1 - Colorado Center for Astrodynamics Research
... To launch a spacecraft from earth to an outer planet, like Jupiter, it is necessary to consider that it is already orbiting the sun with earth. Essentially, this orbit must be adjusted to send the spacecraft out to Jupiter. This can be pictured as three parts; circular orbit around earth, elliptica ...
... To launch a spacecraft from earth to an outer planet, like Jupiter, it is necessary to consider that it is already orbiting the sun with earth. Essentially, this orbit must be adjusted to send the spacecraft out to Jupiter. This can be pictured as three parts; circular orbit around earth, elliptica ...
ASTRONOMY 12 Problem Set 1 – Due Thursday, January 21, 2016
... 4) Consider an astronaut descending feet first into a ten solar mass (one solar mass is 1.99 × 1033 gm) black hole. Assume the astronaut is tall (she soon will be) and has a height of 200 cm and has a mass of 60 kg (6 × 104 gm). a) What would be the tidal force between the bottom of her feet and the ...
... 4) Consider an astronaut descending feet first into a ten solar mass (one solar mass is 1.99 × 1033 gm) black hole. Assume the astronaut is tall (she soon will be) and has a height of 200 cm and has a mass of 60 kg (6 × 104 gm). a) What would be the tidal force between the bottom of her feet and the ...
on his death bed. Retrograde Motion The heliocentric
... • Isaac Newton was born the year Galileo died. • He made major advances in mathematics, physics, and astronomy. • He pioneered the modern studies of motion, optics, and gravity and discovered the mathematical methods of calculus. • It was not until the 20th century that Newton’s laws of motion and ...
... • Isaac Newton was born the year Galileo died. • He made major advances in mathematics, physics, and astronomy. • He pioneered the modern studies of motion, optics, and gravity and discovered the mathematical methods of calculus. • It was not until the 20th century that Newton’s laws of motion and ...
Sample Assessment Items
... The stars in the night sky look as if they are slowly moving because _______________. a. the Earth is moving b. they rotate around the Sun c. they rotate around the Earth d. the Sun blocks them out at times Answer: a Stars are organized into patterns called constellations. One constellation is named ...
... The stars in the night sky look as if they are slowly moving because _______________. a. the Earth is moving b. they rotate around the Sun c. they rotate around the Earth d. the Sun blocks them out at times Answer: a Stars are organized into patterns called constellations. One constellation is named ...
Lecture 08a: Galilean moons - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... Goals Discover the 150+ moons in the outer solar system; • Jupiter’s Galilean satellites as a place for life; • Europa, Europa, Europa! ...
... Goals Discover the 150+ moons in the outer solar system; • Jupiter’s Galilean satellites as a place for life; • Europa, Europa, Europa! ...
The Sun
... • As the sun ages, its core collapses as hydrogen converts to helium, and this increases the gravity and pressure and fusion rate in the core • So, the sun is getting brighter long term • During the life of the solar system, the sun, now middle aged, has increased in luminosity by 25%, and close to ...
... • As the sun ages, its core collapses as hydrogen converts to helium, and this increases the gravity and pressure and fusion rate in the core • So, the sun is getting brighter long term • During the life of the solar system, the sun, now middle aged, has increased in luminosity by 25%, and close to ...
Lecture 3a
... • Very strong proponent of the scientific method – use of observations to test theories. • Early work was on motion, and practical elements like hydrostatics • In 1609 was the first one to use a telescope for astronomy => became the most famous scientist/celebrity in Europe • Last 30 years of hi ...
... • Very strong proponent of the scientific method – use of observations to test theories. • Early work was on motion, and practical elements like hydrostatics • In 1609 was the first one to use a telescope for astronomy => became the most famous scientist/celebrity in Europe • Last 30 years of hi ...
1 UNIT 3 EARTH HISTORY - POSSIBLE TEST QUESTIONS OUR
... 37. Describe the relative movement of this galaxy and its possible consequences to our galaxy. Raw Material for a Solar System 38. Which two atoms (elements) comprises most of our Sun. Solar Systems - General 39. What are planetesimals? Shape and Motion of Solar Systems 40. View from the “top”, whic ...
... 37. Describe the relative movement of this galaxy and its possible consequences to our galaxy. Raw Material for a Solar System 38. Which two atoms (elements) comprises most of our Sun. Solar Systems - General 39. What are planetesimals? Shape and Motion of Solar Systems 40. View from the “top”, whic ...
Lesson 5 - Introduction to the Solar System
... Ceres is the first discovered and largest member of the asteroid belt. It and dozens of other asteroids were considered to be planets for more than half a century, after which they became too numerous and were all demoted and reclassified as asteroids. However, Ceres was once again promoted and recl ...
... Ceres is the first discovered and largest member of the asteroid belt. It and dozens of other asteroids were considered to be planets for more than half a century, after which they became too numerous and were all demoted and reclassified as asteroids. However, Ceres was once again promoted and recl ...
astronomy ch 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... seen from Earth. In the Ptolemaic (geocentric) model, Venus would be seen in only new or crescent phases. However, as Galileo observed, Venus is seen in all phases, which agrees with the Copernican model as shown. ...
... seen from Earth. In the Ptolemaic (geocentric) model, Venus would be seen in only new or crescent phases. However, as Galileo observed, Venus is seen in all phases, which agrees with the Copernican model as shown. ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam: Summer 2013 The successful student will be able to… Unit 1: Our Planetary Neighborhood Write the planets in order of increasing distance from the Sun, Using a ratio determine how much larger one object is compared to another given their diameters, Convert AU ...
... Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam: Summer 2013 The successful student will be able to… Unit 1: Our Planetary Neighborhood Write the planets in order of increasing distance from the Sun, Using a ratio determine how much larger one object is compared to another given their diameters, Convert AU ...
Putting Earth In Its Place
... Place the marble on this mark to represent the sun. All distances will be measured from this point. Look at the Distance Data Table. Find the distance Mercury should be from the model sun. Unroll the adding machine tape and measure the distance from the sun to Mercury on the model. Mark this locatio ...
... Place the marble on this mark to represent the sun. All distances will be measured from this point. Look at the Distance Data Table. Find the distance Mercury should be from the model sun. Unroll the adding machine tape and measure the distance from the sun to Mercury on the model. Mark this locatio ...
Astronomy Chap 1
... 3. Are celestial objects like stars and planets in the daytime sky? 4. What is the relationship between latitude and the angular height of the Sun? 5. Explain how angular height of the Sun in different parts of the country correlate with sunburns. What is the critical angle? 6. Review the Solar Moti ...
... 3. Are celestial objects like stars and planets in the daytime sky? 4. What is the relationship between latitude and the angular height of the Sun? 5. Explain how angular height of the Sun in different parts of the country correlate with sunburns. What is the critical angle? 6. Review the Solar Moti ...
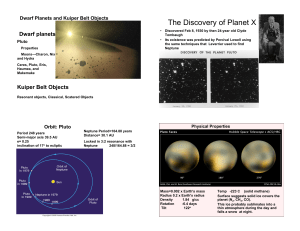
The Discovery of Planet X
... are called plutinos, after their most prominent member, Pluto. Classical Kuiper belt objects (also called cubewanos) have no such resonance, moving on almost circular orbits, unperturbed by Neptune. Examples are Quaoar and Makemake. The scattered disk contains objects further from the Sun, usually w ...
... are called plutinos, after their most prominent member, Pluto. Classical Kuiper belt objects (also called cubewanos) have no such resonance, moving on almost circular orbits, unperturbed by Neptune. Examples are Quaoar and Makemake. The scattered disk contains objects further from the Sun, usually w ...
Chapter 6 Physics
... 13. Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the Sun-Earth system. 14. Determine the escape speeds from (a) Mercury (b) Earth’s Moon 15. A neutron star results from the death of a star about 10 times as massive as the Sun. Composed of tightly packed neutrons, it is small and extremely dense. ...
... 13. Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the Sun-Earth system. 14. Determine the escape speeds from (a) Mercury (b) Earth’s Moon 15. A neutron star results from the death of a star about 10 times as massive as the Sun. Composed of tightly packed neutrons, it is small and extremely dense. ...
File - Mrs. Andrews` CBA classes
... The Planets sometime appear to be large, bright, and close compared to other times when they seem smaller, dimmer, and farther away. Ptolemy tried to shift each planet so that the earth was no longer the center causing an eccentric (off-center circle). Astronomers were offended by this because ...
... The Planets sometime appear to be large, bright, and close compared to other times when they seem smaller, dimmer, and farther away. Ptolemy tried to shift each planet so that the earth was no longer the center causing an eccentric (off-center circle). Astronomers were offended by this because ...
File - Zemali Salem
... are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, They all have roughly circular orbits in the same direction, and most have at least one moon. They vary widely in size, temperature, composition, and distance from the sun. The solar system contains billions of comets, but most of th ...
... are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, They all have roughly circular orbits in the same direction, and most have at least one moon. They vary widely in size, temperature, composition, and distance from the sun. The solar system contains billions of comets, but most of th ...
File - SMIC Physics
... Supergiants and Supernovas • Stars more than 8x massive than Sun → evolution occurs more quickly and more violently • Massive stars → core heats up to higher temps → heavier elements form by fusion (becoz higher temp is needed to fuse bigger elements. Eg : He → C needs higher temp) → star expands i ...
... Supergiants and Supernovas • Stars more than 8x massive than Sun → evolution occurs more quickly and more violently • Massive stars → core heats up to higher temps → heavier elements form by fusion (becoz higher temp is needed to fuse bigger elements. Eg : He → C needs higher temp) → star expands i ...
december 2010 - Holt Planetarium
... Sun. It appears as a dark line starting just below the centre of the disc and disappearing around the lower left edge. This filament is a strand of solar plasma that has been ejected from the surface and is caught up in magnetic field lines emanating from the solar interior. It is more than 700,000 ...
... Sun. It appears as a dark line starting just below the centre of the disc and disappearing around the lower left edge. This filament is a strand of solar plasma that has been ejected from the surface and is caught up in magnetic field lines emanating from the solar interior. It is more than 700,000 ...
Lecture 1: Observations of planetary systems
... We reside in our own planetary system, and much of what we know about planets and their origin comes from observations of the Solar System. The Solar System comprises the Sun, eight planets, and a large number of smaller bodies (including “dwarf planets”, asteroids, comets, etc.). The eight planets ...
... We reside in our own planetary system, and much of what we know about planets and their origin comes from observations of the Solar System. The Solar System comprises the Sun, eight planets, and a large number of smaller bodies (including “dwarf planets”, asteroids, comets, etc.). The eight planets ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.