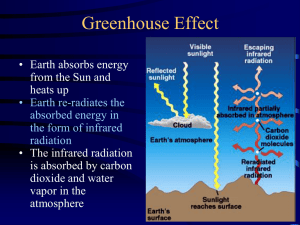
Knows that Earth is the only body in our solar system that
... formations on Venus. Have students create a map that shows any geological regions on Earth that match the geology of other planets or moons. Instruct students to describe these geological formations and indicate which planets have similar structures. ...
... formations on Venus. Have students create a map that shows any geological regions on Earth that match the geology of other planets or moons. Instruct students to describe these geological formations and indicate which planets have similar structures. ...
Life on Jovian Moons
... • The ice grains contained H, so a large amount of mass came together • When large enough, gravity took over from collisions in building a bigger body (‘direct gravitational accumulation’) • 4 large moons, the ‘Galilean Moons’ ...
... • The ice grains contained H, so a large amount of mass came together • When large enough, gravity took over from collisions in building a bigger body (‘direct gravitational accumulation’) • 4 large moons, the ‘Galilean Moons’ ...
Gravity and Orbits
... 1. Find the orbital period and speed of a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude of 1800 km 2. A moon orbits planet Y in a circular path with a radius of 9600 km. If it takes 137 minutes to complete one orbit, find a) the acceleration , b) the mass of planet Y c) If planet Y has a radius of 5600 km ...
... 1. Find the orbital period and speed of a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude of 1800 km 2. A moon orbits planet Y in a circular path with a radius of 9600 km. If it takes 137 minutes to complete one orbit, find a) the acceleration , b) the mass of planet Y c) If planet Y has a radius of 5600 km ...
CelestialSphere
... We see Mercury and Venus follow the Sun around in the sky. They may go down after, or come up before it. If they go down after, we see them in the evening. ...
... We see Mercury and Venus follow the Sun around in the sky. They may go down after, or come up before it. If they go down after, we see them in the evening. ...
CelestialSphere02
... We see Mercury and Venus follow the Sun around in the sky. They may go down after, or come up before it. If they go down after, we see them in the evening. ...
... We see Mercury and Venus follow the Sun around in the sky. They may go down after, or come up before it. If they go down after, we see them in the evening. ...
Sun, Earth, Moon Relationship
... What is the difference between rotation and revolution? 2. What causes the seasons? 3. True/False: The Earth has an axial tilt. ...
... What is the difference between rotation and revolution? 2. What causes the seasons? 3. True/False: The Earth has an axial tilt. ...
The Universe (solucionario)
... b. Planets orbit around satellites. False c. Stars have their own light. True d. Planets follow a path called celestial body. False e. Stars orbit around planets. False ...
... b. Planets orbit around satellites. False c. Stars have their own light. True d. Planets follow a path called celestial body. False e. Stars orbit around planets. False ...
report
... 11. The next day in class, have a group discussion of what they discovered. Review the homework and have one cutout of the sun ( which would be 76.7 inches in diameter relative to the cutouts that they used in their activity). 12. Wrap up the assignment with a discussion of the ...
... 11. The next day in class, have a group discussion of what they discovered. Review the homework and have one cutout of the sun ( which would be 76.7 inches in diameter relative to the cutouts that they used in their activity). 12. Wrap up the assignment with a discussion of the ...
the universe
... When asteroids collide with one another, bits of broken pieces are scattered in space. These pieces are called meteoroids they could also be bits of comets dust or pieces of a planet or a moon hit by an asteroid or a comet. A meteoroid can sometimes burn up as it passes through Earth’s atmosphere. T ...
... When asteroids collide with one another, bits of broken pieces are scattered in space. These pieces are called meteoroids they could also be bits of comets dust or pieces of a planet or a moon hit by an asteroid or a comet. A meteoroid can sometimes burn up as it passes through Earth’s atmosphere. T ...
Extrasolar Planet Populations, Lebo, 8-1
... • Geoff Marcy & Paul Butler quickly confirmed 51 Pegasi • They had lots of archival data from searches for Jupiter-type planets (periods >10 years, so they were still “in progress”) • No one even thought to look for short-period MASSIVE planets (why would they be easier?) • Found many “Hot Jupiters” ...
... • Geoff Marcy & Paul Butler quickly confirmed 51 Pegasi • They had lots of archival data from searches for Jupiter-type planets (periods >10 years, so they were still “in progress”) • No one even thought to look for short-period MASSIVE planets (why would they be easier?) • Found many “Hot Jupiters” ...
