THe SCieNCe OF ASTrONOMY
... Astronomy has been called the oldest of the sciences, because its roots stretch deepest into antiquity. Ancient civilizations did not always practice astronomy in the same ways or for the same reasons that we study it today, but they nonetheless had some amazing achievements. Understanding this anci ...
... Astronomy has been called the oldest of the sciences, because its roots stretch deepest into antiquity. Ancient civilizations did not always practice astronomy in the same ways or for the same reasons that we study it today, but they nonetheless had some amazing achievements. Understanding this anci ...
SRP_Space_Lesson 5 - Scientist in Residence Program
... is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the d ...
... is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the d ...
On Hyperdimensional Physics… and More….
... for over 200 years; in place of Newton, Riemann was proposing that such "apparent forces'" are a direct result of objects moving through 3-space "geometry" ... distorted by the intruding geometry of "4-space!" It is clear that Maxwell and other "giants" of 19th Century physics (Kelvin, for one), as ...
... for over 200 years; in place of Newton, Riemann was proposing that such "apparent forces'" are a direct result of objects moving through 3-space "geometry" ... distorted by the intruding geometry of "4-space!" It is clear that Maxwell and other "giants" of 19th Century physics (Kelvin, for one), as ...
The Case of the Galactic Vacation
... acceleration, and weightlessness. Next stop is Starship 2040, where Mr. Wang of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center explains what tourism in space will be like in about 50 years. Now the detectives realize that no matter where they go in the solar system or galaxy, the current rocket system will not g ...
... acceleration, and weightlessness. Next stop is Starship 2040, where Mr. Wang of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center explains what tourism in space will be like in about 50 years. Now the detectives realize that no matter where they go in the solar system or galaxy, the current rocket system will not g ...
Here
... If we do some careful observations, we find: 1) The length of the daylight hours at a given spot varies throughout the year: the Sun is out a longer time when it is warmer (i.e. summer), and out a shorter time when it is colder. 2) On a given day, the length of the daylight hours depends on where yo ...
... If we do some careful observations, we find: 1) The length of the daylight hours at a given spot varies throughout the year: the Sun is out a longer time when it is warmer (i.e. summer), and out a shorter time when it is colder. 2) On a given day, the length of the daylight hours depends on where yo ...
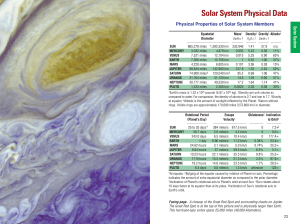
Solar System Tables
... and is also known as 1 astronomical unit (AU). 2The time it takes for light to travel from the Sun to the respective Planet. Light travels at 186,282 miles/sec (299,792 km/sec). 3Earth’s equatorial diameter is 7,926 miles (12,756 km). 4Earth’s mass is 1.32 x 1025 pounds (5.97 x 1024 kg). 5Earth’s vo ...
... and is also known as 1 astronomical unit (AU). 2The time it takes for light to travel from the Sun to the respective Planet. Light travels at 186,282 miles/sec (299,792 km/sec). 3Earth’s equatorial diameter is 7,926 miles (12,756 km). 4Earth’s mass is 1.32 x 1025 pounds (5.97 x 1024 kg). 5Earth’s vo ...
13_Testbank - Lick Observatory
... Answer: We do not yet know how common small, rocky Earth-like planets are around other stars, or what are the characteristics of their orbits. This is the primary motivation for new spacebased missions. We can speculate, however, on the possibility of life on moons around the Jupiter-like planets in ...
... Answer: We do not yet know how common small, rocky Earth-like planets are around other stars, or what are the characteristics of their orbits. This is the primary motivation for new spacebased missions. We can speculate, however, on the possibility of life on moons around the Jupiter-like planets in ...
It`s about Time - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics
... Thus our clocks are now related to an Atomic Time standard which uses Caesium Beam frequency standards to determine the length of the second. But this has not stopped the Earth’s rotation from slowing down, and so very gradually the synchronization between the Sun’s position in the sky and our clock ...
... Thus our clocks are now related to an Atomic Time standard which uses Caesium Beam frequency standards to determine the length of the second. But this has not stopped the Earth’s rotation from slowing down, and so very gradually the synchronization between the Sun’s position in the sky and our clock ...
