How was Earth formed?
... immense amount of energy released. Sun is formed Dust and gases cool and condense in defined orbits around the sun ...
... immense amount of energy released. Sun is formed Dust and gases cool and condense in defined orbits around the sun ...
Middle School Curriculum Standards: Earth Science
... 2.2g Rocks are classified according to their method of formation. The three classes of rocks are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. Most rocks show characteristics that give clues to their formation conditions. 2.2h The rock cycle model shows how types of rock or rock material may be transformed ...
... 2.2g Rocks are classified according to their method of formation. The three classes of rocks are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. Most rocks show characteristics that give clues to their formation conditions. 2.2h The rock cycle model shows how types of rock or rock material may be transformed ...
ASTR100 Homework #5 Solutions Chapter 11 #29, 31 Due
... (a) main-sequence A star (b) main-sequence G star (c) main-sequence M star The colder the star, the longer it takes to burn through its energy source. Hottest stars are O, coldest stars are M (again… O B A F G K M) c) M stars are the coldest, so those will live the longest __________________________ ...
... (a) main-sequence A star (b) main-sequence G star (c) main-sequence M star The colder the star, the longer it takes to burn through its energy source. Hottest stars are O, coldest stars are M (again… O B A F G K M) c) M stars are the coldest, so those will live the longest __________________________ ...
Intro Lecture: Stars - University of Redlands
... Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI produced the first image of Mizar A. That image was the highest angular resolution image ever made in optical astronomy. Since t ...
... Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI produced the first image of Mizar A. That image was the highest angular resolution image ever made in optical astronomy. Since t ...
GSC 1580 Vocabulary/Who`s Who
... Antarctic Circle: Most northerly line in the Southern Hemisphere where 24 hours of darkness or Sunlight is possible. Artic Circle: Most southerly line in the Northern Hemisphere where 24 hours of darkness or Sunlight is possible. astronomical unit: a unit of length used in astronomy equal to the mea ...
... Antarctic Circle: Most northerly line in the Southern Hemisphere where 24 hours of darkness or Sunlight is possible. Artic Circle: Most southerly line in the Northern Hemisphere where 24 hours of darkness or Sunlight is possible. astronomical unit: a unit of length used in astronomy equal to the mea ...
Astronomy
... 25. A visual representation of the temperature and luminosity of stars is called: 26. Relatively dark spots on the sun that contains intense magnetic fields are known as: 27. These reactions join the nuclei of atoms to form more massive nuclei: 28. Eruptions on the solar surface that return back to ...
... 25. A visual representation of the temperature and luminosity of stars is called: 26. Relatively dark spots on the sun that contains intense magnetic fields are known as: 27. These reactions join the nuclei of atoms to form more massive nuclei: 28. Eruptions on the solar surface that return back to ...
The Inverse Square Law and Surface Area
... The power received from a star per metre squared at the Earth is called the intensity (I) of the star’s radiation This is related to the power output per metre squared L of the star’s surface in this way ...
... The power received from a star per metre squared at the Earth is called the intensity (I) of the star’s radiation This is related to the power output per metre squared L of the star’s surface in this way ...
Extrasolar Planets - University of Maryland Astronomy
... Even with that, some 5% of Sun-type stars that have been examined have detected planets, and the fraction is going up. There are also some low-mass stars with planets, but these have been searched less thoroughly because we are interested in systems like ours. This fraction is high enough that plane ...
... Even with that, some 5% of Sun-type stars that have been examined have detected planets, and the fraction is going up. There are also some low-mass stars with planets, but these have been searched less thoroughly because we are interested in systems like ours. This fraction is high enough that plane ...
Astronomy Quiz Units 1 to 3
... “A planet (from Greek πλανήτης, alternative form of πλάνης "wanderer") is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighboring region of planetesimals. “ (Wiki ...
... “A planet (from Greek πλανήτης, alternative form of πλάνης "wanderer") is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighboring region of planetesimals. “ (Wiki ...
What theories account for the origin of the solar system?
... Four inner planets of the solar system Relatively small in size and mass (Earth is the largest and most massive) Rocky surface ...
... Four inner planets of the solar system Relatively small in size and mass (Earth is the largest and most massive) Rocky surface ...
Chapter 25 Teacher Notes
... •Most like Earth of all of the planets •“red planet” because of high iron content on its surface •Last volcanic activity about 100 million years ago •Olympus Mon is largest volcano in solar system. If on Earth, its base would cover the space between Cleveland and Washington D.C. Mars •Very thin atmo ...
... •Most like Earth of all of the planets •“red planet” because of high iron content on its surface •Last volcanic activity about 100 million years ago •Olympus Mon is largest volcano in solar system. If on Earth, its base would cover the space between Cleveland and Washington D.C. Mars •Very thin atmo ...
Shashanka R. Gurumath1, Hiremath KM2, and
... harbor an Earth mass planet is estimated to be ~ 0.2 times the Sun's mass. According to astronomical standard, this estimated mass of a star belongs to spectral type of M stars. It is to be noted that, nearly 70% of stars in our galaxy are belongs to M stars. Hence, this study suggests that, M stars ...
