Exam 1 Q2 Review Sheet
... why they cause a problem. For example, why would DNP be an excellent weight loss drug? 27. It turns out that you need only very small amounts of vitamin B3 (niacin), which is used to make NAD+. The same goes for riboflavin, the vitamin used in the synthesis of FAD. However, you have incredible numbe ...
... why they cause a problem. For example, why would DNP be an excellent weight loss drug? 27. It turns out that you need only very small amounts of vitamin B3 (niacin), which is used to make NAD+. The same goes for riboflavin, the vitamin used in the synthesis of FAD. However, you have incredible numbe ...
Biological monomers and polymers (1)
... There are thousands of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell. If the biochemical reactions involved in this process were reversible, we would convert our macromolecules back to metabolites if we stop eating even for a short period of time. To prevent this from happening, our metabolism is organized i ...
... There are thousands of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell. If the biochemical reactions involved in this process were reversible, we would convert our macromolecules back to metabolites if we stop eating even for a short period of time. To prevent this from happening, our metabolism is organized i ...
Note Set 11 1 GLYCOLYSIS (also known as: EMBDEN
... precursor inositol, pentose phosphate pathway (NADPH, ribose) and more… G6-P is the precursor for synthesis of glycogen and is also used in pentose phosphate pathway to form NADPH •thus the HEX step is not the committed step because product of the reaction goes other places…committed means it only g ...
... precursor inositol, pentose phosphate pathway (NADPH, ribose) and more… G6-P is the precursor for synthesis of glycogen and is also used in pentose phosphate pathway to form NADPH •thus the HEX step is not the committed step because product of the reaction goes other places…committed means it only g ...
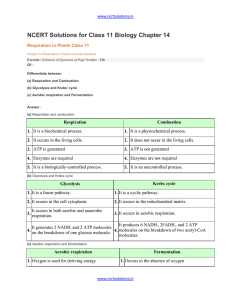
chapter_14_respiration_in_plants
... ETS or electron transport system is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It helps in releasing and utilizing the energy stored in NADH+H+ and FADH2. NADH + H+, which is formed during glycolysis and citric acid cycle, gets oxidized by NADH dehydrogenase (complex I). The electrons so generated ...
... ETS or electron transport system is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It helps in releasing and utilizing the energy stored in NADH+H+ and FADH2. NADH + H+, which is formed during glycolysis and citric acid cycle, gets oxidized by NADH dehydrogenase (complex I). The electrons so generated ...
Notes Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration
... energy and make ATP. It includes anaerobic pathways, which operate in the absence of oxygen, and aerobic respiration, which occurs when oxygen is present. Cellular respiration begins with glycolysis, which takes place in the cytosol of cells. During glycolysis, one glucose molecule is oxidized to ...
... energy and make ATP. It includes anaerobic pathways, which operate in the absence of oxygen, and aerobic respiration, which occurs when oxygen is present. Cellular respiration begins with glycolysis, which takes place in the cytosol of cells. During glycolysis, one glucose molecule is oxidized to ...
Excess portal venous long-chain fatty acids induce syndrome X via
... is associated with a higher incidence of the symptoms of syndrome X than is lower body obesity (4, 22, 32, 49). This is primarily related to the amount of visceral fat rather than to the amount of subcutaneous fat (2–4). Visceral adipose tissue has metabolic characteristics that are unique in compar ...
... is associated with a higher incidence of the symptoms of syndrome X than is lower body obesity (4, 22, 32, 49). This is primarily related to the amount of visceral fat rather than to the amount of subcutaneous fat (2–4). Visceral adipose tissue has metabolic characteristics that are unique in compar ...
Ninety-nine Point Nine Percent of the Time, Nature Uses the... Acids, and We Don’t Know Exactly Why
... protein emerged first and that RNA and protein may have exclusively formed the basis of life for a period in the early history of evolution. Because RNA is far less stable than DNA and is more libel to randomly mutate, it makes sense that during this period the genetic code and the selection of amin ...
... protein emerged first and that RNA and protein may have exclusively formed the basis of life for a period in the early history of evolution. Because RNA is far less stable than DNA and is more libel to randomly mutate, it makes sense that during this period the genetic code and the selection of amin ...
SI Worksheet 7
... 3. _____________ is consumed and ____________ is produced in the overall process of cellular respiration a. CO2 ......H2O b. O2......glucose c. H2O......ATP d. glucose ......CO2 e. ATP.......O2 4. Which of the following describes glycolysis ? a. It begins the oxidation of glucose b. it produces a sm ...
