Slide #1: Chapter #1 - The Earth and Earth Coordinates The earth
... 14-19% greater than the current value of 24,874 statute miles (40,030 kilometers) ...
... 14-19% greater than the current value of 24,874 statute miles (40,030 kilometers) ...
Information extracted from Britannica 97
... likely to be responsible for the relatively high reflectivity of the surface. New ground-based instrumentation available from the early 1990s revealed the presence of frozen carbon monoxide and molecular nitrogen. Brightness fluctuations observed during Charon-Pluto mutual eclipses (see below) revea ...
... likely to be responsible for the relatively high reflectivity of the surface. New ground-based instrumentation available from the early 1990s revealed the presence of frozen carbon monoxide and molecular nitrogen. Brightness fluctuations observed during Charon-Pluto mutual eclipses (see below) revea ...
PHYSICAL SETTING EARTH SCIENCE
... 34 A sample of wood that originally contained 100 grams of carbon-14 now contains only 25 grams of carbon-14. Approximately how many years ago was this sample part of a living tree? (1) 2,850 years (3) 11,400 years (2) 5,700 years (4) 17,100 years ...
... 34 A sample of wood that originally contained 100 grams of carbon-14 now contains only 25 grams of carbon-14. Approximately how many years ago was this sample part of a living tree? (1) 2,850 years (3) 11,400 years (2) 5,700 years (4) 17,100 years ...
The Habitability of Planets Orbiting M
... orbiting other stars1 . Many of these planets are especially captivating because of their orbital distances, which place them in their stars’ canonical habitable zone—the region around a star where an orbiting planet with an Earth-like atmosphere (CO2 -H2 O-N2 ) could maintain water in liquid form o ...
... orbiting other stars1 . Many of these planets are especially captivating because of their orbital distances, which place them in their stars’ canonical habitable zone—the region around a star where an orbiting planet with an Earth-like atmosphere (CO2 -H2 O-N2 ) could maintain water in liquid form o ...
the text the talk here
... entirely his work. Here we see him at his most innovative. Book nine contains a riveting discussion of a major intellectual puzzle: Ptolemy’s data was sufficiently good to reveal two distinct anomalies in the planetary motions that were difficult to untangle. His goal will be ‘to save the appearance ...
... entirely his work. Here we see him at his most innovative. Book nine contains a riveting discussion of a major intellectual puzzle: Ptolemy’s data was sufficiently good to reveal two distinct anomalies in the planetary motions that were difficult to untangle. His goal will be ‘to save the appearance ...
Section 3.5 The Earth, Moon, and Sun
... Early on, people noticed that the fixed stars circle the earth a little more than once a day. We now know that this “motion” is actually due to the rotation of the earth, not to any movement of the stars themselves. If it were not for the planets, people might have assumed the night sky really was n ...
... Early on, people noticed that the fixed stars circle the earth a little more than once a day. We now know that this “motion” is actually due to the rotation of the earth, not to any movement of the stars themselves. If it were not for the planets, people might have assumed the night sky really was n ...
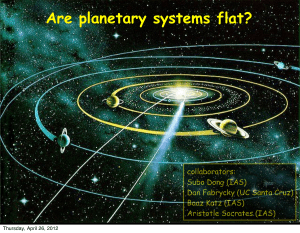
Are planetary systems flat?
... – it is astonishing to see all the planets move around the Sun from west to east, and almost in the same plane; all the satellites move around their planets in the same direction and nearly in the same plane as the planets; finally, the Sun, the planets, and all the satellites that have been observe ...
... – it is astonishing to see all the planets move around the Sun from west to east, and almost in the same plane; all the satellites move around their planets in the same direction and nearly in the same plane as the planets; finally, the Sun, the planets, and all the satellites that have been observe ...
The Discovery of Deep Time
... to a "lapidifying virtue diffused through the whole body of the geocosm." Steno, however, argued that glossopetrae looked like shark teeth because they were shark teeth, that had come from the mouths of once-living sharks, and come to be buried in mud or sand that was now dry land. Steno's work on s ...
