we are very interested in studying comets (“Deep Impact” col ...
... cloud” (a sphere of perhaps 1012 comets, about 50,000 AU from the Sun) • Sometimes perturbed by a passing star and deflected into the Solar System • Made of primitive material that is important for understanding the early Solar System • So we are very interested in studying comets (“Deep Impact” col ...
Document
... the Sun. If we could live on another planet, our birthdays would occur more or less frequently depending on the planet’s revolution period (the time taken to complete one full trip around the Sun). On a few planets, we couldn’t even celebrate our first birthday because we wouldn’t live long enough t ...
... the Sun. If we could live on another planet, our birthdays would occur more or less frequently depending on the planet’s revolution period (the time taken to complete one full trip around the Sun). On a few planets, we couldn’t even celebrate our first birthday because we wouldn’t live long enough t ...
Your Birthday on Another Planet
... the Sun. If we could live on another planet, our birthdays would occur more or less frequently depending on the planet’s revolution period (the time taken to complete one full trip around the Sun). On a few planets, we couldn’t even celebrate our first birthday because we wouldn’t live long enough t ...
... the Sun. If we could live on another planet, our birthdays would occur more or less frequently depending on the planet’s revolution period (the time taken to complete one full trip around the Sun). On a few planets, we couldn’t even celebrate our first birthday because we wouldn’t live long enough t ...
Today`s Powerpoint
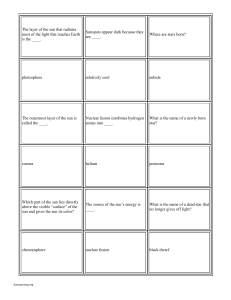
... B: increase by a factor of 2 C: increase by a factor of 4 D: increase by a factor of 16 ...
... B: increase by a factor of 2 C: increase by a factor of 4 D: increase by a factor of 16 ...
Chapter #10 Question #27: (c) Four individual protons. During
... This statement makes sense. Massive stars fuse higher elements in their core during their death. The final result is an iron core which is released to the interstellar space during a high mass star supernova. A massive star supernova that blew up before the formation of the solar system would have r ...
... This statement makes sense. Massive stars fuse higher elements in their core during their death. The final result is an iron core which is released to the interstellar space during a high mass star supernova. A massive star supernova that blew up before the formation of the solar system would have r ...
Scales in the UniverseApollo
... Hubble Deep Field showing galaxies over 10 billion light years away (looking back in time to near the beginning of the universe) ...
... Hubble Deep Field showing galaxies over 10 billion light years away (looking back in time to near the beginning of the universe) ...
Astronomy - Needham.K12.ma.us
... phases) the high tides are MUCH higher than at other times. These are called SPRING TIDES. When the Moon and Sun are at right angles to each other (First and Third Quarter Moon phases) the high tides are lower than at other times. These are called NEAP TIDES. ...
... phases) the high tides are MUCH higher than at other times. These are called SPRING TIDES. When the Moon and Sun are at right angles to each other (First and Third Quarter Moon phases) the high tides are lower than at other times. These are called NEAP TIDES. ...
AUST – HORIZON AND BEYOND part 1
... hot gas. Primarily stars are made up of two gases – 3 quarters hydrogen and 1 quarter helium. They create energy through nuclear reactions (millions of times more powerful than a nuclear bomb). Reactions are caused by squeezing atoms of hydrogen gas deep inside the star. A star will continue to glow ...
... hot gas. Primarily stars are made up of two gases – 3 quarters hydrogen and 1 quarter helium. They create energy through nuclear reactions (millions of times more powerful than a nuclear bomb). Reactions are caused by squeezing atoms of hydrogen gas deep inside the star. A star will continue to glow ...
Lecture Summary (11/22)
... Our Sun formed in a nebula 4.6 billion years ago. Stars like the Sun are born as protostars in regions where the ISM collapses. There are many examples of star-forming nebulae, dusty disks, and infrared stars to support our theories of star formation. As gravity compressed the gas, our protosun form ...
... Our Sun formed in a nebula 4.6 billion years ago. Stars like the Sun are born as protostars in regions where the ISM collapses. There are many examples of star-forming nebulae, dusty disks, and infrared stars to support our theories of star formation. As gravity compressed the gas, our protosun form ...
Big Bang Theory Scientific origin of the Universe
... relatively small bodies * Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars *Gas giant planets – large planets with ...
... relatively small bodies * Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars *Gas giant planets – large planets with ...
How to Become a Planet Hunter-Careers in
... An interferometer combines the light from two or more small telescopes (Mersenne) to yield the angular resolution of a much larger telescope. Interferometer Resolution Interferometer ...
... An interferometer combines the light from two or more small telescopes (Mersenne) to yield the angular resolution of a much larger telescope. Interferometer Resolution Interferometer ...
