Astronomy - Learn Earth Science
... Use the Luminosity & Temperature of Stars diagram on the ESRTs to identify the characteristics of specific stars in relation to Earth’s sun. ...
... Use the Luminosity & Temperature of Stars diagram on the ESRTs to identify the characteristics of specific stars in relation to Earth’s sun. ...
May 2014
... Our guest speaker for the evening is fellow PVAA member Dr. Joann Eisberg with the title of her presentation: "Are We Alone in the Universe? The Search for Another Earth" She started out with a little history starting with Thomas Digges. Thomas was an English mathematician and astronomer. He present ...
... Our guest speaker for the evening is fellow PVAA member Dr. Joann Eisberg with the title of her presentation: "Are We Alone in the Universe? The Search for Another Earth" She started out with a little history starting with Thomas Digges. Thomas was an English mathematician and astronomer. He present ...
Day_39
... Most of the extrasolar planets discovered to date are quite massive and have orbits that are very different from planets in our solar system ...
... Most of the extrasolar planets discovered to date are quite massive and have orbits that are very different from planets in our solar system ...
Orbit by Tega Jessa Everything in the universe circles or “orbits
... been thinking about how to create gravity in space. There are several proposals some already proven and others that are still theory. The first is to us the centripetal force of a rotating hull. This is method is the most trustworthy as the effect has been observed on Earth. Every object in the univ ...
... been thinking about how to create gravity in space. There are several proposals some already proven and others that are still theory. The first is to us the centripetal force of a rotating hull. This is method is the most trustworthy as the effect has been observed on Earth. Every object in the univ ...
SkyMatters Oct-2016 - CIT Blackrock Castle Observatory
... most prominent winter constellations of Taurus and Orion. Neverthless, it is worth a look. Capella is the sixth brightest star in the sky, but it is in fact a multiple star system. The star we see is actually two giant stars in orbit around one another, separated by a distance of less than that betw ...
... most prominent winter constellations of Taurus and Orion. Neverthless, it is worth a look. Capella is the sixth brightest star in the sky, but it is in fact a multiple star system. The star we see is actually two giant stars in orbit around one another, separated by a distance of less than that betw ...
FINAL EXAM
... 56. How many billion yrs did the PreCambrian last 57. What period ended with Dino extinction 58. When did Dinos 1st appear 59. How much can crustal plates move in a year 60. 3 major cloud types 61. Most common form of solid precipitation 62. Warm vs. Cold Front 63. Barometer 64. How is Oxygen added ...
... 56. How many billion yrs did the PreCambrian last 57. What period ended with Dino extinction 58. When did Dinos 1st appear 59. How much can crustal plates move in a year 60. 3 major cloud types 61. Most common form of solid precipitation 62. Warm vs. Cold Front 63. Barometer 64. How is Oxygen added ...
PHS 111 Test 3 Review Chapters 26-28
... gravitational attraction to neighboring stars. the star first ignites. it reaches temperatures of about 3 million K. The determining factor in the stages a star will progress through from birth to death is its: mass. temperature. composition. relative density. What event will eventually move an aver ...
... gravitational attraction to neighboring stars. the star first ignites. it reaches temperatures of about 3 million K. The determining factor in the stages a star will progress through from birth to death is its: mass. temperature. composition. relative density. What event will eventually move an aver ...
PHS 111 Test 3 Review Chapters 26-28
... influx, resulting in core temperatures high enough to begin fusing helium Surface cooling due to hydrogen loss Solar wind ...
... influx, resulting in core temperatures high enough to begin fusing helium Surface cooling due to hydrogen loss Solar wind ...
Chapter 04
... b. It gave a better explanation for the phases of the Moon. c. It was a more elegant explanation of retrograde motion. d. The old system of Ptolemy was never very popular. e. It displaced Earth from the center of the universe. ...
... b. It gave a better explanation for the phases of the Moon. c. It was a more elegant explanation of retrograde motion. d. The old system of Ptolemy was never very popular. e. It displaced Earth from the center of the universe. ...
The Origin of Modern Astronomy(Seeds)
... b. It gave a better explanation for the phases of the Moon. c. It was a more elegant explanation of retrograde motion. d. The old system of Ptolemy was never very popular. e. It displaced Earth from the center of the universe. ...
... b. It gave a better explanation for the phases of the Moon. c. It was a more elegant explanation of retrograde motion. d. The old system of Ptolemy was never very popular. e. It displaced Earth from the center of the universe. ...
A Geometer`s Sketchpad Solar System
... (a) First, drag each planet to the point in its orbit where the dashed-line ray crosses the orbit. This will be the “start line”. (b) When you are ready, animate your solar system. (c) Watch how the planets move around their orbits. Look for such things as: • Which planets stay lined up as they orbi ...
