Amino Acid Metabolism
... Branched-chain -keto acid dehydrogenase complex • In certain body tissues, this enzyme catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of valine, isoleucine, and leucine yielding CO2, and acyl-CoA derivatives. • Shares ancestry with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, -KG dehydrogenase complex – another exam ...
... Branched-chain -keto acid dehydrogenase complex • In certain body tissues, this enzyme catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of valine, isoleucine, and leucine yielding CO2, and acyl-CoA derivatives. • Shares ancestry with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, -KG dehydrogenase complex – another exam ...
effect of protein on gene expression
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
EFFECT OF NUTRIENTS ON THE GENE EXPRESSION: Nutri
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
N x C (N-2)
... The major difference between the β-oxidation cycle in the mitochondria and peroxisomes, apart from the fact that the enzymes are not exactly the same, is in the first step. The reducing power of the FADH2 is wasted in peroxisomes, being “burnt off” by its oxidation with molecular O2. The H2O2 that i ...
... The major difference between the β-oxidation cycle in the mitochondria and peroxisomes, apart from the fact that the enzymes are not exactly the same, is in the first step. The reducing power of the FADH2 is wasted in peroxisomes, being “burnt off” by its oxidation with molecular O2. The H2O2 that i ...
B) Contain an alcohol - LSU School of Medicine
... phosphorylated (for example, to PIP2; Fig. 17.7). ...
... phosphorylated (for example, to PIP2; Fig. 17.7). ...
Exam IV answers
... lymphoid cells, causing its activation and movement to the nucleus where it activates transcription of lipocortin. The lipocortin protein inhibits phospholipase A2, thus reducing the supply of the starting material for eicosanoid biosynthesis. The cortisol/cortisone – receptor complex also represses ...
... lymphoid cells, causing its activation and movement to the nucleus where it activates transcription of lipocortin. The lipocortin protein inhibits phospholipase A2, thus reducing the supply of the starting material for eicosanoid biosynthesis. The cortisol/cortisone – receptor complex also represses ...
CHAPTER 6
... Regulated in Cells? • AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is the cellular energy sensor – Metabolic inputs to this sensor determine whether its output (protein kinase activity) takes place – When ATP is high, AMPK is inactive – When ATP is low, AMPK is allosterically activated and phosphorylates man ...
... Regulated in Cells? • AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is the cellular energy sensor – Metabolic inputs to this sensor determine whether its output (protein kinase activity) takes place – When ATP is high, AMPK is inactive – When ATP is low, AMPK is allosterically activated and phosphorylates man ...
Proteins - Northern Highlands
... different conformations determined by the primary sequence of amino acids. α-Helix: formation is stabilized by H-bonds between amino nitrogens and carbonyl carbons of the peptide bonds every 4 amino acids apart. Helical coiling of the peptide backbone results - Keratin (hair), Myosin (muscles), Fibr ...
... different conformations determined by the primary sequence of amino acids. α-Helix: formation is stabilized by H-bonds between amino nitrogens and carbonyl carbons of the peptide bonds every 4 amino acids apart. Helical coiling of the peptide backbone results - Keratin (hair), Myosin (muscles), Fibr ...
Document
... They are present in the cytoplasm of all cells They help to speed up the chemical reactions in the cell There are hundreds of different enzymes but each enzyme speeds up only one kind of reaction For example, glucose and fructose might join up slowly to form sucrose ...
... They are present in the cytoplasm of all cells They help to speed up the chemical reactions in the cell There are hundreds of different enzymes but each enzyme speeds up only one kind of reaction For example, glucose and fructose might join up slowly to form sucrose ...
The Chemicals of Living Things
... They are present in the cytoplasm of all cells They help to speed up the chemical reactions in the cell There are hundreds of different enzymes but each enzyme speeds up only one kind of reaction For example, glucose and fructose might join up slowly to form sucrose ...
