REGULATORY MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION I
... The large number of inhibitors of cellular respiration hitherto described have been reported to act by inhibiting the activity of enzyme systems. They do so (1) by combining with the activating protein, either through some groups essential for activity (for example, the - S H groups), through denatu ...
... The large number of inhibitors of cellular respiration hitherto described have been reported to act by inhibiting the activity of enzyme systems. They do so (1) by combining with the activating protein, either through some groups essential for activity (for example, the - S H groups), through denatu ...
The Intermediary Metabolism of Cholesterol
... by Rittenberg and Schoenheimer8 who administered heavy water to mice and studied the rate at which isotopic hydrogen was incorporated into the tissues' lipids. The incorporation of deuterium into cholesterol from a heavy-water medium is the result of chemical reactions and the speed at which it occu ...
... by Rittenberg and Schoenheimer8 who administered heavy water to mice and studied the rate at which isotopic hydrogen was incorporated into the tissues' lipids. The incorporation of deuterium into cholesterol from a heavy-water medium is the result of chemical reactions and the speed at which it occu ...
European Journal of Biochemistry
... incorporation of phospholipid into protein d/lipopolysaccharide complexes, indicating that phospholipids are part of the environment of the phage K3 receptor in cells of this mutant, but not in wildtype cells ...
... incorporation of phospholipid into protein d/lipopolysaccharide complexes, indicating that phospholipids are part of the environment of the phage K3 receptor in cells of this mutant, but not in wildtype cells ...
Liver glucose metabolism in humans
... Fructose taken up by hepatocytes may be converted into either fructose 6-phosphate by hexokinase isoenzymes or fructose 1phosphate by fructokinase [16]. The two initial products of hepatic fructose metabolism have opposite effects on the glucokinase regulatory protein. Glucokinase activators have be ...
... Fructose taken up by hepatocytes may be converted into either fructose 6-phosphate by hexokinase isoenzymes or fructose 1phosphate by fructokinase [16]. The two initial products of hepatic fructose metabolism have opposite effects on the glucokinase regulatory protein. Glucokinase activators have be ...
ppt
... The Fate of the Pyruvate • The pyruvate passes from the cytoplasm (where its produced thru glycolysis) and crosses the outer & inner membranes of the mitochondria ...
... The Fate of the Pyruvate • The pyruvate passes from the cytoplasm (where its produced thru glycolysis) and crosses the outer & inner membranes of the mitochondria ...
The final publication is available at Copyright - RiuNet
... Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, (Asteraceae family) is a perennial plant from Brazil and Paraguay [1]. The ...
... Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, (Asteraceae family) is a perennial plant from Brazil and Paraguay [1]. The ...
ch 9ppt
... Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? What are the reactants and products of glycolysis? Which has more energy available: ADP or ATP? ...
... Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? What are the reactants and products of glycolysis? Which has more energy available: ADP or ATP? ...
1 Regulation of Substrate Oxidation Preferences in Muscle by the
... Recent evidence suggests that the peptide hormone adropin plays a role in energy homeostasis (1; 2). These studies linked adropin actions to the control of lipid glucose metabolism, however the exact role remains unclear (1; 2). Adropin is mainly expressed in liver (1), and its expression in this or ...
... Recent evidence suggests that the peptide hormone adropin plays a role in energy homeostasis (1; 2). These studies linked adropin actions to the control of lipid glucose metabolism, however the exact role remains unclear (1; 2). Adropin is mainly expressed in liver (1), and its expression in this or ...
Glucose Regulation by Dr Sarma
... Can convert glucose to glycogen. Can convert glucose to pyruvate through glycolysis further metabolized to lactate or transaminated to alanine or channeled into the TCA cycle. ...
... Can convert glucose to glycogen. Can convert glucose to pyruvate through glycolysis further metabolized to lactate or transaminated to alanine or channeled into the TCA cycle. ...
Module 3
... B. CMP C. AMP D. * GMP E. All of these 69. Which of the following is not an essential attribute that a biological molecule would need to be a useful genetic material? A. * It must carry all of the information needed to direct the specific organization and metabolic activities of the cell B. It must ...
