Studying Space
... Parallax of stars • Aids scientists in measuring distance. • It is the apparent shift of a star over a 6 month period. • It is just like when you shut 1 eye & look at an object; then open the other & the object appears to have moved. ...
... Parallax of stars • Aids scientists in measuring distance. • It is the apparent shift of a star over a 6 month period. • It is just like when you shut 1 eye & look at an object; then open the other & the object appears to have moved. ...
Answers to Science Semester 1Review Possible hazards in the lab
... vaccine. 7. Some technology that harms society are super bacteria and pollution. 8. Technology is developed, built, and improved all over the world. It can benefit any culture. 9. Society influences technology development by using and purchasing existing technology. 10. Law tells why something happe ...
... vaccine. 7. Some technology that harms society are super bacteria and pollution. 8. Technology is developed, built, and improved all over the world. It can benefit any culture. 9. Society influences technology development by using and purchasing existing technology. 10. Law tells why something happe ...
Meteors - Little Worksheets
... really stars. Of course, we see the moon. Some of the other lights in the sky are planets. Planets revolve around the sun like earth does. Once in awhile someone will see what they call a shooting star. A shooting star looks like a star that is moving quickly across the sky. Some people believe that ...
... really stars. Of course, we see the moon. Some of the other lights in the sky are planets. Planets revolve around the sun like earth does. Once in awhile someone will see what they call a shooting star. A shooting star looks like a star that is moving quickly across the sky. Some people believe that ...
Exploring Space What’s Out There?
... Earth’s magnetic field and atmosphere – Aurora Borealis at the North Pole – Aurora Australis at the South Pole ...
... Earth’s magnetic field and atmosphere – Aurora Borealis at the North Pole – Aurora Australis at the South Pole ...
KS2 Earth and Space
... huge the distances involved are. Pupils will learn about how gravity keeps our solar system together. We then focus in to the Earth with pupils exploring the rotation of the Earth, day, night and shadows by getting hands-on with globes and torches. Pupils can see at first hand why it is that differe ...
... huge the distances involved are. Pupils will learn about how gravity keeps our solar system together. We then focus in to the Earth with pupils exploring the rotation of the Earth, day, night and shadows by getting hands-on with globes and torches. Pupils can see at first hand why it is that differe ...
Old Sample Exam #2
... _____ 1) How big is a red supergiant? As big as: a) a comet b) the Sun c) Mars orbit d) Jupiter e) Earth _____ 2) What is the luminosity of a white dwarf with surface temperature equal to the Sun? (in solar luminosities) a) 104 b) 102 c) 1 d) 10-2 e) 10-4 _____ 3) How long can a star run on gravity ...
... _____ 1) How big is a red supergiant? As big as: a) a comet b) the Sun c) Mars orbit d) Jupiter e) Earth _____ 2) What is the luminosity of a white dwarf with surface temperature equal to the Sun? (in solar luminosities) a) 104 b) 102 c) 1 d) 10-2 e) 10-4 _____ 3) How long can a star run on gravity ...
Astronomical history
... (a) Use the diagram to describe Ptolemy’s model of the universe. Ptolemy’s theory of earth place in the universe was called a geocentric model. This means that he thought that the earth was at the centre of the universe. This also explained to the people about how in religion “god” had made the eart ...
... (a) Use the diagram to describe Ptolemy’s model of the universe. Ptolemy’s theory of earth place in the universe was called a geocentric model. This means that he thought that the earth was at the centre of the universe. This also explained to the people about how in religion “god” had made the eart ...
The Scale of the Cosmos
... planets, the stars, and the galaxies? • The Milky Way Galaxy is just one of billions of galaxies arranged in great clusters, clouds, walls, and filaments that fill the universe. ...
... planets, the stars, and the galaxies? • The Milky Way Galaxy is just one of billions of galaxies arranged in great clusters, clouds, walls, and filaments that fill the universe. ...
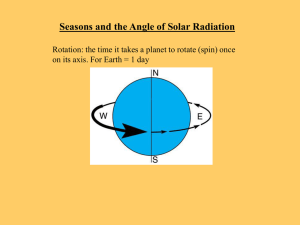
Seasons
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
Chapter 19 I. The Sun, Earth and Moon A. Sun is our closest star B
... I. The Sun, Earth and Moon A. Sun is our closest star B. Everything revolves around the Sun C. Planets and distant stars are visible in the night sky D. Earth is part of Solar System E. Gravity holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the attractive force that pulls us to th ...
... I. The Sun, Earth and Moon A. Sun is our closest star B. Everything revolves around the Sun C. Planets and distant stars are visible in the night sky D. Earth is part of Solar System E. Gravity holds the solar system together 1. We usually think of gravity as the attractive force that pulls us to th ...
answer key
... the sun (the two “loops” cross in only two places, and both earth and moon have to be at the “cross” at the same time for an eclipse to occur) 16.If their moon is the same angular diameter as their star OR LARGER, YES. Otherwise it’s called a transit.*** 17.The apparent motion of a nearer object aga ...
... the sun (the two “loops” cross in only two places, and both earth and moon have to be at the “cross” at the same time for an eclipse to occur) 16.If their moon is the same angular diameter as their star OR LARGER, YES. Otherwise it’s called a transit.*** 17.The apparent motion of a nearer object aga ...