... They are present in the cytoplasm of all cells They help to speed up the chemical reactions in the cell There are hundreds of different enzymes but each enzyme speeds up only one kind of reaction For example, glucose and fructose might join up slowly to form sucrose ...
Chap 15 Study Outline
... Certain body cells (neurons) need a continuous supply of glucose to survive; if glucose is scarce, noncarbohydrates such as _______________ _______________ may be converted into glucose. Carbohydrate requirements: The need for carbohydrates varies with a person's ____________ requirements; the minim ...
... Certain body cells (neurons) need a continuous supply of glucose to survive; if glucose is scarce, noncarbohydrates such as _______________ _______________ may be converted into glucose. Carbohydrate requirements: The need for carbohydrates varies with a person's ____________ requirements; the minim ...
Explain advantages of Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins
... and fat from being used for energy. Foods rich in carbohydrates are high in minerals and vitamins, which are essential nutrients for good health. These foods are also high in fiber and cut down your risk of getting certain chronic diseases. Lipids are a concentrated energy source and also structural ...
... and fat from being used for energy. Foods rich in carbohydrates are high in minerals and vitamins, which are essential nutrients for good health. These foods are also high in fiber and cut down your risk of getting certain chronic diseases. Lipids are a concentrated energy source and also structural ...
NOV 28 20
... The products Vegetarian DHA Flax Oil and Udo's DHA Oil disease. This statement is about omega-3 fatty acids and a reduced risk of coronary heart 21 U .S .C. 343(r)(lj,(B) not a claim subject to 21 U.S .C. 343(r)(6), but a claim subject to disease or health relat~d because it represents that the prod ...
... The products Vegetarian DHA Flax Oil and Udo's DHA Oil disease. This statement is about omega-3 fatty acids and a reduced risk of coronary heart 21 U .S .C. 343(r)(lj,(B) not a claim subject to 21 U.S .C. 343(r)(6), but a claim subject to disease or health relat~d because it represents that the prod ...
All fatty acids are not equal: discrimination in plant membrane lipids
... development of enzymes, which either have altered substrate specificities, or can catalyse closely related but modified reactions14. Many of the unusual fatty acids are found in taxonomically dispersed families (Fig. 1), implying that the recruitment of enzymes for the ...
... development of enzymes, which either have altered substrate specificities, or can catalyse closely related but modified reactions14. Many of the unusual fatty acids are found in taxonomically dispersed families (Fig. 1), implying that the recruitment of enzymes for the ...
Amino Acids and Proteins
... - the proteins which must die are marked for degradation by binding to UBIQUITIN which is a 74-aa polypeptide - ubiquitin is an ancient technology, and is exactly the same in bacteria as well as humans - the ubiquitin then drags the doomed proteinoff to a proteosome for degradation ...
... - the proteins which must die are marked for degradation by binding to UBIQUITIN which is a 74-aa polypeptide - ubiquitin is an ancient technology, and is exactly the same in bacteria as well as humans - the ubiquitin then drags the doomed proteinoff to a proteosome for degradation ...
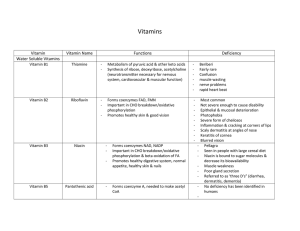
167
... Seen in people with large cereal diet Niacin is bound to sugar molecules & decrease its bioavailability Muscle weakness Poor gland secretion Referred to as ‘three D’s” (diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia) No deficiency has been identified in humans ...
... Seen in people with large cereal diet Niacin is bound to sugar molecules & decrease its bioavailability Muscle weakness Poor gland secretion Referred to as ‘three D’s” (diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia) No deficiency has been identified in humans ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Electron transport chain, proteins within inner mitochondrial membrane, controls ...
