ziggynotes
... Knowing the orbital period and distance to this very large “Moon”, you can at least constrain a few orbital parameters. Let us hypothesize that Ziggy is much more massive than the “Moon”, so that Ziggy is essentially stationary while the “Moon” orbits us. We roughly know the radius of the Moon’s orb ...
... Knowing the orbital period and distance to this very large “Moon”, you can at least constrain a few orbital parameters. Let us hypothesize that Ziggy is much more massive than the “Moon”, so that Ziggy is essentially stationary while the “Moon” orbits us. We roughly know the radius of the Moon’s orb ...
13 Universal Gravitation
... 13.8 Weight and Weightlessness Stand on a bathroom scale that is supported on a stationary floor. The gravitational force between you and Earth pulls you against the supporting floor and scale. Between you and the supporting floor is a spring-like gauge inside the bathroom scale. This pair of forces ...
... 13.8 Weight and Weightlessness Stand on a bathroom scale that is supported on a stationary floor. The gravitational force between you and Earth pulls you against the supporting floor and scale. Between you and the supporting floor is a spring-like gauge inside the bathroom scale. This pair of forces ...
The Sun and Stars
... Gravitational forces cause denser regions of the nebula to collapse, forming a protostar. A protostar is the earliest stage in the life cycle of a star. The gases at the center of the protostar continue to collapse, causing pressure and temperature to rise. A protostar becomes a star when the temper ...
... Gravitational forces cause denser regions of the nebula to collapse, forming a protostar. A protostar is the earliest stage in the life cycle of a star. The gases at the center of the protostar continue to collapse, causing pressure and temperature to rise. A protostar becomes a star when the temper ...
Spring 2012 - Union College
... and time. The outer part of the blue circle is marked with days of the year, while the outer part of the grey overlay is marked with times. The stars within the grey oval are the ones visible on a particular day at the time that lines up with that day. To see the sky at a different date and time, si ...
... and time. The outer part of the blue circle is marked with days of the year, while the outer part of the grey overlay is marked with times. The stars within the grey oval are the ones visible on a particular day at the time that lines up with that day. To see the sky at a different date and time, si ...
Introduction
... mark will not be given if this form is not signed and returned with your work. The form is available from the course webpage on WebCT or can be downloaded from the School’s website. ...
... mark will not be given if this form is not signed and returned with your work. The form is available from the course webpage on WebCT or can be downloaded from the School’s website. ...
Discovery
... Centaur Asteroids – Centaur asteroids orbit far from the Sun. For example: Hidalgo, the first to be discovered, orbits from the inner edge of the main belt out almost as far as Saturn, Chiron orbits between Saturn and Uranus 9, the orbit of Damocles ranges from near Mars to beyond Uranus, and Pholus ...
... Centaur Asteroids – Centaur asteroids orbit far from the Sun. For example: Hidalgo, the first to be discovered, orbits from the inner edge of the main belt out almost as far as Saturn, Chiron orbits between Saturn and Uranus 9, the orbit of Damocles ranges from near Mars to beyond Uranus, and Pholus ...
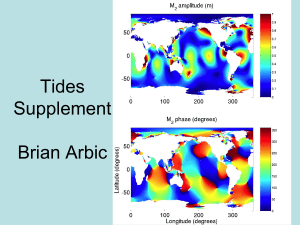
Tides Supplement
... • Recall from the tsunami exercise that the phase speed of shallow water waves in a 4000 m ocean is about 200 m/s • What is the speed that waves would need to stay under the moon as it orbits around the Earth? • Compute 2πR/(24 hours 50 minutes), where R is the Earth’s radius. Put your answer in uni ...
... • Recall from the tsunami exercise that the phase speed of shallow water waves in a 4000 m ocean is about 200 m/s • What is the speed that waves would need to stay under the moon as it orbits around the Earth? • Compute 2πR/(24 hours 50 minutes), where R is the Earth’s radius. Put your answer in uni ...
FREE Sample Here
... 26. Assume the size of the Sun is represented by a baseball with the Earth is about 15 meters (150 million km or 8 light minutes) away. How far away, to scale, would the nearest stars to the Sun be? Pick the closest answer. a. About the distance between New York and Boston. (330 km) b. 100 meters aw ...
... 26. Assume the size of the Sun is represented by a baseball with the Earth is about 15 meters (150 million km or 8 light minutes) away. How far away, to scale, would the nearest stars to the Sun be? Pick the closest answer. a. About the distance between New York and Boston. (330 km) b. 100 meters aw ...
Chapter-by-Chapter Guide
... the farther away they are located, the faster they are moving away. While at first this might seem to suggest that we are at the center of the universe, a little more reflection indicates that this is not the case. If we imagine a raisin cake rising, we can see that every raisin will move away from ...
... the farther away they are located, the faster they are moving away. While at first this might seem to suggest that we are at the center of the universe, a little more reflection indicates that this is not the case. If we imagine a raisin cake rising, we can see that every raisin will move away from ...