Dorn_projectF08 - Bowling Green State University
... Earth's Moon Earth's Moon is a singular unique satellite wholly created by the debris of a massive impact millions of years ago. Since man has occupied this planet he has looked in the night sky and marveled at the ever changing appearance of its surface. The Moon orbits at roughly 380,000 km. dista ...
... Earth's Moon Earth's Moon is a singular unique satellite wholly created by the debris of a massive impact millions of years ago. Since man has occupied this planet he has looked in the night sky and marveled at the ever changing appearance of its surface. The Moon orbits at roughly 380,000 km. dista ...
Catching Planets in Formation with GMT
... GMTIFS offset to “planet” location. Use spatial information to correct for scattered light at each wavelength. Preferable to long slit. ...
... GMTIFS offset to “planet” location. Use spatial information to correct for scattered light at each wavelength. Preferable to long slit. ...
Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1
... common. The fact that we find giant Jupiter-like planets very close to the stars demonstrates, however, that planets can move considerable distances from their birthplaces as they interact with the protostellar disk and other planets. The nebular theory of planet formation is therefore being adjuste ...
... common. The fact that we find giant Jupiter-like planets very close to the stars demonstrates, however, that planets can move considerable distances from their birthplaces as they interact with the protostellar disk and other planets. The nebular theory of planet formation is therefore being adjuste ...
Chapter 10
... 4. Describe the interior of Jupiter and draw a labeled sketch of a cross section through Jupiter. 5. Be able to identify by sight, and to describe the Galilean satellites of Jupiter, including the origin and properties of their surface features. How can these moons be warm even though they are so sm ...
... 4. Describe the interior of Jupiter and draw a labeled sketch of a cross section through Jupiter. 5. Be able to identify by sight, and to describe the Galilean satellites of Jupiter, including the origin and properties of their surface features. How can these moons be warm even though they are so sm ...
4P38.pdf
... that the solar high-energy flux was about 3 times the present value 2.5 Gyr ago and about 6 times the present value about 3.5 Gyr ago (when life arose on Earth). In summary, compelling observational evidence indicates that the Sun underwent a much more active phase in the past. The enhanced activity ...
... that the solar high-energy flux was about 3 times the present value 2.5 Gyr ago and about 6 times the present value about 3.5 Gyr ago (when life arose on Earth). In summary, compelling observational evidence indicates that the Sun underwent a much more active phase in the past. The enhanced activity ...
Lecture 7: Extrasolar Planets 01/08/2013 update: 725 exoplanets
... Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. According to Einstein, when the light emanating from a star passes very close to another star on its way to an observer on Earth, the gravity of the intermediary star will slightly bend the light rays from the source star, causing the two stars to appear fart ...
... Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. According to Einstein, when the light emanating from a star passes very close to another star on its way to an observer on Earth, the gravity of the intermediary star will slightly bend the light rays from the source star, causing the two stars to appear fart ...
Enceladus` Water Vapor Plume - Laboratory for Atmospheric and
... egress locations are summarized in Table 1. In the HSP and FUV data for the gamma Orionis occultation ingress, which occurred at –76- latitude, the signal was attenuated as the star passed behind Enceladus_ plume (Fig. 2). The starlight started to decrease at È24 s before ingress, at a ray altitude ...
... egress locations are summarized in Table 1. In the HSP and FUV data for the gamma Orionis occultation ingress, which occurred at –76- latitude, the signal was attenuated as the star passed behind Enceladus_ plume (Fig. 2). The starlight started to decrease at È24 s before ingress, at a ray altitude ...
The Solar System
... earth. It was formed about 22,000 years ago by the impact of a giant metallic nickel-iron meteorite, which arrived from space at a speed of about 50,000 kilometers per hour, and weighed many hundreds of tons. Friction with the atmosphere does not really slow such a mighty mass, which smashed into th ...
... earth. It was formed about 22,000 years ago by the impact of a giant metallic nickel-iron meteorite, which arrived from space at a speed of about 50,000 kilometers per hour, and weighed many hundreds of tons. Friction with the atmosphere does not really slow such a mighty mass, which smashed into th ...