Topic Eleven - Science - Miami
... the length of year and/or the relationship between distance Astronomical Unit, Asteroid, Meteor, ellipse from the Sun and average surface temperature. Technology: Identify and/or explain the role that gravity plays in the 1. Pearson: Pearson: My science online, My Planet Diary; formation and motion ...
... the length of year and/or the relationship between distance Astronomical Unit, Asteroid, Meteor, ellipse from the Sun and average surface temperature. Technology: Identify and/or explain the role that gravity plays in the 1. Pearson: Pearson: My science online, My Planet Diary; formation and motion ...
Components of the Solar System Learning Targets
... Target 8: Comets are mixtures of rock, ice and dust. They travel in LONG elliptical orbits. There is a solid inner part that is called a nucleus. As the comet gets closer to the sun, the heat from the sun causes the solid part to melt and we see the particles as the sun shines on them. This is the t ...
... Target 8: Comets are mixtures of rock, ice and dust. They travel in LONG elliptical orbits. There is a solid inner part that is called a nucleus. As the comet gets closer to the sun, the heat from the sun causes the solid part to melt and we see the particles as the sun shines on them. This is the t ...
Jupiter-Mars Encounter 17 October 2015
... Institute have been watching the red planet Mars in the predawn skies since late July when it emerged from the morning twilight after passing behind the sun on June 14. In September Jupiter also emerged from its August 28 conjunction behind the sun and joined both Mars and Venus in the morning twili ...
... Institute have been watching the red planet Mars in the predawn skies since late July when it emerged from the morning twilight after passing behind the sun on June 14. In September Jupiter also emerged from its August 28 conjunction behind the sun and joined both Mars and Venus in the morning twili ...
The Solar System - MHS-Integrated
... What is the Solar System? The Solar System is made up of all the planets, moons, comets and asteroids that orbit our Sun. ...
... What is the Solar System? The Solar System is made up of all the planets, moons, comets and asteroids that orbit our Sun. ...
Section 26.3 - CPO Science
... 26.3 The planets The planets are commonly classified in two groups. The terrestrial planets include Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. ...
... 26.3 The planets The planets are commonly classified in two groups. The terrestrial planets include Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. ...
Pocket Planetarium 3C V9N4.W1T
... than we had in 2003, especially through a telescope. In fact, conditions for observing Mars won’t be this favourable again for another 15 years! This means Mars will be the number one target for astronomers this Fall. However, high expectations usually result in disappointment, especially for novice ...
... than we had in 2003, especially through a telescope. In fact, conditions for observing Mars won’t be this favourable again for another 15 years! This means Mars will be the number one target for astronomers this Fall. However, high expectations usually result in disappointment, especially for novice ...
Astronomy Exam review
... 40. Planets are most easily distinguised from stars in the night time sky with your eye, because they 41.The _____ planets are characterized by deep atmospheres, many satellites, and a solar-like elemental abundance. 42.The _____ planets are relatively slow rotators, are dense, and have few satellit ...
... 40. Planets are most easily distinguised from stars in the night time sky with your eye, because they 41.The _____ planets are characterized by deep atmospheres, many satellites, and a solar-like elemental abundance. 42.The _____ planets are relatively slow rotators, are dense, and have few satellit ...
supplementary notes for space
... o Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system and is characterized by violent storms (the Red Spot is a huge storm!); it also has many moons ASTEROIDS are rocky or metallic bodies that travel in space. They can be hundreds of kilometres across, or just a few meters wide COMETS are called “dirt ...
... o Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system and is characterized by violent storms (the Red Spot is a huge storm!); it also has many moons ASTEROIDS are rocky or metallic bodies that travel in space. They can be hundreds of kilometres across, or just a few meters wide COMETS are called “dirt ...
Terestialplanets
... of Earth’s rotation • Additionally, planets move with respect to the fixed stars, that’s why they are called planets (greek: wanderers) • Due to the planet’s movement in their orbit, and Earth’s orbital motion, this additional motion – the apparent motion of the planet as seen from Earth - looks com ...
... of Earth’s rotation • Additionally, planets move with respect to the fixed stars, that’s why they are called planets (greek: wanderers) • Due to the planet’s movement in their orbit, and Earth’s orbital motion, this additional motion – the apparent motion of the planet as seen from Earth - looks com ...
mid term exam crossword
... is the most elliptical and is tilted compared to the rest 120. most of Venus' atmosphere 122. the inner planets have ___ moons 123. rocks, mountains, beaches, and all the physical features on earth 124. the lower the magnitude the ___ the star is 128. when contour lines form circles or ovals, it ind ...
... is the most elliptical and is tilted compared to the rest 120. most of Venus' atmosphere 122. the inner planets have ___ moons 123. rocks, mountains, beaches, and all the physical features on earth 124. the lower the magnitude the ___ the star is 128. when contour lines form circles or ovals, it ind ...
Studying Space Chapter 26 Notes
... Studying astronomy leads to the discovery of planets, stars, black holes, formation of our earth Benefits to humans may include finding new sources of energy May help protect us from disasters such as collisions between Earth and Asteroids ...
... Studying astronomy leads to the discovery of planets, stars, black holes, formation of our earth Benefits to humans may include finding new sources of energy May help protect us from disasters such as collisions between Earth and Asteroids ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.