Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... Rank images of the Moon in different phases in order of occurrence first to last. Characterize the Moon’s apparent motion given its phase and the time of year. Explain why the lunar sidereal period is different than the time for a cycle of lunar phases. Describe the essentials of the geocentri ...
... Rank images of the Moon in different phases in order of occurrence first to last. Characterize the Moon’s apparent motion given its phase and the time of year. Explain why the lunar sidereal period is different than the time for a cycle of lunar phases. Describe the essentials of the geocentri ...
Why do things move?
... 392 3= 6.56 x 10-23 m/s2 ie. almost zero! or a = 5.98 x 1024 Example: 3 billion people jumping off boxes all at same time (mass 100 kg each) ...
... 392 3= 6.56 x 10-23 m/s2 ie. almost zero! or a = 5.98 x 1024 Example: 3 billion people jumping off boxes all at same time (mass 100 kg each) ...
Origin of Modern Astronomy
... 1. The path of each planet around the sun is an ellipse, with the sun at one focus. The other focus is symmetrically located at the opposite end of the ellipse. 2. Each planet revolves so that an imaginary line connecting it to the sun sweeps over equal areas in equal time intervals. If a planet is ...
... 1. The path of each planet around the sun is an ellipse, with the sun at one focus. The other focus is symmetrically located at the opposite end of the ellipse. 2. Each planet revolves so that an imaginary line connecting it to the sun sweeps over equal areas in equal time intervals. If a planet is ...
Starlight and What it Tells Us
... Radiation is Reflected from Some Other Source • The Sun Emits Black-Body Radiation, the Moon Does Not ...
... Radiation is Reflected from Some Other Source • The Sun Emits Black-Body Radiation, the Moon Does Not ...
Gen1_14 - Amador Bible Studies
... between the day and between the night. And they will be for signs and for appointed times and for days and years.” Explanation: 1. God the Father gives the command to concentrate the dispersed light, which was restored on day one into luminaries or light bearers. This is the creation of our solar sy ...
... between the day and between the night. And they will be for signs and for appointed times and for days and years.” Explanation: 1. God the Father gives the command to concentrate the dispersed light, which was restored on day one into luminaries or light bearers. This is the creation of our solar sy ...
THE PLANETS C - White-Thomson Publishing Services
... Mars is about half the size of Earth, but the two planets y have the same amount of dr land. This is because there is no liquid water on Mars. ...
... Mars is about half the size of Earth, but the two planets y have the same amount of dr land. This is because there is no liquid water on Mars. ...
Astronomical Constants
... 27) Circle the seven planets of the ancient world from the alphabetic list presented below. Earth Jupiter Mars ...
... 27) Circle the seven planets of the ancient world from the alphabetic list presented below. Earth Jupiter Mars ...
Are We Alone in the Universe?
... ✤ Now we know of nearly 2,000! Some estimates put the number of Earth-like planets in habitable zones at 20% of all stars! ✤ 400 billion stars in the Milky Way x 20% = 80 billion potentially habitable planets! Statistically, the answer is: There have to be other life forms out there ...
... ✤ Now we know of nearly 2,000! Some estimates put the number of Earth-like planets in habitable zones at 20% of all stars! ✤ 400 billion stars in the Milky Way x 20% = 80 billion potentially habitable planets! Statistically, the answer is: There have to be other life forms out there ...
What is Pluto?
... What is Pluto? • Strange object; located far out from the Sun with gas giants but small size and very elliptical and highly inclined orbit • Pluto is a mixture of ices and rocks • composition similar to satellites of giant planets • Could be captured Kuiper Belt Object (e.g. comet)? ...
... What is Pluto? • Strange object; located far out from the Sun with gas giants but small size and very elliptical and highly inclined orbit • Pluto is a mixture of ices and rocks • composition similar to satellites of giant planets • Could be captured Kuiper Belt Object (e.g. comet)? ...
grade v and vi - Sacred Heart CMI Public School
... eight major planets. Nearest the Sun there are four fairly small, rocky planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Beyond Mars is the asteroid belt – a region populated by millions of rocky objects. These are left-over’s from the formation of the planets, 4.5 billion years ago. On the far side of the a ...
... eight major planets. Nearest the Sun there are four fairly small, rocky planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Beyond Mars is the asteroid belt – a region populated by millions of rocky objects. These are left-over’s from the formation of the planets, 4.5 billion years ago. On the far side of the a ...
intro.phys.psu.edu
... Aristarchus thought that the large star could not rotate with the small star, and if the Earth and the other stars rotated around the sun, celestial motion could be easily understood. ...
... Aristarchus thought that the large star could not rotate with the small star, and if the Earth and the other stars rotated around the sun, celestial motion could be easily understood. ...
