Chapter 23 The Digestive System
... • Carbohydrate-rich chyme moves quickly through the duodenum • Fatty chyme remains in the duodenum _________________________________________ Small Intestine: Gross Anatomy • Major organ of digestion and absorption • 2–4 m long; from pyloric sphincter to ileocecal valve ...
... • Carbohydrate-rich chyme moves quickly through the duodenum • Fatty chyme remains in the duodenum _________________________________________ Small Intestine: Gross Anatomy • Major organ of digestion and absorption • 2–4 m long; from pyloric sphincter to ileocecal valve ...
D-lactic acidosis: Turning sugar into acids in the gastrointestinal tract
... (b) Bacterial populations. Not all bacteria produce organic acids tive, several biochemical and metabolic considerations must be in general, or the specific ones such as D- versus L-lactic acid at appreciated. Our approach to this problem will be as follows: first, equivalent rates. For example, the ...
... (b) Bacterial populations. Not all bacteria produce organic acids tive, several biochemical and metabolic considerations must be in general, or the specific ones such as D- versus L-lactic acid at appreciated. Our approach to this problem will be as follows: first, equivalent rates. For example, the ...
Lab 11
... Introduction ( Why the experiment is important? ) – State a hypothesis (an “if then” statement, may require multiple sentences) that is clear and appropriately addresses the purpose of this laboratory exercise. ...
... Introduction ( Why the experiment is important? ) – State a hypothesis (an “if then” statement, may require multiple sentences) that is clear and appropriately addresses the purpose of this laboratory exercise. ...
Ans
... phosphorylation, on the other hand, takes place along the electron transport chain, where ATP is synthesized indirectly from the creation of a proton gradient and the movement of these protons back accross the membrane through the protein channel, ATP synthase. As the protons pass through, ATP is cr ...
... phosphorylation, on the other hand, takes place along the electron transport chain, where ATP is synthesized indirectly from the creation of a proton gradient and the movement of these protons back accross the membrane through the protein channel, ATP synthase. As the protons pass through, ATP is cr ...
energy - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... • Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. • Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy (G). • In cells, energy-transforming reactions are often coupled: ...
... • Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. • Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy (G). • In cells, energy-transforming reactions are often coupled: ...
Antioxidant Activity Associated with Lipid and Phenolic Mobilization
... E, but tocotrienols are less widely distributed in nature. Tocopherols naturally present in foods have been strongly correlated with the polyunsaturated fatty acid because it counteracts the potential oxidative deterioration caused by fats in the diet (Anttolainen et al., 1995). Moreover, tocotrieno ...
... E, but tocotrienols are less widely distributed in nature. Tocopherols naturally present in foods have been strongly correlated with the polyunsaturated fatty acid because it counteracts the potential oxidative deterioration caused by fats in the diet (Anttolainen et al., 1995). Moreover, tocotrieno ...
101 -- 2006
... a) They combine molecules into more complex and energy rich molecules. b) They are usually coupled with anabolic pathways to which they supply energy in the form of ATP. c) They involve endergonic reactions that break complex molecules into simpler ones. d) They are spontaneous and do not need enzym ...
... a) They combine molecules into more complex and energy rich molecules. b) They are usually coupled with anabolic pathways to which they supply energy in the form of ATP. c) They involve endergonic reactions that break complex molecules into simpler ones. d) They are spontaneous and do not need enzym ...
Nucleotides, Vitamins, Cosubstrates, and Coenzymes
... If a vitamin is present at insufficient quantities or is completely lacking in the diet a deficiency disease often results. The effects of a diet lacking a single nutrient were determined using laboratory animals. The results were then extrapolated to the human animal. Whether a deficiency disease d ...
... If a vitamin is present at insufficient quantities or is completely lacking in the diet a deficiency disease often results. The effects of a diet lacking a single nutrient were determined using laboratory animals. The results were then extrapolated to the human animal. Whether a deficiency disease d ...
TCA cycle cross products (also known as “nothing is simple” My
... A pathway leading to the fixation of two molecules of CO2 and the production of one molecule of acetyl-CoA; essentially the oxidative TCA cycle running in reverse. Acetyl-CoA is reductively carboxylated to pyruvate, from which all other central metabolites can be formed. Most of the enzymes of reduc ...
... A pathway leading to the fixation of two molecules of CO2 and the production of one molecule of acetyl-CoA; essentially the oxidative TCA cycle running in reverse. Acetyl-CoA is reductively carboxylated to pyruvate, from which all other central metabolites can be formed. Most of the enzymes of reduc ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... catalyzed by an enzyme complex attached to the inner mitochondrial membrane. • The acetyl group is added to coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA. One NADH + H+ is generated during this reaction. ...
... catalyzed by an enzyme complex attached to the inner mitochondrial membrane. • The acetyl group is added to coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA. One NADH + H+ is generated during this reaction. ...
STRUCTURE OF ATP
... amount of energy in the chemical bonds.The breaking of Complex organic substances through oxidation releases energy.This process is called respiration. All living organism required energy to carry out various activities. This energy is obtained through respiration which is a catabolic process. It oc ...
... amount of energy in the chemical bonds.The breaking of Complex organic substances through oxidation releases energy.This process is called respiration. All living organism required energy to carry out various activities. This energy is obtained through respiration which is a catabolic process. It oc ...
Guided Reading Activities
... 1. What must proteins be broken down into before they can be burned as energy? Refer to Figure 6.15 on page 102 in your textbook. 2. Fats are hydrophobic and carbohydrates are hydrophilic. Use this information to explain why humans store the majority of their excess energy as fat and not carbo ...
