Extrasolar Planets: An Amateur`s Search
... those stars actually with planets due to planet forming factors, fp, dictate the fraction of stars with extrasolar planets forming. Np in this case is the total number of extrasolar planets in the galaxy that form or formed per Earth year. Thus, using best estimated values given above, there should ...
... those stars actually with planets due to planet forming factors, fp, dictate the fraction of stars with extrasolar planets forming. Np in this case is the total number of extrasolar planets in the galaxy that form or formed per Earth year. Thus, using best estimated values given above, there should ...
Astrophysics - Cathkin High School
... thought that the Sun revolved around the Earth because that is what it seems to do! Similarly most people were sure that the Earth was flat until there was definite proof from sailors who had ventured round the world and not fallen off! It may prove useful therefore to give a brief historical introd ...
... thought that the Sun revolved around the Earth because that is what it seems to do! Similarly most people were sure that the Earth was flat until there was definite proof from sailors who had ventured round the world and not fallen off! It may prove useful therefore to give a brief historical introd ...
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite
... The study of exoplanets—planets outside our Solar System—is one of the most exciting and rapidly advancing fields of science. Especially valuable are systems in which a planet’s orbit carries it directly across the face of its host star. For such a “transiting” planet, it is possible to determine th ...
... The study of exoplanets—planets outside our Solar System—is one of the most exciting and rapidly advancing fields of science. Especially valuable are systems in which a planet’s orbit carries it directly across the face of its host star. For such a “transiting” planet, it is possible to determine th ...
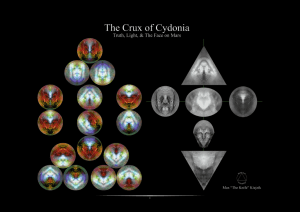
The Crux of Cydonia
... That is exactly what The Face on Mars represents. In order to be able to begin to comprehend how deep this rabbit hole goes, one must first be willing to consider at least six impossible things before breakfast. 1. We are not alone nor are we the most intelligent species in the universe. 2. Cydonia ...
... That is exactly what The Face on Mars represents. In order to be able to begin to comprehend how deep this rabbit hole goes, one must first be willing to consider at least six impossible things before breakfast. 1. We are not alone nor are we the most intelligent species in the universe. 2. Cydonia ...
Assessing the massive young Sun hypothesis to solve the warm
... ceptible to photodissociation by solar UV, it can remain in the atmosphere for much longer and methanogenic bacteria could maintain the required atmospheric levels (Pavlov et al. 2000). Were there adequate populations of methanogenic bacteria available in the early Archean? With only trace amounts o ...
... ceptible to photodissociation by solar UV, it can remain in the atmosphere for much longer and methanogenic bacteria could maintain the required atmospheric levels (Pavlov et al. 2000). Were there adequate populations of methanogenic bacteria available in the early Archean? With only trace amounts o ...
Introduction to Astronomy - Northumberland Astronomical Society
... Galileo used a telescope to make astronomical observations. He discovered: The moons of Jupiter Mountains and craters on the Moon The Milky Way is comprised of countless stars The phases of Venus Sunspots on the Sun ...
... Galileo used a telescope to make astronomical observations. He discovered: The moons of Jupiter Mountains and craters on the Moon The Milky Way is comprised of countless stars The phases of Venus Sunspots on the Sun ...
SACE 2 Physics Key Ideas Textbook Third Edition Part 2 sample
... 98 to the equator. This means they are in retrograde orbits – they orbit in the opposite direction to which the Earth turns. The advantage of this particular orbit is that the satellites cover (i.e can “see”) the same part of the Earth’s surface at the same time each day, and they do this day after ...
... 98 to the equator. This means they are in retrograde orbits – they orbit in the opposite direction to which the Earth turns. The advantage of this particular orbit is that the satellites cover (i.e can “see”) the same part of the Earth’s surface at the same time each day, and they do this day after ...
The Formation of Planetary Systems
... gas clouds, fallen meteorites, and Earth’s Moon, as well as of the various planets observed with ground-based telescopes and planetary space probes. Ironically, studies of Earth itself do not help much, because information about our planet’s early stages eroded away long ago. Meteorites and comets p ...
