Metabolomics based gene function annotation in Escherichia coli
... 3-Ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III catalyzes the first carbon-carbon bondforming reaction (Claisen condensation) of type II fatty acid synthesis systems in bacteria and plant plastids. In E. coli, KASIII is encoded by the fabH gene. FabH deletion mutants were originally thought to be letha ...
... 3-Ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III catalyzes the first carbon-carbon bondforming reaction (Claisen condensation) of type II fatty acid synthesis systems in bacteria and plant plastids. In E. coli, KASIII is encoded by the fabH gene. FabH deletion mutants were originally thought to be letha ...
2 - Holy Trinity Diocesan High School
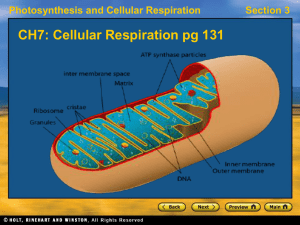
... molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD) represents stored energy that is tapp ...
... molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD) represents stored energy that is tapp ...
Plant Physiology 66:
... Transmission of Soluble Nitrogenous Compounds by the Seedcoats. In the earliest stages of postfertilization development, the integuments of the ovule release a nutrient-rich fluid that fills the embryo sac and bathes the expanding embryo asymmetrically (18). A clear distinction may be drawn between ...
... Transmission of Soluble Nitrogenous Compounds by the Seedcoats. In the earliest stages of postfertilization development, the integuments of the ovule release a nutrient-rich fluid that fills the embryo sac and bathes the expanding embryo asymmetrically (18). A clear distinction may be drawn between ...
Marine alga Sargassum horneri active component
... are antiporters, which require an extra amino acid for transport. For example, glutamine is imported into the cell by SLC1A5, and the imported glutamine is then exported by the bidirectional amino acid transporter SLC7A5, which transports the extracellular essential amino acids into cells [11,44]. T ...
... are antiporters, which require an extra amino acid for transport. For example, glutamine is imported into the cell by SLC1A5, and the imported glutamine is then exported by the bidirectional amino acid transporter SLC7A5, which transports the extracellular essential amino acids into cells [11,44]. T ...
Chapter 10 - Clayton State University
... • Fats are highly reduced compounds that liberate more energy per gram upon oxidation than do carbohydrates • They are a long-term energy storage form for many organisms • Most fat is stored as deposits of triacylglycerols, neutral triesters of glycerol and long-chain fatty acids © 2012 Pearson Educ ...
... • Fats are highly reduced compounds that liberate more energy per gram upon oxidation than do carbohydrates • They are a long-term energy storage form for many organisms • Most fat is stored as deposits of triacylglycerols, neutral triesters of glycerol and long-chain fatty acids © 2012 Pearson Educ ...
Effect of Tannic Acid on Growth and Acid Production of Candida
... are toxic to fungi, bacteria and viruses, and inhibit their growth.20,21 This is in agreement with the results of the present study which showed that Tannic Acid has fungistatic and fungicidal effects on the growth of C. albicans. In addition, the findings of our study demonstrated an inhibitory eff ...
... are toxic to fungi, bacteria and viruses, and inhibit their growth.20,21 This is in agreement with the results of the present study which showed that Tannic Acid has fungistatic and fungicidal effects on the growth of C. albicans. In addition, the findings of our study demonstrated an inhibitory eff ...
Cholesterol Homeostasis - Sigma
... the body. It is a structural component of all cell membranes and is also a precursor to steroid hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids that aid in digestion. Within membranes the cholesterol to polar lipid ratios affect stability, permeability, and protein mobility. The hormones produced from cholester ...
... the body. It is a structural component of all cell membranes and is also a precursor to steroid hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids that aid in digestion. Within membranes the cholesterol to polar lipid ratios affect stability, permeability, and protein mobility. The hormones produced from cholester ...
FAT/CD36 is located on the outer mitochondrial membrane
... investigated the location of FAT/CD36 on rat mitochondrial membranes via two separate experiments. Following OMMspecific digestion by digitonin, FAT/CD36 and Bcl-2 (a protein located on the OMM [31]) were both reduced (∼20 %, P < 0.05) (Figures 2A and 2B). In contrast, PDHE1α (an IMM-specific protei ...