Lab Script
... with it to get used to what your “world” looks like. In the very upper-left corner is your tool selection tool. By default, SN opens in adaptive mode which allows you to click and drag around the scene, and brings up information when you hover over objects in the sky. You can play around with the ot ...
... with it to get used to what your “world” looks like. In the very upper-left corner is your tool selection tool. By default, SN opens in adaptive mode which allows you to click and drag around the scene, and brings up information when you hover over objects in the sky. You can play around with the ot ...
Chapter 3
... and, moreover, with unpredictable irregularities, GMT (UT) and UTC tend to drift apart. For practical reasons, it is desirable to keep the difference between GMT (UT) and UTC sufficiently small. To ensure that the difference, DUT, never exceeds ±0.9 s, UTC is synchronized with UT by inserting or omi ...
... and, moreover, with unpredictable irregularities, GMT (UT) and UTC tend to drift apart. For practical reasons, it is desirable to keep the difference between GMT (UT) and UTC sufficiently small. To ensure that the difference, DUT, never exceeds ±0.9 s, UTC is synchronized with UT by inserting or omi ...
CHAPTER XI
... directly, we should have arrived at no greater precision, and we[Pg 295] should, moreover, have had to plan out a journey which in itself is the most insurmountable of all the problems. The Moon is at the frontier of our little terrestrial province: one might say that it traces the limits of our dom ...
... directly, we should have arrived at no greater precision, and we[Pg 295] should, moreover, have had to plan out a journey which in itself is the most insurmountable of all the problems. The Moon is at the frontier of our little terrestrial province: one might say that it traces the limits of our dom ...
Astro 101 Final F15 - Nicholls State University
... d. The force from the planets’ fast rotation rates made them fly off. ____ 24. It would be difficult for humans to survive on the surface of Mars for long periods of time because: a. there is not enough oxygen in the atmosphere. b. the range in temperature between day and night is too large. c. ther ...
... d. The force from the planets’ fast rotation rates made them fly off. ____ 24. It would be difficult for humans to survive on the surface of Mars for long periods of time because: a. there is not enough oxygen in the atmosphere. b. the range in temperature between day and night is too large. c. ther ...
Kepler Telescope Spots Smallest Exoplanet Yet The Night Sky
... After dinnertime at this time of year, four carnivore constellations stand in a row from the northeast to south. They're all seen in profile with their noses pointed up and their feet (if any) to the right: Ursa Major in the northeast (with the Big Dipper as its brightest part), Leo in the east, Hyd ...
... After dinnertime at this time of year, four carnivore constellations stand in a row from the northeast to south. They're all seen in profile with their noses pointed up and their feet (if any) to the right: Ursa Major in the northeast (with the Big Dipper as its brightest part), Leo in the east, Hyd ...
Life on Other Worlds
... THE INVESTIGATION of the structure of the universe may be said to commence with the work of William Herschel (1738-1822). B y profession a musician, Herschel came to England from Hanover at the age of nineteen to improve his fortunes. H e earned his living by playing the organ and teaching music, an ...
... THE INVESTIGATION of the structure of the universe may be said to commence with the work of William Herschel (1738-1822). B y profession a musician, Herschel came to England from Hanover at the age of nineteen to improve his fortunes. H e earned his living by playing the organ and teaching music, an ...
earth science
... The Marcellus shale is a black shale formation that was formed during the Middle Devonian Period. The shale extends from New York State as far south as Alabama. The Marcellus shale is exposed at the surface in the northern Finger Lakes region, and is buried 2.1 kilometers below the surface along the ...
... The Marcellus shale is a black shale formation that was formed during the Middle Devonian Period. The shale extends from New York State as far south as Alabama. The Marcellus shale is exposed at the surface in the northern Finger Lakes region, and is buried 2.1 kilometers below the surface along the ...
Pata Picante Simon
... _____ Explain the greenhouse effect; include the major greenhouse gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone). _____ Compare and contrast the major greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, fluorocarbons), their abundance and heat trapping capacity. _____ D ...
... _____ Explain the greenhouse effect; include the major greenhouse gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone). _____ Compare and contrast the major greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, fluorocarbons), their abundance and heat trapping capacity. _____ D ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.