... gas clouds, fallen meteorites, and Earth’s Moon, as well as of the various planets observed with ground-based telescopes and planetary space probes. Ironically, studies of Earth itself do not help much, because information about our planet’s early stages eroded away long ago. Meteorites and comets p ...
DIPLOMA THESIS Spectroscopic study of the star 70 Virginis and its
... spectacular achievements in the extra-solar planets research. While in the middle of 1980’s there were no extra-solar planets proved to be, nowadays (according to [16] The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopedia) more than 240 planets within about 210 star systems are known. This research deals with essenti ...
... spectacular achievements in the extra-solar planets research. While in the middle of 1980’s there were no extra-solar planets proved to be, nowadays (according to [16] The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopedia) more than 240 planets within about 210 star systems are known. This research deals with essenti ...
A Modern View of the Universe
... astronomy, many of the distances are so large that kilometers are not the most convenient unit. Instead, we often use two other units: • One astronomical unit (AU) is Earth’s average distance from the Sun, which is about 150 million kilometers (93 million miles). We commonly describe distances with ...
... astronomy, many of the distances are so large that kilometers are not the most convenient unit. Instead, we often use two other units: • One astronomical unit (AU) is Earth’s average distance from the Sun, which is about 150 million kilometers (93 million miles). We commonly describe distances with ...
unit 23 - Institute for School Partnership
... This icon highlights an opportunity to check for understanding through a formal or informal assessment. ...
... This icon highlights an opportunity to check for understanding through a formal or informal assessment. ...
or view
... processes, which are believed to have played an important role in climate evolution. The main processes of removing mass from the atmosphere are the sputtering of atmospheric species by oxygen pick-up ions at the exobase level, and photochemical escape (Kass & Yung, 1995; Jakosky et al., 1994). The ...
... processes, which are believed to have played an important role in climate evolution. The main processes of removing mass from the atmosphere are the sputtering of atmospheric species by oxygen pick-up ions at the exobase level, and photochemical escape (Kass & Yung, 1995; Jakosky et al., 1994). The ...
Asteroids, Comets & Meteors Teacher's Guide
... as they fall through Earth’s upper atmosphere. 99.9% of all meteors seen are very small rocks no larger than single grains of sand or even specks of dust. The small particles are often the remains of dust and pebbles released from comets. The 0.1% remaining meteors are often larger and burn much bri ...
... as they fall through Earth’s upper atmosphere. 99.9% of all meteors seen are very small rocks no larger than single grains of sand or even specks of dust. The small particles are often the remains of dust and pebbles released from comets. The 0.1% remaining meteors are often larger and burn much bri ...
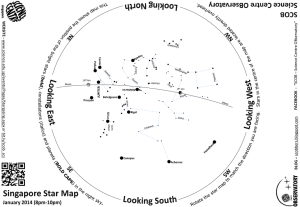
Star Map - Science Centre
... The Big Dipper is one of the most famous asterisms (star patterns) throughout history. In some places of the Northern Hemisphere, its seven brightest stars can be seen all year round. Further South near the equator, it is only visible for a few months. Merak and Dubhe are known as The Pointers, poin ...
... The Big Dipper is one of the most famous asterisms (star patterns) throughout history. In some places of the Northern Hemisphere, its seven brightest stars can be seen all year round. Further South near the equator, it is only visible for a few months. Merak and Dubhe are known as The Pointers, poin ...
C - ScienceWilmeth5
... If this day continues to be sunny, what will most likely happen to the length of the shadow from 2P.M. to 4P.M.? A. The length of the shadow will stay the same. B. The length of the shadow will decrease and then increase. C. The length of the shadow will increase. D. The length of the shadow will de ...
... If this day continues to be sunny, what will most likely happen to the length of the shadow from 2P.M. to 4P.M.? A. The length of the shadow will stay the same. B. The length of the shadow will decrease and then increase. C. The length of the shadow will increase. D. The length of the shadow will de ...
Moon Search Algorithms for NASA`s Dawn
... clear its neighborhood of debris [17]. In other words, it should be the dominant gravitational body in its orbit. Any object, like Pluto, that meets the first two requirements but not the third one is called a dwarf planet. Finally, most recently, in July of 2011, Pluto’s fourth moon was discovered ...
