Universal Gravitation
... 2. Draw the position of the planet when it is nearest the star. 3. Determine the distance from these positions to the star’s center (below). Analysis: 1. Choose one of the planets in the solar system. 2. Calculate the gravitational force when the planet is at perihelion and aphelion. You will need t ...
... 2. Draw the position of the planet when it is nearest the star. 3. Determine the distance from these positions to the star’s center (below). Analysis: 1. Choose one of the planets in the solar system. 2. Calculate the gravitational force when the planet is at perihelion and aphelion. You will need t ...
Chapter 1 Section Misconception Truth Distances in the Universe
... of nearby objects just as clearly in a space 10 times larger. Big ground‐based telescopes are already seeing most of the way back to the edge of the Universe (actually, to the beginning of time), so it is not possible to see 10 times farther. ...
... of nearby objects just as clearly in a space 10 times larger. Big ground‐based telescopes are already seeing most of the way back to the edge of the Universe (actually, to the beginning of time), so it is not possible to see 10 times farther. ...
KEPLER`S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION NAME: Date: Purpose
... Purpose: To understand Kepler’s Laws describing the movements of planets in the solar system. Background: In the 1500s, Nicolaus Copernicus challenged the GEOCENTRIC (earth-centered) model of the solar system that had been promoted and accepted by philosophers and astronomers such as Aristotle and P ...
... Purpose: To understand Kepler’s Laws describing the movements of planets in the solar system. Background: In the 1500s, Nicolaus Copernicus challenged the GEOCENTRIC (earth-centered) model of the solar system that had been promoted and accepted by philosophers and astronomers such as Aristotle and P ...
Solar System
... • These planets are named terrestrial because of their solid, rocky surfaces. • These planets are sometimes called the inner planets. ...
... • These planets are named terrestrial because of their solid, rocky surfaces. • These planets are sometimes called the inner planets. ...
Final Study Guide Questions Earth Science Spring 2016 Mr. Traeger 1
... Chapter 26, 27, and 29: Earth’s Motion, Models of the Solar System, and the Sun ...
... Chapter 26, 27, and 29: Earth’s Motion, Models of the Solar System, and the Sun ...
The red planet is called Mars The sun is our closest star. Laika was
... Mars is known as the red planet The sun is our nearest star Olympus Mons is the largest volcano in space Laika was the first living creature sent in to space There is no gravity in space It takes 24 hours for the earth to spin once A Russian astronaut is called a cosmonaut Mercury is the closest pla ...
... Mars is known as the red planet The sun is our nearest star Olympus Mons is the largest volcano in space Laika was the first living creature sent in to space There is no gravity in space It takes 24 hours for the earth to spin once A Russian astronaut is called a cosmonaut Mercury is the closest pla ...
Tycho Brahe & Johannes Kepler
... to help in analyzing the data he had collected. • Brahe started him out on his hardest problem: determine the orbit of Mars. • Mars has the largest observed retrograde motion and no circular orbit could be found to match Brahe’s observations. Brahe and assistants making observations ...
... to help in analyzing the data he had collected. • Brahe started him out on his hardest problem: determine the orbit of Mars. • Mars has the largest observed retrograde motion and no circular orbit could be found to match Brahe’s observations. Brahe and assistants making observations ...
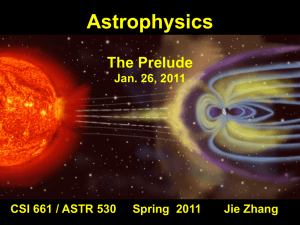
The Prelude - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... from the center One of 200 billion stars in our Galaxy ...
... from the center One of 200 billion stars in our Galaxy ...
Planet Jupiter
... liquid hydrogen. Within the planet pressure and temperature are so high that there is no clear boundary between the gas and liquid. Jupiter probably has a central core of rocky material about 1.5 times the diameter of Earth and 10 to 15 times more massive. Over this may rest an enormous mantle of li ...
... liquid hydrogen. Within the planet pressure and temperature are so high that there is no clear boundary between the gas and liquid. Jupiter probably has a central core of rocky material about 1.5 times the diameter of Earth and 10 to 15 times more massive. Over this may rest an enormous mantle of li ...
Planet Jupiter
... liquid hydrogen. Within the planet pressure and temperature are so high that there is no clear boundary between the gas and liquid. Jupiter probably has a central core of rocky material about 1.5 times the diameter of Earth and 10 to 15 times more massive. Over this may rest an enormous mantle of li ...
... liquid hydrogen. Within the planet pressure and temperature are so high that there is no clear boundary between the gas and liquid. Jupiter probably has a central core of rocky material about 1.5 times the diameter of Earth and 10 to 15 times more massive. Over this may rest an enormous mantle of li ...