... investigated the location of FAT/CD36 on rat mitochondrial membranes via two separate experiments. Following OMMspecific digestion by digitonin, FAT/CD36 and Bcl-2 (a protein located on the OMM [31]) were both reduced (∼20 %, P < 0.05) (Figures 2A and 2B). In contrast, PDHE1α (an IMM-specific protei ...
Anaerobic Glucose and Serine Metabolism in Staphy
... isomerase, phosphofructokinase, fructose 1,Qbisphosphate aldolase, triosephosphate isomerase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, lactate dehydrogenase, acetate kinase, serine dehydratase, ribokinase, transaldolase, transketolase, NADH oxidase, NADPH oxidase and NADPH-NAD transhydrogenase weIe ...
... isomerase, phosphofructokinase, fructose 1,Qbisphosphate aldolase, triosephosphate isomerase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, lactate dehydrogenase, acetate kinase, serine dehydratase, ribokinase, transaldolase, transketolase, NADH oxidase, NADPH oxidase and NADPH-NAD transhydrogenase weIe ...
17 The Digestion and Absorption of Food
... chapter only with the liver’s exocrine functions that are directly related to the secretion of bile. Bile contains bicarbonate ions, cholesterol, phospholipids, bile pigments, a number of organic wastes and—most important—a group of substances collectively termed bile salts. The bicarbonate ions, li ...
... chapter only with the liver’s exocrine functions that are directly related to the secretion of bile. Bile contains bicarbonate ions, cholesterol, phospholipids, bile pigments, a number of organic wastes and—most important—a group of substances collectively termed bile salts. The bicarbonate ions, li ...
Discovering the Interaction Propensities of Amino Acids and
... maximum H-A distance of 2.5 Å, and minimum D-H-A and H-A-AA angels set to 90, where AA is an acceptor antecedent. Water-mediated ligand interactions are essential in biological processes. The presence of water at the interface is revealed by methods such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrosc ...
... maximum H-A distance of 2.5 Å, and minimum D-H-A and H-A-AA angels set to 90, where AA is an acceptor antecedent. Water-mediated ligand interactions are essential in biological processes. The presence of water at the interface is revealed by methods such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrosc ...
Transport proteins regulate the flux of metabolites and cofactors
... In land plants, peroxisomes play key roles in various metabolic pathways, including the most prominent examples, that is lipid mobilization and photorespiration. Given the large number of substrates that are exchanged across the peroxisomal membrane, a wide spectrum of metabolite and cofactor transp ...
... In land plants, peroxisomes play key roles in various metabolic pathways, including the most prominent examples, that is lipid mobilization and photorespiration. Given the large number of substrates that are exchanged across the peroxisomal membrane, a wide spectrum of metabolite and cofactor transp ...
Slide 1 - Annals of Internal Medicine
... Urate production pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of gout.The de novo synthesis starts with 5'-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate (PRPP), which is produced by addition of a further phosphate group from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to the modified sugar ribose-5-phosphate. This step is performed b ...
... Urate production pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of gout.The de novo synthesis starts with 5'-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate (PRPP), which is produced by addition of a further phosphate group from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to the modified sugar ribose-5-phosphate. This step is performed b ...
Influence of the Side Chain in the Structure and Fragmentation of
... for the radical cation. This is not surprising considering that structures A and B differ on the relative orientation the carboxylic group with respect to the CH3 side chain. For example, the OCCN dihedral angles for structures IIA and IIB are 169° and -167°, respectively. However, ionization introd ...
... for the radical cation. This is not surprising considering that structures A and B differ on the relative orientation the carboxylic group with respect to the CH3 side chain. For example, the OCCN dihedral angles for structures IIA and IIB are 169° and -167°, respectively. However, ionization introd ...
Relationships between Methionine Supply, Nitrogen Retention and
... between Met level and N retention clearly indicated the In growing goats, Sun et al. (2007) found that trend. supplementing ruminally-protected Met and Lys significantly decreased urinary N and increased N retention. Plasma parameters In dairy cows, Cho et al. (2007) found that supplementing Stubbs ...