World Geography - Seneca High School
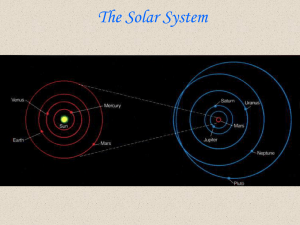
... The Solar System The Earth and Sun Relationships The Earth System ...
... The Solar System The Earth and Sun Relationships The Earth System ...
Untitled
... The Moon rotates on its …………………………., which takes 29.5 days. Its …………………………. around the Earth also takes 29.5 days. Because of this, we always see the same …………………………. of the Moon. The Moon does not produce its own light; it …………………………. sunlight. Obviously, we can only see the illuminated part that i ...
... The Moon rotates on its …………………………., which takes 29.5 days. Its …………………………. around the Earth also takes 29.5 days. Because of this, we always see the same …………………………. of the Moon. The Moon does not produce its own light; it …………………………. sunlight. Obviously, we can only see the illuminated part that i ...
2-The Earth in space
... The outer planets are giant balls of gases with very small, solid cores. The outer planets rotate quickly, which makes for a short day; however, these planets take a long time to revolve once around the sun. Therefore, they have short days but long years. ...
... The outer planets are giant balls of gases with very small, solid cores. The outer planets rotate quickly, which makes for a short day; however, these planets take a long time to revolve once around the sun. Therefore, they have short days but long years. ...
Grade 9 Applied Science
... long…). To make memorizing these terms easier, you may wish to do only one page at a time. Learn all the terms, go away, two hours later try and do the page again by testing your recall. If you can do Page 1 correctly, go to Page 2. Repeat this process for all pages. As well, come back and do Page 1 ...
... long…). To make memorizing these terms easier, you may wish to do only one page at a time. Learn all the terms, go away, two hours later try and do the page again by testing your recall. If you can do Page 1 correctly, go to Page 2. Repeat this process for all pages. As well, come back and do Page 1 ...
Stars - Sun
... density of a star so tightly in the core that the electrons are stripped away and the bare nuclei of atoms almost touch each other. • Nuclear fusion occurs. ...
... density of a star so tightly in the core that the electrons are stripped away and the bare nuclei of atoms almost touch each other. • Nuclear fusion occurs. ...
The Milky Way
... b. Jupiter swept up so much material that not enough was left to form a planet. c. Mars was once larger and collided with a large planetesimal from the inner Solar System that sent debris outward. d. Jupiter formed early, and its gravitational influence altered the orbits of nearby accreting planete ...
... b. Jupiter swept up so much material that not enough was left to form a planet. c. Mars was once larger and collided with a large planetesimal from the inner Solar System that sent debris outward. d. Jupiter formed early, and its gravitational influence altered the orbits of nearby accreting planete ...
The Planets in our Solar System
... Dynamic atmosphere with a main clouds of methane ice crystals. Composition: Hydrogen and other elements mixed into an icy liquid (outer mantle), slushy mixture rich in water, methane, and ammonia (inner mantle), and an icy & rocky (core) Orbit is almost perfectly circular Sunlight strength: 0.1% of ...
... Dynamic atmosphere with a main clouds of methane ice crystals. Composition: Hydrogen and other elements mixed into an icy liquid (outer mantle), slushy mixture rich in water, methane, and ammonia (inner mantle), and an icy & rocky (core) Orbit is almost perfectly circular Sunlight strength: 0.1% of ...
The solar system
... Rotates on its axis slowly when compared to Earth, it completes one rotation in about 6 days and 9 minutes Is sometimes known as a double-planet because it has a moon (Charon) that orbits it Has a total of 1 moon ...
... Rotates on its axis slowly when compared to Earth, it completes one rotation in about 6 days and 9 minutes Is sometimes known as a double-planet because it has a moon (Charon) that orbits it Has a total of 1 moon ...
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3
... a) terrestrial and Jovian. b) comets and asteroids. c) meteorites and meteoroids. d) moons and stars. ...
... a) terrestrial and Jovian. b) comets and asteroids. c) meteorites and meteoroids. d) moons and stars. ...
Science Project
... • Earth's magnetic field stops its atmosphere from being stripped away by the solar wind . Venus and Mars do not have magnetic fields , and as a result, the solar wind causes their atmospheres to gradually bleed away into space . Coronal mass ejections and similar events blow magnetic field and hug ...
... • Earth's magnetic field stops its atmosphere from being stripped away by the solar wind . Venus and Mars do not have magnetic fields , and as a result, the solar wind causes their atmospheres to gradually bleed away into space . Coronal mass ejections and similar events blow magnetic field and hug ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.