... 1. What must proteins be broken down into before they can be burned as energy? Refer to Figure 6.15 on page 102 in your textbook. 2. Fats are hydrophobic and carbohydrates are hydrophilic. Use this information to explain why humans store the majority of their excess energy as fat and not carbo ...
Bio 20 6.2 6.3 notes
... The material that remains in the small intestine after nutrients are absorbed enters the last part of the digestive system : the large intestine. 1. Why is it called LARGE if it is so much smaller that the small intestine? 2. Does digestion occur in the large intestine? 3. What is the main function ...
... The material that remains in the small intestine after nutrients are absorbed enters the last part of the digestive system : the large intestine. 1. Why is it called LARGE if it is so much smaller that the small intestine? 2. Does digestion occur in the large intestine? 3. What is the main function ...
a ANSWER - Cornerstone Charter Academy
... • The surface region of the protein in the interior of the membrane is mostly hydrophobic. • The surface region of the protein in the interior of the membrane is mostly hydrophillic. • The surface region exposed to the outer environment is hydrophobic. • The surface region exposed to the interior en ...
... • The surface region of the protein in the interior of the membrane is mostly hydrophobic. • The surface region of the protein in the interior of the membrane is mostly hydrophillic. • The surface region exposed to the outer environment is hydrophobic. • The surface region exposed to the interior en ...
Cell Respiration State that oxidation involves the loss of electrons
... molecules of ATP are produced when two molecules of pyruvate are formed. Coupled with the loss of two ATP molecules in phosphorylation, the net gain of ATP in glycolysis is two. The triose phosphate is oxidised to form pyruvic acid. The phosphate is donated to ADP to form the ATP. Pyruvic acid is al ...
... molecules of ATP are produced when two molecules of pyruvate are formed. Coupled with the loss of two ATP molecules in phosphorylation, the net gain of ATP in glycolysis is two. The triose phosphate is oxidised to form pyruvic acid. The phosphate is donated to ADP to form the ATP. Pyruvic acid is al ...
Cellular Respiration
... Happens in cytoplasm The first step is glycolysis. The pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactic acid. ...
... Happens in cytoplasm The first step is glycolysis. The pyruvate is converted to ethanol or lactic acid. ...
cell resp
... 35. 35 Under which condition would you expect the mitochondrial proton gradient to be highest and therefore ATP synthesis to proceed? A) pyruvate (present)-oxygen (present)-ATP levels (high) B) pyruvate (present)-oxygen (present)-ATP levels (low) C) pyruvate (present)-oxygen (absent)-ATP levels (hig ...
... 35. 35 Under which condition would you expect the mitochondrial proton gradient to be highest and therefore ATP synthesis to proceed? A) pyruvate (present)-oxygen (present)-ATP levels (high) B) pyruvate (present)-oxygen (present)-ATP levels (low) C) pyruvate (present)-oxygen (absent)-ATP levels (hig ...
Introduction to Biomolecules
... The complexity of even the simplest of life forms, the single cell, cannot be overstated. Nevertheless, from a chemical perspective, cellular components can be segregated into macromolecules (DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.), relatively simple molecules (amino acids, monosaccharides, and lipids), and their ...
... The complexity of even the simplest of life forms, the single cell, cannot be overstated. Nevertheless, from a chemical perspective, cellular components can be segregated into macromolecules (DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.), relatively simple molecules (amino acids, monosaccharides, and lipids), and their ...
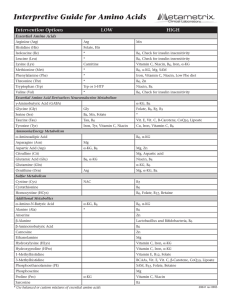
Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric acid cycle via mechanisms requiring biotin and B12. Alanine ...
... the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric acid cycle via mechanisms requiring biotin and B12. Alanine ...
UNIT I - apbiologypathways
... yield carbon dioxide, water, and energy. The principle source of energy for organisms is glucose. Structurally a sugar consists of a carbon backbone of three or more carbon atoms with either an aldehyde or carbonyl group on one carbon and hydroxyl groups on each of the other carbons. The most common ...
... yield carbon dioxide, water, and energy. The principle source of energy for organisms is glucose. Structurally a sugar consists of a carbon backbone of three or more carbon atoms with either an aldehyde or carbonyl group on one carbon and hydroxyl groups on each of the other carbons. The most common ...
FUNCTIONS OF PLASMA PROTEINS
... separation into albumin, fibrinogen, alpha, beta and gamma globulins Paper electrophoresis Ultracentrifugation Affinity chromatography Fractional precipitation method Immune electrophoresis ...
... separation into albumin, fibrinogen, alpha, beta and gamma globulins Paper electrophoresis Ultracentrifugation Affinity chromatography Fractional precipitation method Immune electrophoresis ...
Today`s Plan: 1/5/09
... a glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains Main component of phospholipids, which form micells in water and are responsible for? Saturated fats contain all single bonds on the main hydrocarbon chain, while unsaturated fats contain double or triple bonds. What’s a trans-fat? ...
... a glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains Main component of phospholipids, which form micells in water and are responsible for? Saturated fats contain all single bonds on the main hydrocarbon chain, while unsaturated fats contain double or triple bonds. What’s a trans-fat? ...
Classification and substrate head-group specificity of membrane
... This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). ...
... This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). ...
Energy Conversion Pathways 1. Substrate level phosphorylation
... 5. Because NAD+ is not being regenerated by the lactate dehydrogenase reaction which will lead to the inhibition of Gly 3-P dehydrogenase and block ATP generation by substrate level ...
... 5. Because NAD+ is not being regenerated by the lactate dehydrogenase reaction which will lead to the inhibition of Gly 3-P dehydrogenase and block ATP generation by substrate level ...