... between Met level and N retention clearly indicated the In growing goats, Sun et al. (2007) found that trend. supplementing ruminally-protected Met and Lys significantly decreased urinary N and increased N retention. Plasma parameters In dairy cows, Cho et al. (2007) found that supplementing Stubbs ...
Cellular Respiration - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... When O2 is available, each NADH molecule carries two highenergy electrons to the electron transport chain and becomes NAD+ again. In this way, NAD+ is recycled and used again. The addition of inorganic phosphate results in a high-energy phosphate group on each C3 molecule. These phosphate groups are ...
... When O2 is available, each NADH molecule carries two highenergy electrons to the electron transport chain and becomes NAD+ again. In this way, NAD+ is recycled and used again. The addition of inorganic phosphate results in a high-energy phosphate group on each C3 molecule. These phosphate groups are ...
CHAPTER 1 SAMPLE TEST
... e. I, II, III, IV and V c. I, II, IV and V only In the electron transport chain of the mitochondria, electrons are commonly transferred from one molecule to another. In one such reaction a Fe3+ ion in a cytochrome is converted to a Fe2+ ion. This is known as a. isomer formation d. hydrolysis b. redu ...
... e. I, II, III, IV and V c. I, II, IV and V only In the electron transport chain of the mitochondria, electrons are commonly transferred from one molecule to another. In one such reaction a Fe3+ ion in a cytochrome is converted to a Fe2+ ion. This is known as a. isomer formation d. hydrolysis b. redu ...
Vitamins
... For everything you have missed, you have gained something else, and for everything you gain, you lose something else. -Ralph Waldo Emerson ...
... For everything you have missed, you have gained something else, and for everything you gain, you lose something else. -Ralph Waldo Emerson ...
Effect of Coleus Forskohlii Root Extracts on Liver Marker
... The significant increase (p<0.05) of ALP in the serum of experimental mice treated with DLA cells may be associated with possible leakage of the enzyme from the liver into the serum. Normally, enzyme will not always be found in the serum except there is damage to one or more organs or tissues of the ...
... The significant increase (p<0.05) of ALP in the serum of experimental mice treated with DLA cells may be associated with possible leakage of the enzyme from the liver into the serum. Normally, enzyme will not always be found in the serum except there is damage to one or more organs or tissues of the ...
Fat burners: nutrition supplements that increase fat metabolism
... moderate intensity, long-chain fatty acids are the main energy sources used by most tissues, including skeletal muscle. The primary function of L-carnitine is to transport long-chain fatty acids across the mitochondrial inner membrane, as the inner membrane is impermeable to both longchain fatty aci ...
... moderate intensity, long-chain fatty acids are the main energy sources used by most tissues, including skeletal muscle. The primary function of L-carnitine is to transport long-chain fatty acids across the mitochondrial inner membrane, as the inner membrane is impermeable to both longchain fatty aci ...
Sequence Specific Modeling of E. coli Cell-Free Protein
... (17, 22) and protein structures (GEM-PRO) (23, 24). These expansions have greatly increased the scope of questions these models can explore. Thus, constraint based methods are powerful tools to estimate the performance of metabolic networks with very few adjustable parameters. However, constraint ba ...
... (17, 22) and protein structures (GEM-PRO) (23, 24). These expansions have greatly increased the scope of questions these models can explore. Thus, constraint based methods are powerful tools to estimate the performance of metabolic networks with very few adjustable parameters. However, constraint ba ...
Camp 1 - University of California, Santa Cruz
... important pathway for the regeneration of NAD+ is reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Pyruvate, the oxidizing agent, is reduced to lactate. ...
... important pathway for the regeneration of NAD+ is reduction of pyruvate to lactate. Pyruvate, the oxidizing agent, is reduced to lactate. ...
PDF
... response has already been described in Ranafusca (Brachet, 1934) and R.pipiens eggs (Cohen, 1955), and has served to support the idea of an 'oxidative reserve' in the eggs of these vertebrates (Brachet, 1934). An alternate interpretation to explain the use of the oxygen absorbed during the payment o ...
... response has already been described in Ranafusca (Brachet, 1934) and R.pipiens eggs (Cohen, 1955), and has served to support the idea of an 'oxidative reserve' in the eggs of these vertebrates (Brachet, 1934). An alternate interpretation to explain the use of the oxygen absorbed during the payment o ...