... to a "lapidifying virtue diffused through the whole body of the geocosm." Steno, however, argued that glossopetrae looked like shark teeth because they were shark teeth, that had come from the mouths of once-living sharks, and come to be buried in mud or sand that was now dry land. Steno's work on s ...
A Stargazers Guide to Astronomy
... Introduction to Color Color is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum and has always existed, but the first explanation of color was provided by Sir Isaac Newton in 1666. Newton passed a narrow beam of sunlight through a prism located in a dark room. Of course all the visible spectrum (red, orange, ...
... Introduction to Color Color is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum and has always existed, but the first explanation of color was provided by Sir Isaac Newton in 1666. Newton passed a narrow beam of sunlight through a prism located in a dark room. Of course all the visible spectrum (red, orange, ...
CHAPTER 8 Survey of Solar Systems
... Earth’s North Pole, and this is the same direction in which the Sun itself spins. As the planets orbit the Sun, each also spins on its rotation axis. The spin is generally in the same direction as the planets’ orbital motion around the Sun (again, counterclockwise, as seen from above the Earth’s Nor ...
... Earth’s North Pole, and this is the same direction in which the Sun itself spins. As the planets orbit the Sun, each also spins on its rotation axis. The spin is generally in the same direction as the planets’ orbital motion around the Sun (again, counterclockwise, as seen from above the Earth’s Nor ...
Notes for Class 7, March 2
... o So far, too close to star, too hot o If planets around other stars are common, maybe there will be some planets with the right conditions, and maybe some of them will have life ...
... o So far, too close to star, too hot o If planets around other stars are common, maybe there will be some planets with the right conditions, and maybe some of them will have life ...
Daily Communication Skills
... Example #1: You are on trial for a crime and learn that the jury is “disinterested” in your case. Is this good or bad news? The word “disinterested” means ‘unbiased, and that characteristic of a jury is good if you are ever on trial. Example #2: What do “rotation” and “revolution” mean? Is it correc ...
... Example #1: You are on trial for a crime and learn that the jury is “disinterested” in your case. Is this good or bad news? The word “disinterested” means ‘unbiased, and that characteristic of a jury is good if you are ever on trial. Example #2: What do “rotation” and “revolution” mean? Is it correc ...
EARTH SCIENCE, PAGE I. Introduction Earth Science
... - history of the planet and its life forms from its origin to the present 2. Oceanography - study of the oceans and ocean phenomena 3. Meteorology - study of the atmosphere and atmospheric phenomena - includes studies of weather and climate 4. Astronomy - study of the universe B. The Earth's Environ ...
... - history of the planet and its life forms from its origin to the present 2. Oceanography - study of the oceans and ocean phenomena 3. Meteorology - study of the atmosphere and atmospheric phenomena - includes studies of weather and climate 4. Astronomy - study of the universe B. The Earth's Environ ...
Regulus, June-July 1990 - RASC Kingston Centre
... Dickinson this long eclipse disappearance and concluded that there were several reasons for this: The Jovian atmosphere bends some of the sunlight and we can, with a larger telescope, see it actually going stage by stage into the shadow since Ganymede is a disk and not just a dot, and there may be a ...
... Dickinson this long eclipse disappearance and concluded that there were several reasons for this: The Jovian atmosphere bends some of the sunlight and we can, with a larger telescope, see it actually going stage by stage into the shadow since Ganymede is a disk and not just a dot, and there may be a ...
2.4 Statistical properties of radial velocity planets
... – for about 1 % of the stars a close in (<0.1 AU), hot Jupiter with mP sin i > 0.1MJ is detected, – for about 15 % of the stars a giant planet with mP sin i > 0.1MJ out to a separation of 5 AU is present, – RV-surveys can not say much about the frequency of giant planets at large separation > 5 AU, ...
... – for about 1 % of the stars a close in (<0.1 AU), hot Jupiter with mP sin i > 0.1MJ is detected, – for about 15 % of the stars a giant planet with mP sin i > 0.1MJ out to a separation of 5 AU is present, – RV-surveys can not say much about the frequency of giant planets at large separation > 5 AU, ...
03_Testbank - Lick Observatory
... E) We don't know how he did it since all his writings were destroyed. Answer: C 16) Which of the following statements about scientific models is true? A) A model tries to represent all aspects of nature. B) A model tries to represent only one aspect of nature. C) A model can be used to explain and p ...