... B. CMP C. AMP D. * GMP E. All of these 69. Which of the following is not an essential attribute that a biological molecule would need to be a useful genetic material? A. * It must carry all of the information needed to direct the specific organization and metabolic activities of the cell B. It must ...
Yeast lipid metabolism at a glance
... In contrast, the mitochondrial FA synthase complex consists of six proteins, each harboring only one enzymatic activity. These proteins are as follows: acyl-carrier protein Acp1p, b-ketoacyl-ACP synthase Cem1p, 3-oxoacyl-acyl-carrier protein reductase Oar1p, 3-hydroxyacylthioester dehydratase Htd2p, ...
... In contrast, the mitochondrial FA synthase complex consists of six proteins, each harboring only one enzymatic activity. These proteins are as follows: acyl-carrier protein Acp1p, b-ketoacyl-ACP synthase Cem1p, 3-oxoacyl-acyl-carrier protein reductase Oar1p, 3-hydroxyacylthioester dehydratase Htd2p, ...
Mechanism of Carbanion Stabilization by PLP, Cont`d
... – That is, electron withdrawal toward the cationic nitrogen atom of the imine and into the electron sink of the pyridoxal ring from the a carbon atom of the attached amino acid activates all three of the substituents on this carbon atom for reactions which require electron withdrawal from this atom” ...
... – That is, electron withdrawal toward the cationic nitrogen atom of the imine and into the electron sink of the pyridoxal ring from the a carbon atom of the attached amino acid activates all three of the substituents on this carbon atom for reactions which require electron withdrawal from this atom” ...
End-product control of enzymes of branched
... isoleucine-valine pathway, the combination of all three amino acids gave in individual experiments activities 0.12-0.19 of those with no supplementation, the ratio of the means being 0.16. Supplementation with threonine, or with leucine, isoleucine or valine singly or in pairwise combinations, gave ...
... isoleucine-valine pathway, the combination of all three amino acids gave in individual experiments activities 0.12-0.19 of those with no supplementation, the ratio of the means being 0.16. Supplementation with threonine, or with leucine, isoleucine or valine singly or in pairwise combinations, gave ...
Transport of dicarboxylates in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... carbohydrates, such as the polysaccharide glycogen and the disaccharide trehalose, are main sources of endogenous substrates for mitochondria. Biosynthesis of these reserve carbohydrates is activated by a decrease in the level of endogenous substrates [33, 35]. Their utilization increases upon exhau ...
... carbohydrates, such as the polysaccharide glycogen and the disaccharide trehalose, are main sources of endogenous substrates for mitochondria. Biosynthesis of these reserve carbohydrates is activated by a decrease in the level of endogenous substrates [33, 35]. Their utilization increases upon exhau ...
Cellular Respiration
... acid enters the pathways of aerobic respiration. (Aerobic respiration is covered in detail in the next section.) In anaerobic conditions (when oxygen is absent), however, some cells can convert pyruvic acid into other compounds through additional biochemical pathways that occur in the cytosol. The c ...
... acid enters the pathways of aerobic respiration. (Aerobic respiration is covered in detail in the next section.) In anaerobic conditions (when oxygen is absent), however, some cells can convert pyruvic acid into other compounds through additional biochemical pathways that occur in the cytosol. The c ...
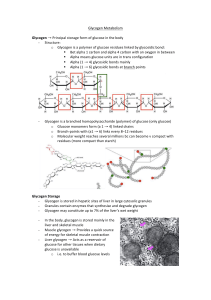
Glycogen!Metabolism! ! Glycogen$→!Principal!storage!form!of
... o Branch=points!with!(a1!→!6)!links!every!8–12!residues!! o Molecular!weight!reaches!several!millions!bc!can!become!v!compact!with! residues!(more!compact!than!starch)! ...
... o Branch=points!with!(a1!→!6)!links!every!8–12!residues!! o Molecular!weight!reaches!several!millions!bc!can!become!v!compact!with! residues!(more!compact!than!starch)! ...