... Electron transport chain, proteins within inner mitochondrial membrane, controls ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... conversion for biological organisms Examples include: Pyruvate produced from glycolysis undergoes oxidative decarboxylation for form acetyl coenzyme A, which then enters the citric acid cycle.. In the citric acid cycle, the acetate is transferred to oxaloacetate to form the six carbon molecule, citr ...
... conversion for biological organisms Examples include: Pyruvate produced from glycolysis undergoes oxidative decarboxylation for form acetyl coenzyme A, which then enters the citric acid cycle.. In the citric acid cycle, the acetate is transferred to oxaloacetate to form the six carbon molecule, citr ...
Biology 20 Lecture Quiz #3 – Take Home Cellular Respiration
... 7. Enzymes such as succinic acid dehydrogenase (SDH) are important in the citric acid cycle. They can be found? a) cytosol; b) mitochondrial matrix; c) inner membrane of the mitochondria; d) thylakoid; e) damn…I should have paid more attention yesterday! 8. The molecule that serves as the final elec ...
... 7. Enzymes such as succinic acid dehydrogenase (SDH) are important in the citric acid cycle. They can be found? a) cytosol; b) mitochondrial matrix; c) inner membrane of the mitochondria; d) thylakoid; e) damn…I should have paid more attention yesterday! 8. The molecule that serves as the final elec ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... plate section. Substrates for lipid synthesis enter the cells via the glucose transporter (GLUT1), a glycerol transporter, as amino acids, or as preformed fatty acids via a fatty acid transport protein (FATP). Glycolysis leads to the production of both glycerol-3-phosphate and pyruvate from glucose. ...
... plate section. Substrates for lipid synthesis enter the cells via the glucose transporter (GLUT1), a glycerol transporter, as amino acids, or as preformed fatty acids via a fatty acid transport protein (FATP). Glycolysis leads to the production of both glycerol-3-phosphate and pyruvate from glucose. ...
Name: : : ______ Human Digestive System Project Nutrition Science
... Absorption is an important function. Active transport moves glucose and amino acids into the intestinal cells, then out where they are picked up by capillaries. Production of some digestive enzymes. The stomach stores up to 2 liters of food. Gastric glands within the stomach produce secret ...
... Absorption is an important function. Active transport moves glucose and amino acids into the intestinal cells, then out where they are picked up by capillaries. Production of some digestive enzymes. The stomach stores up to 2 liters of food. Gastric glands within the stomach produce secret ...
Digestive System Review #2 - Mr. Lesiuk
... 2. Gastrin is produced by endocrine glands of the stomach. 3. The glands that produce and secrete Gastrin, are ENDOCRINE glands as they release this hormone into the bloodstream. 4. After Gastrin is secreted it is carried through the bloodstream and as it lands on target cells that have the proper s ...
... 2. Gastrin is produced by endocrine glands of the stomach. 3. The glands that produce and secrete Gastrin, are ENDOCRINE glands as they release this hormone into the bloodstream. 4. After Gastrin is secreted it is carried through the bloodstream and as it lands on target cells that have the proper s ...
Lipoproteins
... Secretion of bile salts & cholesterol into the bile by liver is the only mechanism by which cholesterol is excreted. Most cholesterol & bile acids are reabsorbed in the small intestine, returned to the liver via the portal vein, & may be re-secreted. This is the enterohepatic cycle. Agents that int ...
... Secretion of bile salts & cholesterol into the bile by liver is the only mechanism by which cholesterol is excreted. Most cholesterol & bile acids are reabsorbed in the small intestine, returned to the liver via the portal vein, & may be re-secreted. This is the enterohepatic cycle. Agents that int ...
Omnipresent and multifunctional – amino acids in
... is a characteristic phenomenon of this substance class. These specific compounds are also called inner salts or betaines, shown in the following example of glycine (aminoacetic acid): H2N-CH2-COOH ...
... is a characteristic phenomenon of this substance class. These specific compounds are also called inner salts or betaines, shown in the following example of glycine (aminoacetic acid): H2N-CH2-COOH ...