Six Weeks: 3rd ALLEN Subject: Science Grade: 3 TEKS Covering
... What is the center of our Solar System? What are the planets that make up our Solar System (8) Earth and space. The student knows that there are recognizable patterns in the natural world and among the Sun, Earth, and Moon system. The student is expected to: (A) differentiate between weather and cli ...
... What is the center of our Solar System? What are the planets that make up our Solar System (8) Earth and space. The student knows that there are recognizable patterns in the natural world and among the Sun, Earth, and Moon system. The student is expected to: (A) differentiate between weather and cli ...
Stars
... Ball of hot gas (hydrogen and helium) that gives off light Have different colors, sizes, and patterns. ...
... Ball of hot gas (hydrogen and helium) that gives off light Have different colors, sizes, and patterns. ...
Mercury - alexanderscience8
... What IS a Planet? As of 2006, a planet is defined by three criteria: 1) It is a celestial body that orbits the Sun. 2) It is massive enough that its own gravity causes it to form a spherical shape. 3) It has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit. Under this definition our solar system has eight ...
... What IS a Planet? As of 2006, a planet is defined by three criteria: 1) It is a celestial body that orbits the Sun. 2) It is massive enough that its own gravity causes it to form a spherical shape. 3) It has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit. Under this definition our solar system has eight ...
Chapter03
... I’ve found that many students think anyone who lived before 1900 (or perhaps even 1980) was hopelessly ignorant and dull. I love to use the accomplishments of the later Greek astronomers to teach them otherwise. Students seem impressed by Aristarchus’s work showing the enormous size of the solar sys ...
... I’ve found that many students think anyone who lived before 1900 (or perhaps even 1980) was hopelessly ignorant and dull. I love to use the accomplishments of the later Greek astronomers to teach them otherwise. Students seem impressed by Aristarchus’s work showing the enormous size of the solar sys ...
Day-6
... All halo stars have some heavy elements, so at least one prior generation of stars must have existed. Halo objects were formed before interstellar gas was all concentrated into the disk. Later star formation was all in the disk. ...
... All halo stars have some heavy elements, so at least one prior generation of stars must have existed. Halo objects were formed before interstellar gas was all concentrated into the disk. Later star formation was all in the disk. ...
Star Study Guide Chapter 21 Test
... shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star ...
... shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star ...
exam1guide - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... elements created during the Big Bang. Stars: star birth, star life cycle, gravity, pressure, hydrogen fusion, luminosity, absolute luminosity, star color and surface temperature, characteristics of main sequence stars, star size and lifespan, nucleosynthesis (production of new elements) in old stars ...
... elements created during the Big Bang. Stars: star birth, star life cycle, gravity, pressure, hydrogen fusion, luminosity, absolute luminosity, star color and surface temperature, characteristics of main sequence stars, star size and lifespan, nucleosynthesis (production of new elements) in old stars ...
Moon Obs #1 Due!
... hard surfaces, but cloud formations in their atmospheres • Jovian planets are much larger then the terrestrials! ...
... hard surfaces, but cloud formations in their atmospheres • Jovian planets are much larger then the terrestrials! ...
Stars Galaxies Sun
... The Sun is similar to most other stars in our galaxy: ►A large ball of gas made mostly of hydrogen and helium held together ...
... The Sun is similar to most other stars in our galaxy: ►A large ball of gas made mostly of hydrogen and helium held together ...
the Study Guide
... Alien: A foreigner. A space alien would be an alien from outer space. Android: A robot with a human form. Atmosphere: The canopy of air surrounding the Earth. It is divided into five layers or "spheres": the Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere and Exosphere. The Thermosphere is also ...
... Alien: A foreigner. A space alien would be an alien from outer space. Android: A robot with a human form. Atmosphere: The canopy of air surrounding the Earth. It is divided into five layers or "spheres": the Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere and Exosphere. The Thermosphere is also ...
solar system form
... Much smaller than other planets Icy, comet-like composition Pluto’s moon Charon is similar in size to Pluto ...
... Much smaller than other planets Icy, comet-like composition Pluto’s moon Charon is similar in size to Pluto ...
SNC1PL The Life Cycle of Stars
... Massive stars (larger than the Sun) supernova and leave behind a neutron star (an extremely dense star composed of tightly packed neutrons) Neutron stars have immense gravitational force and tend to spin quickly. This spinning creates highfrequency radio waves, which have been detected by astronom ...
... Massive stars (larger than the Sun) supernova and leave behind a neutron star (an extremely dense star composed of tightly packed neutrons) Neutron stars have immense gravitational force and tend to spin quickly. This spinning creates highfrequency radio waves, which have been detected by astronom ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.