... E) We don't know how he did it since all his writings were destroyed. Answer: C 16) Which of the following statements about scientific models is true? A) A model tries to represent all aspects of nature. B) A model tries to represent only one aspect of nature. C) A model can be used to explain and p ...
Notes (PowerPoint)
... o Acceleration = rate of change in velocity (speed and/or direction) o Constant speed in a straight line: no acceleration, no force o Inverse also true: no force means no acceleration, result is no change in velocity = no change in speed and no change in direction • “An object in motion tends to sta ...
... o Acceleration = rate of change in velocity (speed and/or direction) o Constant speed in a straight line: no acceleration, no force o Inverse also true: no force means no acceleration, result is no change in velocity = no change in speed and no change in direction • “An object in motion tends to sta ...
Terrestrial Planets
... the light emanating from a star passes very close to another star on its way to an observer on Earth, the gravity of the intermediary star will slightly bend the light rays from the source star, causing the two stars to appear farther apart than they normally would. This effect was used by Sir Arthu ...
... the light emanating from a star passes very close to another star on its way to an observer on Earth, the gravity of the intermediary star will slightly bend the light rays from the source star, causing the two stars to appear farther apart than they normally would. This effect was used by Sir Arthu ...
NATS 1311-From the Cosmos to Earth
... north/south of zenith. Sun can also be used if you know the date and the Sun’s declination on that date. ...
... north/south of zenith. Sun can also be used if you know the date and the Sun’s declination on that date. ...
Earth Science Exams and answer keys 2015 Season
... A) 1 million years ago B) 67 million years ago C) 208 million years ago D) 580 million years ago 48. Uranium has a radioactive half-life of about 4.5 billion years. The earth is estimated to be about 4.5 billion years old. The oldest rocks found on earth would have a ratio of uranium atoms to lead a ...
... A) 1 million years ago B) 67 million years ago C) 208 million years ago D) 580 million years ago 48. Uranium has a radioactive half-life of about 4.5 billion years. The earth is estimated to be about 4.5 billion years old. The oldest rocks found on earth would have a ratio of uranium atoms to lead a ...
iaf2001_paper (doc - 1.8 MB)
... is connected to the chemical composition near the stellar core. The second order differences ...
... is connected to the chemical composition near the stellar core. The second order differences ...
Lecture 2: ppt, 5 MB
... Supernovae: Massive stars end in glorious explosions. Hubble found three mysterious rings of material encircling a doomed star that exploded as a supernova in 1987. During the years since the eruption, Hubble spied brightened spots on the ...
... Supernovae: Massive stars end in glorious explosions. Hubble found three mysterious rings of material encircling a doomed star that exploded as a supernova in 1987. During the years since the eruption, Hubble spied brightened spots on the ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Section 1
... • The apparent motion of stars, or motion as it appears from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear ...
... • The apparent motion of stars, or motion as it appears from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear ...
Mars-Bound Comet Siding Spring Sprouts Multiple Jets Eastern
... This is an orbit diagram for the outer solar system. The Sun and Terrestrial planets are at the center. The orbits of the four giant planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, are shown by purple solid circles. The Kuiper Belt, including Pluto, is shown by the dotted light blue region just beyond ...
... This is an orbit diagram for the outer solar system. The Sun and Terrestrial planets are at the center. The orbits of the four giant planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, are shown by purple solid circles. The Kuiper Belt, including Pluto, is shown by the dotted light blue region just beyond ...
September 2016
... comes as close as 7.4 million kilometres to its parent star. If Proxima Centauri were like our Sun, the planet would be blazingly hot but because red dwarfs are much dimmer, scientists estimate Proxima b should have an Earth-like range of temperatures, from -30°C on its dark side to +30°C on its lig ...
... comes as close as 7.4 million kilometres to its parent star. If Proxima Centauri were like our Sun, the planet would be blazingly hot but because red dwarfs are much dimmer, scientists estimate Proxima b should have an Earth-like range of temperatures, from -30°C on its dark side to +30°C on its lig ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.