The Jovian Planets + Pluto and the TNOs Jupiter 12 of Jupiter`s
... the Sun ☼ Discarded ideas for source of energy: nuclear fusion in core:- temperature and pressure aren’t high enough fuelled by gravitational collapse:- like the Sun, Jupiter is too old for this mechanism to still work ...
... the Sun ☼ Discarded ideas for source of energy: nuclear fusion in core:- temperature and pressure aren’t high enough fuelled by gravitational collapse:- like the Sun, Jupiter is too old for this mechanism to still work ...
How Big is the Solar System?
... suddenly larger leap of 95 paces (more than twice as as the total distance walked up till then). This gap marks the boundary between the inner and outer solar systems. The inner solar system contains the four small, hard, "terrestrial" (Earth-like) planet; the outer solar system contains the four la ...
... suddenly larger leap of 95 paces (more than twice as as the total distance walked up till then). This gap marks the boundary between the inner and outer solar systems. The inner solar system contains the four small, hard, "terrestrial" (Earth-like) planet; the outer solar system contains the four la ...
ppt
... • composed of 90% hydrogen and 10% helium, with small amounts of CH4, NH3, H2O vapor and other compounds • At great depths within Jupiter, the pressure is so great that the hydrogen atoms are broken up, freeing the electrons so that the resulting atoms consist of bare protons. This produces a state ...
... • composed of 90% hydrogen and 10% helium, with small amounts of CH4, NH3, H2O vapor and other compounds • At great depths within Jupiter, the pressure is so great that the hydrogen atoms are broken up, freeing the electrons so that the resulting atoms consist of bare protons. This produces a state ...
The Solar System Interplanetary Matter and the Birth of the Planets
... The idea that the solar system was born from the collapse of a cloud of dust and gas for proposed by Immanuel Kant (1755) and by Pierre Simon Laplace (40 years later). During the first part of the 20th century, some proposed that the solar system was the result of a near collision of the Sun with an ...
... The idea that the solar system was born from the collapse of a cloud of dust and gas for proposed by Immanuel Kant (1755) and by Pierre Simon Laplace (40 years later). During the first part of the 20th century, some proposed that the solar system was the result of a near collision of the Sun with an ...
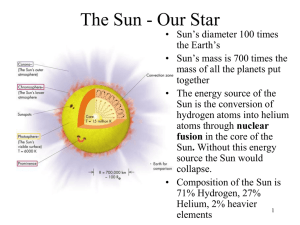
The Sun - Our Star - Academic Computer Center
... • The Sun is not burning. If it were burning fuel like coal it would have exhausted its fuel long ago. • The slow collapse of the Sun was once thought to be the energy source but that wouldn’t have lasted more than a few million years. • It wasn’t until the 20th century that physicists understood th ...
... • The Sun is not burning. If it were burning fuel like coal it would have exhausted its fuel long ago. • The slow collapse of the Sun was once thought to be the energy source but that wouldn’t have lasted more than a few million years. • It wasn’t until the 20th century that physicists understood th ...
Life Beyond our Solar System: Discovering New Planets
... • First, a brief look at our solar system is a must in search of habitable planets • Our solar system contains one star, our sun, at the center • Total of eight planets • And… ...
... • First, a brief look at our solar system is a must in search of habitable planets • Our solar system contains one star, our sun, at the center • Total of eight planets • And… ...
Chapter13_New
... The perihelion distances of scattered disk objects are close enough to Neptune's orbit that they will eventually experience an encounter with Neptune and move into the planetary system. stellar Trans-Neptunian Object (TNO) – A small, icy solar system body in an orbit beyond Neptune. ...
... The perihelion distances of scattered disk objects are close enough to Neptune's orbit that they will eventually experience an encounter with Neptune and move into the planetary system. stellar Trans-Neptunian Object (TNO) – A small, icy solar system body in an orbit beyond Neptune. ...
Brock physics - Brock University
... (d) [None of the above.] 16. Comparing stars S3 and S7 , which one has the larger radius? (a) S3 . (b) S7 . 17. Which of the following stars is a main sequence star? (a) S1 . (b) S2 . (c) S3 . (d) S7 . 18. Which of the following stars has the largest mass? (a) S3 (b) S4 (c) S5 (d) S6 19. Stars on th ...
... (d) [None of the above.] 16. Comparing stars S3 and S7 , which one has the larger radius? (a) S3 . (b) S7 . 17. Which of the following stars is a main sequence star? (a) S1 . (b) S2 . (c) S3 . (d) S7 . 18. Which of the following stars has the largest mass? (a) S3 (b) S4 (c) S5 (d) S6 19. Stars on th ...
15.Giant Planets - University of New Mexico
... •slow rotators ( 24 hours) •few satellites •close to Sun ( 1.6 AU) •Thin atmospheres •Weak or no magnetic field ...
... •slow rotators ( 24 hours) •few satellites •close to Sun ( 1.6 AU) •Thin atmospheres •Weak or no magnetic field ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.