... clear its neighborhood of debris [17]. In other words, it should be the dominant gravitational body in its orbit. Any object, like Pluto, that meets the first two requirements but not the third one is called a dwarf planet. Finally, most recently, in July of 2011, Pluto’s fourth moon was discovered ...
by Kendrick Frazier Pluto turns out not to be responsible for
... he began his account, "I perceived one that appeared visibly larger than the rest." Because it had a measurable diameter, it could not be a star. H e continued his observations over the next several nights and observed definite motion. He thought his discovery was a comet, but within two months othe ...
... he began his account, "I perceived one that appeared visibly larger than the rest." Because it had a measurable diameter, it could not be a star. H e continued his observations over the next several nights and observed definite motion. He thought his discovery was a comet, but within two months othe ...
Herschel
... the Solar System placed beyond the orbit of Neptune (30 UA) up to ~55 UA. It is similar to the asteroid belt but 20 times wider and 20-200 times more massive. ...
... the Solar System placed beyond the orbit of Neptune (30 UA) up to ~55 UA. It is similar to the asteroid belt but 20 times wider and 20-200 times more massive. ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... v’ is the speed of the Moon measured by the two astronomers, which is defined as the distance travelled S divided by the time interval (tE(1) − tO(1)). Since we know the distance and we measure the times, this quantity is known. We need to calculate vo. The problem of [1] is assuming OO,OE both at 3 ...
... v’ is the speed of the Moon measured by the two astronomers, which is defined as the distance travelled S divided by the time interval (tE(1) − tO(1)). Since we know the distance and we measure the times, this quantity is known. We need to calculate vo. The problem of [1] is assuming OO,OE both at 3 ...
TASC Science Blueprint Overview (GHI)
... relationship among the net force on a macroscopic object, its mass, and its acceleration. Use mathematical representations to support the claim that the total momentum of a system of objects is conserved when there is no net force on the system. Apply scientific and engineering ideas to design ...
... relationship among the net force on a macroscopic object, its mass, and its acceleration. Use mathematical representations to support the claim that the total momentum of a system of objects is conserved when there is no net force on the system. Apply scientific and engineering ideas to design ...
an all-sky extrasolar planet survey with multiple object, dispersed
... challenges for the fields of planetary origins and evolution, but also indicate that a large sample of planets is required to obtain a general understanding of the nature of extrasolar planets and their formation and evolution. Although the high-precision echelle Doppler instruments have proven quit ...
... challenges for the fields of planetary origins and evolution, but also indicate that a large sample of planets is required to obtain a general understanding of the nature of extrasolar planets and their formation and evolution. Although the high-precision echelle Doppler instruments have proven quit ...
“And God Said, Let There Be Lights in the Firmament of Heaven”
... although we do not understand the specifics of the processes by which stars produce hot coronas and accelerate energetic particles we have identified the essential ingredients of these processes those ingredients are ions rotation and internal motion all stars possess the first two and most possess ...
... although we do not understand the specifics of the processes by which stars produce hot coronas and accelerate energetic particles we have identified the essential ingredients of these processes those ingredients are ions rotation and internal motion all stars possess the first two and most possess ...
Planet-finding Activity Guide How do we find planets around other
... The importance of scale: If you were to shrink the Sun to the size of the foam ball (approximately 3”), one light year would be equivalent to about 330 miles. Jupiter would be about 150 feet away (halfway down a football field). The nearest star (Alpha Centauri – at roughly 4 light years) is about 1 ...
... The importance of scale: If you were to shrink the Sun to the size of the foam ball (approximately 3”), one light year would be equivalent to about 330 miles. Jupiter would be about 150 feet away (halfway down a football field). The nearest star (Alpha Centauri – at roughly 4 light years) is about 1 ...
Course Description: This is an introductory course in Descriptive
... d) Distinguishing four separate types of rocks and describing how each is formed. e) Explaining the process of radioactive dating of rocks. f) Describing the general properties of oceans and other bodies of water on Earth and how they interact with continents and the atmosphere. g) Labeling Earth’s ...
... d) Distinguishing four separate types of rocks and describing how each is formed. e) Explaining the process of radioactive dating of rocks. f) Describing the general properties of oceans and other bodies of water on Earth and how they interact with continents and the atmosphere. g) Labeling Earth’s ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.