HISTORY OF ASTRONOMY Largely on the basis of
... (1842-1907) in Germany, the science of astrophysics was born. By spreading the light of the celestial bodies into the constituent colors of the SPECTRUM, each interspersed with lines characteristic of the elements present, a powerful new tool was given to the astronomer. The ability to determine the ...
... (1842-1907) in Germany, the science of astrophysics was born. By spreading the light of the celestial bodies into the constituent colors of the SPECTRUM, each interspersed with lines characteristic of the elements present, a powerful new tool was given to the astronomer. The ability to determine the ...
SOFIA Science - Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy
... > IR: objects much cooler than normal stars like the Sun for example: stars and planets in the process of forming; > IR: objects embedded in, or behind, opaque ISM dust clouds; SOFIA’s instruments can see into and through those clouds > IR: organic molecules in space, which have many of their spectr ...
... > IR: objects much cooler than normal stars like the Sun for example: stars and planets in the process of forming; > IR: objects embedded in, or behind, opaque ISM dust clouds; SOFIA’s instruments can see into and through those clouds > IR: organic molecules in space, which have many of their spectr ...
2007-8 Astronomy Outline
... **Night Sky Journal Entry 1 Example** Date: Time: (try to go out around the same time each night) Light Conditions: (here is where you state how dark it is; cloud cover; how much light is coming in from other houses aka light pollution) Location: where you are and the direction you are facing Observ ...
... **Night Sky Journal Entry 1 Example** Date: Time: (try to go out around the same time each night) Light Conditions: (here is where you state how dark it is; cloud cover; how much light is coming in from other houses aka light pollution) Location: where you are and the direction you are facing Observ ...
Waves
... marks left behind by the organism while it was alive, such as the footprint or feces of a reptile ...
... marks left behind by the organism while it was alive, such as the footprint or feces of a reptile ...
The Search for Worlds Like Our Own
... his so-called ‘‘great question’’ can also be formulated as a clearly defined science goal. Since the origin of life most likely requires a stable supply of energy, planets that could host life are likely to orbit within what is known as the habitable zone (HZ), a region relatively close to the paren ...
... his so-called ‘‘great question’’ can also be formulated as a clearly defined science goal. Since the origin of life most likely requires a stable supply of energy, planets that could host life are likely to orbit within what is known as the habitable zone (HZ), a region relatively close to the paren ...
Formation of the Solar System Chapter 8
... the result of a near collision of the Sun with another star. Planets formed from debris of the collision. But we know now that collision (or near collisions) between two stars are very, very rare. Considering that collision are rare, the proposed idea of the collision may explain a unique event on h ...
... the result of a near collision of the Sun with another star. Planets formed from debris of the collision. But we know now that collision (or near collisions) between two stars are very, very rare. Considering that collision are rare, the proposed idea of the collision may explain a unique event on h ...
Session Two - A Sidewalk Astronomer in Charlottetown
... difference is that a star is a point of light, whereas a galaxy has a larger apparent surface area. The entire luminosity of the object is summed over it's area. The magnitude is then the same as a point source like a star emitting the luminosity. Therefore, large objects appear dimmer than stars th ...
... difference is that a star is a point of light, whereas a galaxy has a larger apparent surface area. The entire luminosity of the object is summed over it's area. The magnitude is then the same as a point source like a star emitting the luminosity. Therefore, large objects appear dimmer than stars th ...
Key Notes for Test 1
... planet (i.e. R2) = Total IR out from Earth But Total IR out = IR out per unit area (watts m-2 ) x surface area of planet (4R2) This gives IR out per unit area as 345 (watts m-2 ), then we use the Stefan-Boltzmann Law , E (Joules m-2 s-1 ) = Teq4 , to work out the temperature. This tells us that t ...
... planet (i.e. R2) = Total IR out from Earth But Total IR out = IR out per unit area (watts m-2 ) x surface area of planet (4R2) This gives IR out per unit area as 345 (watts m-2 ), then we use the Stefan-Boltzmann Law , E (Joules m-2 s-1 ) = Teq4 , to work out the temperature. This tells us that t ...
The Color of Plants on Other Worlds
... by splitting water vapor. But the gas is quickly rained out, as well as consumed through oxidation of rocks and volcanic gases. Therefore, if a planet with liquid water has abundant oxygen, some additional source must be producing the gas. Oxygenic photosynthesis is the leading candidate. Ozone (O3 ...
... by splitting water vapor. But the gas is quickly rained out, as well as consumed through oxidation of rocks and volcanic gases. Therefore, if a planet with liquid water has abundant oxygen, some additional source must be producing the gas. Oxygenic photosynthesis is the leading candidate. Ozone (O3 ...
Eratosthenes - Allendale School
... So, just how did Eratosthenes measure the earth’s circumference over 2,000 years ago? Eratosthenes had been told that at noon on the June Solstice, if someone looked down into a deep well in a city called Syene (now Aswan, Egypt), located on the Tropic of Cancer, their reflection blocked the reflect ...
... So, just how did Eratosthenes measure the earth’s circumference over 2,000 years ago? Eratosthenes had been told that at noon on the June Solstice, if someone looked down into a deep well in a city called Syene (now Aswan, Egypt), located on the Tropic of Cancer, their reflection blocked the reflect ...
Ellipses, Parallax, and Retrograde Motion
... 13. T or F All planets as observed from Earth will exhibit retrograde motion at some time. 14. T or F There are only two inferior planets in our Solar System. 15. T or F Retrograde motion is an apparent motion. 16. T or F Mars is brightest in our night sky when it is seen during retrograde cycle. 17 ...