... (a) First, drag each planet to the point in its orbit where the dashed-line ray crosses the orbit. This will be the “start line”. (b) When you are ready, animate your solar system. (c) Watch how the planets move around their orbits. Look for such things as: • Which planets stay lined up as they orbi ...
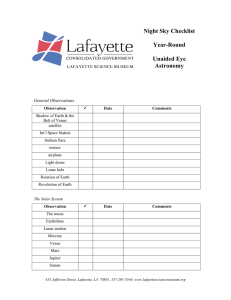
Night Sky Checklist Year-Round Unaided Eye Astronomy
... go to www.heavens-above.com . Once there you must set up for your location. The easiest way is to click on “from database” in the Configuration area, choose your country, then follow the instructions. Once configured, bookmark the site and it will set up for your location when you return each time. ...
... go to www.heavens-above.com . Once there you must set up for your location. The easiest way is to click on “from database” in the Configuration area, choose your country, then follow the instructions. Once configured, bookmark the site and it will set up for your location when you return each time. ...
The Solar System
... Lighter molecules move faster, because on average Kinetic Energy is higher at higher temperatures • Recall (½)m = (3/2)kT where m is the mass
of the particle (atom or molecule) moving at
velocity v, in a medium of temperature T
• So for a given temperature, higher mass
...
... Lighter molecules move faster, because on average Kinetic Energy is higher at higher temperatures • Recall (½)m
Heliocentric model
... – Greatest elongation – for Venus and Mercury, when they are at their greatest angular separation from the Sun. Can be either eastern or western ...
... – Greatest elongation – for Venus and Mercury, when they are at their greatest angular separation from the Sun. Can be either eastern or western ...
SDO | SOLAR DYNAMICS OBSERVATORY HTTP://WWW.NASA
... AGE: Our sun is a healthy, happy middle-age of about 4.6 billion years. Space may appear empty but it's actually quite full of dust and gas. Thanks to gravity, this material gathers together to form large clouds. This is how our solar system began, so many years ago. Over vast amounts of time, a clo ...
... AGE: Our sun is a healthy, happy middle-age of about 4.6 billion years. Space may appear empty but it's actually quite full of dust and gas. Thanks to gravity, this material gathers together to form large clouds. This is how our solar system began, so many years ago. Over vast amounts of time, a clo ...
Midterm 1 Short Answer (+1-3pts) Record the answers to these
... Sun and because of this, life was able to move from the water (which protected it from the ultra-violet radiation) to live on land. Note: Many of you got this question partially correct by mentioning that it helped to block dangerous radiation from the Sun, but I was looking for specifically what ty ...
... Sun and because of this, life was able to move from the water (which protected it from the ultra-violet radiation) to live on land. Note: Many of you got this question partially correct by mentioning that it helped to block dangerous radiation from the Sun, but I was looking for specifically what ty ...
The Sun
... only a small distance before it is absorbed. It is then re-emitted in a random direction, absorbed after a small distance, remitted, and so on until it reaches the surface, which takes about hundred thousand years. ...
... only a small distance before it is absorbed. It is then re-emitted in a random direction, absorbed after a small distance, remitted, and so on until it reaches the surface, which takes about hundred thousand years. ...
Earth Science Library wk 1.cwk (WP)
... That is what office hours are for! Factual: Mt. Ranier is a stratovolcano. Conceptual: Why? What geologic processes lead to it being a stratovolcano? Why do stratovolcanoes look and behave the way they do? Factual: Which direction do winds blow around a high pressure system? ...
... That is what office hours are for! Factual: Mt. Ranier is a stratovolcano. Conceptual: Why? What geologic processes lead to it being a stratovolcano? Why do stratovolcanoes look and behave the way they do? Factual: Which direction do winds blow around a high pressure system? ...
The Night Sky
... beginning of July. The sun is now starting to move northward on its yearly cycle around the sky. As a result of this, sunsets start arriving later in the evening and sunrises start arriving earlier in the morning. January’s full moon, known in folklore as the wolf moon, rises at sunset on January 26 ...
... beginning of July. The sun is now starting to move northward on its yearly cycle around the sky. As a result of this, sunsets start arriving later in the evening and sunrises start arriving earlier in the morning. January’s full moon, known in folklore as the wolf moon, rises at sunset on January 26 ...
Moons
... probably high in iron content approximately 240 km in diameter • Liquid iron outer core and an area of partially melted boundary between core and mantle ...
... probably high in iron content approximately 240 km in diameter • Liquid iron outer core and an area of partially melted boundary between core and mantle ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.