Jupiter
... gravitational force at any particular distance from the center of a spherical planet, even at a distance that is inside the planet. This gravitational force must be balanced by the pressure of the material making up the planet at that radius (i.e. at that distance from the center of the planet). Bal ...
... gravitational force at any particular distance from the center of a spherical planet, even at a distance that is inside the planet. This gravitational force must be balanced by the pressure of the material making up the planet at that radius (i.e. at that distance from the center of the planet). Bal ...
EVOLUTIONARY TRACKS OF THE CLIMATE OF EARTH
... in the HZ is initially warm or hot, and the liquid water can exist: the pCO2 is high enough owing to high CO2 degassing rate from planetary interiors in its early evolution even though the insolation is low owing to the low luminosity of the young star (Figure 2). The climate of the planet in the in ...
... in the HZ is initially warm or hot, and the liquid water can exist: the pCO2 is high enough owing to high CO2 degassing rate from planetary interiors in its early evolution even though the insolation is low owing to the low luminosity of the young star (Figure 2). The climate of the planet in the in ...
19. Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning
... • Briefly describe the galaxy’s star-gas-star cycle. • Stars are born from the gravitational collapse of gas clumps in molecular clouds. Near the ends of their lives, stars more massive than our Sun create elements heavier than hydrogen and helium and expel them into space through supernovae and ste ...
... • Briefly describe the galaxy’s star-gas-star cycle. • Stars are born from the gravitational collapse of gas clumps in molecular clouds. Near the ends of their lives, stars more massive than our Sun create elements heavier than hydrogen and helium and expel them into space through supernovae and ste ...
01_planetary motion and copernican revolution
... 1.3 The Laws of Planetary Motion The Dimensions of the solar system • The distance from Earth to the Sun is called an astronomical unit. Its actual length may be measured by bouncing a radar signal off Venus and measuring the transit time. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. and R. Fisher ...
... 1.3 The Laws of Planetary Motion The Dimensions of the solar system • The distance from Earth to the Sun is called an astronomical unit. Its actual length may be measured by bouncing a radar signal off Venus and measuring the transit time. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. and R. Fisher ...
What is a white dwarf?
... degeneracy pressure doesn't depend on temperature • Is there a limit to how much you can shrink a white dwarf? (That is, how much mass a WD can have?) ...
... degeneracy pressure doesn't depend on temperature • Is there a limit to how much you can shrink a white dwarf? (That is, how much mass a WD can have?) ...
Chapter 15
... the hydrogen fuel in its core to make helium. The helium is basically just sitting there, so it's not producing any energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that ...
... the hydrogen fuel in its core to make helium. The helium is basically just sitting there, so it's not producing any energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that ...
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... A tilted ring won’t stay flat very long • Particle orbits will precess at different rates • Collisions will soon destroy the ring ...
... A tilted ring won’t stay flat very long • Particle orbits will precess at different rates • Collisions will soon destroy the ring ...
The Astrobiology Primer
... The benefits of this interdisciplinary collaboration have been, and continue to be, immense. The input of scientists from multiple areas has forced researchers to become aware of their basic assumptions and why they do science the way they do. Cooperation has led to insights about the many connectio ...
... The benefits of this interdisciplinary collaboration have been, and continue to be, immense. The input of scientists from multiple areas has forced researchers to become aware of their basic assumptions and why they do science the way they do. Cooperation has led to insights about the many connectio ...
Star-S_Teacher_Guide - The University of Texas at Dallas
... comes from initially so that fusion can begin. The answer is gravity. As a forming star collapses, it heats up. When the core is sufficiently dense and hot, fusion begins. The energy released by fusion keeps the star from collapsing much further. Your students may also wonder what stars are made of; ...
... comes from initially so that fusion can begin. The answer is gravity. As a forming star collapses, it heats up. When the core is sufficiently dense and hot, fusion begins. The energy released by fusion keeps the star from collapsing much further. Your students may also wonder what stars are made of; ...
General Astrophysics And Comparative Planetology
... Earth-sized based only on visual observations and an assumed surface reflectance. This estimate was reduced when Pluto’s icy nature was guessed. Finally the Charon-Pluto eclipses during the late 1980s constrained Pluto’s radius to be much smaller—0.18 Earth radii. Sedna is a recently discovered smal ...
... Earth-sized based only on visual observations and an assumed surface reflectance. This estimate was reduced when Pluto’s icy nature was guessed. Finally the Charon-Pluto eclipses during the late 1980s constrained Pluto’s radius to be much smaller—0.18 Earth radii. Sedna is a recently discovered smal ...
Earth is between the Sun and the Moon.
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
Solution
... the red one must be smaller. But by Stefan-Boltzmann's Law, its luminosity/area must also be smaller, and they are the same size. So the red one is less luminous. 3. ( T F ) Using parallax, astronomers can now reliably measure the distance of most of the stars in our galaxy. False. Sad to say, most ...
... the red one must be smaller. But by Stefan-Boltzmann's Law, its luminosity/area must also be smaller, and they are the same size. So the red one is less luminous. 3. ( T F ) Using parallax, astronomers can now reliably measure the distance of most of the stars in our galaxy. False. Sad to say, most ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.