... 13. T or F All planets as observed from Earth will exhibit retrograde motion at some time. 14. T or F There are only two inferior planets in our Solar System. 15. T or F Retrograde motion is an apparent motion. 16. T or F Mars is brightest in our night sky when it is seen during retrograde cycle. 17 ...
Habitability of planets around Red Dwarf Stars
... extraction of carbon from atmospheric CO2 ) and subsequent burial of a fraction of the organic carbon produced (which will be assisted – see De Marais et al., (1992) – by rifting and basin formation in a planet’s crust). CO2 is of key interest for the present discussion because of its role as a gree ...
... extraction of carbon from atmospheric CO2 ) and subsequent burial of a fraction of the organic carbon produced (which will be assisted – see De Marais et al., (1992) – by rifting and basin formation in a planet’s crust). CO2 is of key interest for the present discussion because of its role as a gree ...
The Earth in Context: Universe and Solar System
... (earth has high oxygen and low carbon dioxide environment because of plant life and photosynthesis) ...
... (earth has high oxygen and low carbon dioxide environment because of plant life and photosynthesis) ...
Sep 2012 - Bays Mountain Park
... This month we celebrate the accomplishments of a spacecraft that exceeded expectations. Launched in November of 1996, it was on September 11, 1997 that Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) arrived at Mars and entered into orbit. This was the first U.S. spacecraft to successfully visit Mars in 20 years. Placed ...
... This month we celebrate the accomplishments of a spacecraft that exceeded expectations. Launched in November of 1996, it was on September 11, 1997 that Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) arrived at Mars and entered into orbit. This was the first U.S. spacecraft to successfully visit Mars in 20 years. Placed ...
Quiz Reviews - Orion Observatory
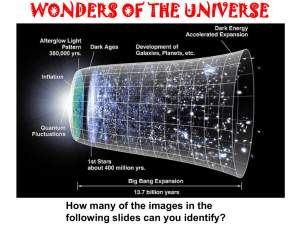
... 3. How was the term “Big Bang” coined, and did any steady-state theorists deny the Big Bang after the cosmic microwave background was discovered? 4. What is the cosmic microwave background radiation? Why did it have to exist? How was it discovered? Who got credit for discovering it? 5. Why did ripp ...
... 3. How was the term “Big Bang” coined, and did any steady-state theorists deny the Big Bang after the cosmic microwave background was discovered? 4. What is the cosmic microwave background radiation? Why did it have to exist? How was it discovered? Who got credit for discovering it? 5. Why did ripp ...
Astronomy Through the Ages: 2 Middle ages through Renaissance
... “In the same way that someone in a boat going forward sees an unmoving objects going backward, so someone on earth sees the unmoving stars going uniformly westward…’’ ...
... “In the same way that someone in a boat going forward sees an unmoving objects going backward, so someone on earth sees the unmoving stars going uniformly westward…’’ ...
Final Exam Space Unit Review
... 2) Currently accepted theory: Heliocentric model or Sun-centered model • 1500’s Nicholas Copernicus created a model that has the sun at the centre of the universe • all the planets orbit the sun and the stars are external to our solar system • When Galileo designed a telescope that could look into s ...
... 2) Currently accepted theory: Heliocentric model or Sun-centered model • 1500’s Nicholas Copernicus created a model that has the sun at the centre of the universe • all the planets orbit the sun and the stars are external to our solar system • When Galileo designed a telescope that could look into s ...
Inferior planets.
... Among many other things, the “Principia” vastly simplified a great range of behavior associated with moving objects into three apparently “simple” laws. But first Newton introduced a new concept, mass. Mass is the quantity of matter, of stuff, that an object has. The mass of an object is the same o ...
... Among many other things, the “Principia” vastly simplified a great range of behavior associated with moving objects into three apparently “simple” laws. But first Newton introduced a new concept, mass. Mass is the quantity of matter, of stuff, that an object has. The mass of an object is the same o ...
The Reason for the Seasons
... Northern Hemisphere (Sun directly over Tropic of Capricorn-23.5°S-at noon) Summer Solstice is the longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere (Sun directly over Tropic of Cancer-23.5°N-at noon ...
... Northern Hemisphere (Sun directly over Tropic of Capricorn-23.5°S-at noon) Summer Solstice is the longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere (Sun directly over Tropic of Cancer-23.5°N-at noon ...
AST301.Ch6.15.SolarSystems - University of Texas Astronomy
... several techniques available, but we’ll just discuss a few. 1. Direct detection—not possible at present. Reflected light from planet is about a billion times less than that of the star (less in the infrared, but still about a million or more—see illustration below), and the distance from the planet ...
... several techniques available, but we’ll just discuss a few. 1. Direct detection—not possible at present. Reflected light from planet is about a billion times less than that of the star (less in the infrared, but still about a million or more—see illustration below), and the distance from the planet ...
The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) The solar system consists of the Sun
... several techniques available, but we’ll just discuss a few. 1. Direct detection—not possible at present. Reflected light from planet is about a billion times less than that of the star (less in the infrared, but still about a million or more—see illustration below), and the distance from the planet ...
... several techniques available, but we’ll just discuss a few. 1. Direct detection—not possible at present. Reflected light from planet is about a billion times less than that of the star (less in the infrared, but still about a million or more—see illustration below), and the distance from the planet ...
Response to Matthew Miller re Geocentrism
... Miller: Update: Venus: If the Earth was the center of the solar system the current calculations for predicting a Transit of Venus simply wouldn't work, if transits still happened at all. Remember we're dealing with a sun slightly larger than the moon, orbiting a distance not that far beyond it. Venu ...
... Miller: Update: Venus: If the Earth was the center of the solar system the current calculations for predicting a Transit of Venus simply wouldn't work, if transits still happened at all. Remember we're dealing with a sun slightly larger than the moon, orbiting a distance not that far beyond it. Venu ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.