... harbor an Earth mass planet is estimated to be ~ 0.2 times the Sun's mass. According to astronomical standard, this estimated mass of a star belongs to spectral type of M stars. It is to be noted that, nearly 70% of stars in our galaxy are belongs to M stars. Hence, this study suggests that, M stars ...
Earth Science Library wk 2 (WP)
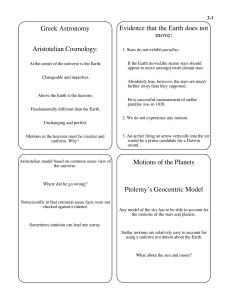
... However, because the orbits are actually elliptical, the Also, provides natural explanations for many aspects of the planetary motions which are puzzling in model still used some small epicycles. Ptolemy’s system: Why does the sun’s period (1 year) show up in all of the other planet’s motions in Pto ...
... However, because the orbits are actually elliptical, the Also, provides natural explanations for many aspects of the planetary motions which are puzzling in model still used some small epicycles. Ptolemy’s system: Why does the sun’s period (1 year) show up in all of the other planet’s motions in Pto ...
Solar System PPT
... 1. What is the gravitational force that keeps our solar system together? Explain. 2. How are rotation, revolution, and orbit different? 3. Explain how the seasons occur. When do we experience summer and winter? 4. Explain why we have leap years. 5. How do we see the moon? List the phases of the moon ...
... 1. What is the gravitational force that keeps our solar system together? Explain. 2. How are rotation, revolution, and orbit different? 3. Explain how the seasons occur. When do we experience summer and winter? 4. Explain why we have leap years. 5. How do we see the moon? List the phases of the moon ...
Earth Patterns, Cycles & Changes SOL 4.7
... 4.6 billion years old.” Does not move its location 869,959 miles around (diameter) ...
... 4.6 billion years old.” Does not move its location 869,959 miles around (diameter) ...
Microlensing
... Milestones: A. An optimised planetary microlens follow-up network, including feedback from fully-automated real-time modelling. B. The first census of the cold planet population, involving planets of Neptune to super-Earth (few M⊕ to 20 M⊕) with host star separations around 2 AU. C. Under highly fav ...
... Milestones: A. An optimised planetary microlens follow-up network, including feedback from fully-automated real-time modelling. B. The first census of the cold planet population, involving planets of Neptune to super-Earth (few M⊕ to 20 M⊕) with host star separations around 2 AU. C. Under highly fav ...
Tayler Vence PHYS 1010 5/5/2013 The Copernican Revolution The
... As time passed and it was possible to collect more accurate data, it became apparent that simple epicycles could not account for all of the irregularities in the planetary motions. In response to this many medieval astronomers proposed more complex epicycles. In these new epicycles circles moved alo ...
... As time passed and it was possible to collect more accurate data, it became apparent that simple epicycles could not account for all of the irregularities in the planetary motions. In response to this many medieval astronomers proposed more complex epicycles. In these new epicycles circles moved alo ...
Science CRCT Jeopardy 1
... A. The stars in a constellation revolve around the Earth together. B. The stars in a constellation rotate very slowly on their axes. C. Earth’s gravity attracts the stars and holds them in place. D. Stars appear not to move because they are so far away from the Earth. ...
... A. The stars in a constellation revolve around the Earth together. B. The stars in a constellation rotate very slowly on their axes. C. Earth’s gravity attracts the stars and holds them in place. D. Stars appear not to move because they are so far away from the Earth. ...
Gravity and Motion Motion in astronomy Newton`s Laws of Motion
... The stars are very distant; their relative pattern stays fixed while the pattern as a whole rotates due to the rotation of the Earth ...
... The stars are very distant; their relative pattern stays fixed while the pattern as a whole rotates due to the rotation of the Earth ...
In Retrospect: Kepler`s Astronomia Nova
... commemorates the 400th anniversary of two great discoveries: Galileo Galilei’s detection of Jupiter’s four major moons and the publication of Johannes Kepler’s monumental book Astronomia Nova. In this 1609 work, Kepler demonstrated that planets follow elliptical paths about the Sun, a breakthrough t ...
... commemorates the 400th anniversary of two great discoveries: Galileo Galilei’s detection of Jupiter’s four major moons and the publication of Johannes Kepler’s monumental book Astronomia Nova. In this 1609 work, Kepler demonstrated that planets follow elliptical paths about the Sun, a breakthrough t ...
Mid-term Exam 3 - Practice Version
... show that outflows from young stars usually prevent disks from forming around them. reveal that double stars are usually required to form planets. show that giant planets should be uncommon. ...
... show that outflows from young stars usually prevent disks from forming around them. reveal that double stars are usually required to form planets. show that giant planets should be uncommon. ...
122final10
... the Earth would be pulled into the black hole the tides on the Earth would increase in height the Earth's orbit would be essentially unaffected the earth would be violently ejected from its orbit the earth would be orbiting inside the event horizon of this black hole ...
... the Earth would be pulled into the black hole the tides on the Earth would increase in height the Earth's orbit would be essentially unaffected the earth would be violently ejected from its orbit the earth would be orbiting inside the event horizon of this black hole ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.