Life of stars, formation of elements
... • 1500 LY away from us • The central “star” in Orion’s sword. Ionizing O star ...
... • 1500 LY away from us • The central “star” in Orion’s sword. Ionizing O star ...
Winter Interim Assessment Review
... •Most small objects are found in three areas: •Asteroid belt- region of the solar system between Jupiter and Mars. •Kuiper belt- extends to about 100 times Earth’s distance from the sun. •Oort cloud- stretches out more than 1,000 times the distance between the sun and Neptune. DWARF PLANETS •These o ...
... •Most small objects are found in three areas: •Asteroid belt- region of the solar system between Jupiter and Mars. •Kuiper belt- extends to about 100 times Earth’s distance from the sun. •Oort cloud- stretches out more than 1,000 times the distance between the sun and Neptune. DWARF PLANETS •These o ...
The Star
... above the entrance was now a fused stump, but even the first long-range photographs told us that here was the work of intelligence. A little later we detected the continent-wide pattern of radioactivity that had been buried in the rock. Even if the pylon above the Vault had been destroyed, this woul ...
... above the entrance was now a fused stump, but even the first long-range photographs told us that here was the work of intelligence. A little later we detected the continent-wide pattern of radioactivity that had been buried in the rock. Even if the pylon above the Vault had been destroyed, this woul ...
Stars
... neutron star will rotate, as did the original star, but much faster (think about a twirling ice skater). Charged particles trapped by the magnetic field will radiate energy at radio wavelengths, but most of this radiation comes out along the poles of the pulsar. The radio emissions are like a search ...
... neutron star will rotate, as did the original star, but much faster (think about a twirling ice skater). Charged particles trapped by the magnetic field will radiate energy at radio wavelengths, but most of this radiation comes out along the poles of the pulsar. The radio emissions are like a search ...
Red Giants
... Eventually, the layer just outside the core called the ``shell layer'' gets hot and dense enough for fusion to start. The fusion in the layer just outside the core is called shell burning. This fusion is very rapid because the shell layer is still compressing and increasing in temperature. The lumin ...
... Eventually, the layer just outside the core called the ``shell layer'' gets hot and dense enough for fusion to start. The fusion in the layer just outside the core is called shell burning. This fusion is very rapid because the shell layer is still compressing and increasing in temperature. The lumin ...
Solar Energy
... difficult to get a true feel for how big it is because nothing in our daily life comes even close. Imagine, if the Sun were a hallow ball, it would take about one million Earths to fill it. Now that is big! ...
... difficult to get a true feel for how big it is because nothing in our daily life comes even close. Imagine, if the Sun were a hallow ball, it would take about one million Earths to fill it. Now that is big! ...
planets suitable for life
... A wide range of uncertainty suggests a tremendous difficulty involved in making an estimation of NHP. The number 4 x 106 still seems to be an optimistic estimate, if giant Moon is necessary to make Earth suitable for life. The same number could well be a pessimistic estimate, if migration of Jovian ...
... A wide range of uncertainty suggests a tremendous difficulty involved in making an estimation of NHP. The number 4 x 106 still seems to be an optimistic estimate, if giant Moon is necessary to make Earth suitable for life. The same number could well be a pessimistic estimate, if migration of Jovian ...
Friday Feb 25th, 2000
... period = against the stars) ~ month – Similar to a woman’s cycle – Luna always a female association in all cultures ...
... period = against the stars) ~ month – Similar to a woman’s cycle – Luna always a female association in all cultures ...
Exploring the Universe
... spend 90% of their life. i. A diagonal band running from the bright, hot stars on the upper left to the dim, cool stars on the lower right ii. Example: The Sun lies in the main sequence iii. The sun is a yellow star (medium sized) that does fusion of hydrogen ...
... spend 90% of their life. i. A diagonal band running from the bright, hot stars on the upper left to the dim, cool stars on the lower right ii. Example: The Sun lies in the main sequence iii. The sun is a yellow star (medium sized) that does fusion of hydrogen ...
Copernican Revolution Part 1
... equality, and the contrast is drawn between the absolute equality we think of in mathematics and the rough, approximate equality which is what we have to be content with in dealing with objects with our senses. About heavenly motion in circles at uniform speed Eudoxus – concentric spheres (first m ...
... equality, and the contrast is drawn between the absolute equality we think of in mathematics and the rough, approximate equality which is what we have to be content with in dealing with objects with our senses. About heavenly motion in circles at uniform speed Eudoxus – concentric spheres (first m ...
Semester 1 Earth Science Gallery Review
... EARTH SCIENCE Gallery REVIEW Lab Station 1 1. Describe how the universe was formed: ...
... EARTH SCIENCE Gallery REVIEW Lab Station 1 1. Describe how the universe was formed: ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.