11 L8, Hepathobiliary function, B
... 2. Biliverdin is then converted into bilirubin, which is transported in blood bound to albumin forming a water soluble compound called hemobilirubin (unconjugated bilirubin) which is rapidly transported to hepatocytes for further metabolism (even when bound to albumin, it’s called free bilirubin). 3 ...
... 2. Biliverdin is then converted into bilirubin, which is transported in blood bound to albumin forming a water soluble compound called hemobilirubin (unconjugated bilirubin) which is rapidly transported to hepatocytes for further metabolism (even when bound to albumin, it’s called free bilirubin). 3 ...
Multiple Disturbances of Free Fatty Acid Metabolism in
... subjects had a history of temporary insulin therapy). Previous antidiabetic therapy was stopped at least 1 mo before the study. No subjects were taking any medication at the time of the study, and all had a normal physical examination, electrocardiogram, and blood tests (liver function tests, blood ...
... subjects had a history of temporary insulin therapy). Previous antidiabetic therapy was stopped at least 1 mo before the study. No subjects were taking any medication at the time of the study, and all had a normal physical examination, electrocardiogram, and blood tests (liver function tests, blood ...
Organic Chemistry Notes Student
... A. Carbohydrates - ______________________________________ Monosaccharides are the simplest ______________________. • The carbohydrate monomers are ___________________ • A monosaccharide has a formula that is a multiple of CH2O ______________________ ...
... A. Carbohydrates - ______________________________________ Monosaccharides are the simplest ______________________. • The carbohydrate monomers are ___________________ • A monosaccharide has a formula that is a multiple of CH2O ______________________ ...
Lecture 9 – Cellular Respiration
... Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD+) represents stored energy that is tapped to synthesize ATP. Each NADH produces 3 ATPs in the e- transport chain NSCC BIOL211 ...
... Each NADH (the reduced form of NAD+) represents stored energy that is tapped to synthesize ATP. Each NADH produces 3 ATPs in the e- transport chain NSCC BIOL211 ...
ATP production in isolated mitochondria of procyclic Trypanosoma
... The single mitochondrion of insect stage T. brucei has three in part overlapping ATP production pathways (1, 2)(Fig. 1). First, as in mitochondria from other organisms ATP is produced by oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in a cyanide-sensitive electron transport chain. Second, as expected one step ...
... The single mitochondrion of insect stage T. brucei has three in part overlapping ATP production pathways (1, 2)(Fig. 1). First, as in mitochondria from other organisms ATP is produced by oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in a cyanide-sensitive electron transport chain. Second, as expected one step ...
A Review on Bio-butyric Acid Production and its Optimization
... acetoacetyl-CoA and butyryl-CoA are formed from pyruvate as key intermediates in the main branch (Jones and Woods, 1986). Butyric acid can be produced consequently in case of presence of high levels of enzymes that are concerned with the pathway of butyryl-CoA to butyrate. During the conversion of a ...
... acetoacetyl-CoA and butyryl-CoA are formed from pyruvate as key intermediates in the main branch (Jones and Woods, 1986). Butyric acid can be produced consequently in case of presence of high levels of enzymes that are concerned with the pathway of butyryl-CoA to butyrate. During the conversion of a ...
Biology 6 Test 1 Study Guide
... iv. Energy harvesting steps 1. 4 ATPs and 2 NADHs produced in 5 steps. Remember, these totals reflect doubling of reactions because of 2C3 molecules. 2. These ATPs are made by substrate level phosphorylation (direct transfer of phosphate by intermediate). e. Acetyl -CoA formation (Fig. 5.13) i. Yiel ...
... iv. Energy harvesting steps 1. 4 ATPs and 2 NADHs produced in 5 steps. Remember, these totals reflect doubling of reactions because of 2C3 molecules. 2. These ATPs are made by substrate level phosphorylation (direct transfer of phosphate by intermediate). e. Acetyl -CoA formation (Fig. 5.13) i. Yiel ...