... 3. _____________ is consumed and ____________ is produced in the overall process of cellular respiration a. CO2 ......H2O b. O2......glucose c. H2O......ATP d. glucose ......CO2 e. ATP.......O2 4. Which of the following describes glycolysis ? a. It begins the oxidation of glucose b. it produces a sm ...
The malonyl CoA axis as a potential target for treating ischaemic
... or converted to long-chain fatty acyl carnitine by CPT-I.7 Fatty acid b-oxidation occurs predominantly in the mitochondria and to a smaller extent in the peroxisomes.15 For mitochondrial fatty acid b-oxidation to begin, the cytoplasmic long-chain fatty acyl CoA must first be transported into the mito ...
... or converted to long-chain fatty acyl carnitine by CPT-I.7 Fatty acid b-oxidation occurs predominantly in the mitochondria and to a smaller extent in the peroxisomes.15 For mitochondrial fatty acid b-oxidation to begin, the cytoplasmic long-chain fatty acyl CoA must first be transported into the mito ...
Fate of Carbon Skeleton
... It is removed by the liver that converts it to urea, which is less toxic, water soluble and easily excreted in the urine. ...
... It is removed by the liver that converts it to urea, which is less toxic, water soluble and easily excreted in the urine. ...
Clinical Applications of Enzymes
... should be avoided Anticoagulants shouldn't inhibit the assays Hemolysis should be avoided in order not to release enzymes of the blood cells ...
... should be avoided Anticoagulants shouldn't inhibit the assays Hemolysis should be avoided in order not to release enzymes of the blood cells ...
Met1 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... exercise at previous level of activity after brief rest - switching to utilization of fatty acids). between attacks, muscle strength, diagnostic test results are normal (may become abnormal with advancing age). ...
... exercise at previous level of activity after brief rest - switching to utilization of fatty acids). between attacks, muscle strength, diagnostic test results are normal (may become abnormal with advancing age). ...
printed handout sheet
... signal via heterotrimeric G proteins, all of which require GTP. Different G subunits may either stimulate or inhibit enzymes on the inner surface of the plasmalemma. 5. Adenyl cyclase is normally bound to the inner surface of the plasmalemma where it converts tiny amounts of ATP into 3'5' cyclic AM ...
... signal via heterotrimeric G proteins, all of which require GTP. Different G subunits may either stimulate or inhibit enzymes on the inner surface of the plasmalemma. 5. Adenyl cyclase is normally bound to the inner surface of the plasmalemma where it converts tiny amounts of ATP into 3'5' cyclic AM ...
READ MORE - MindBody Medicine Center
... Since NAD is so fundamental to good health, how is it that we can become deficient in this powerful molecule? First of all, the vitamins, minerals, complex carbohydrates, proteins and fats come from o ...
... Since NAD is so fundamental to good health, how is it that we can become deficient in this powerful molecule? First of all, the vitamins, minerals, complex carbohydrates, proteins and fats come from o ...
Premigratory fat metabolism in hummingbirds: A Rumsfeldian
... close to 500 µmol g-1 min-1 (Suarez et al. 1990; Welch et al. 2007). In the fed state, as the birds go from flower to flower, such ATP turnover rates are supported by glucose oxidation rates close to the maximal biochemical capacities for glucose phosphorylation, i.e., the Vmax values of muscle hexo ...
... close to 500 µmol g-1 min-1 (Suarez et al. 1990; Welch et al. 2007). In the fed state, as the birds go from flower to flower, such ATP turnover rates are supported by glucose oxidation rates close to the maximal biochemical capacities for glucose phosphorylation, i.e., the Vmax values of muscle hexo ...
NITROGEN METABOLISM: An Overview
... • Oxidative Deamination: Reaction catalyzed by the enzyme Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH); • Oxidative Deamination is the Oxidative removal of Ammonium ion (NH4+) from Glutamate; • GDH reaction occurs in the Mitochondria; • -Amino groups of most amino acids are ultimately transferred to -Oxoglutarat ...
... • Oxidative Deamination: Reaction catalyzed by the enzyme Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH); • Oxidative Deamination is the Oxidative removal of Ammonium ion (NH4+) from Glutamate; • GDH reaction occurs in the Mitochondria; • -Amino groups of most amino acids are ultimately transferred to -Oxoglutarat ...
Structure, function and selective inhibition of bacterial acetyl
... discovering small molecule inhibitors of bacterial ACC with clinical potential. Inhibition of the human homologues ACC1 and ACC2, or other off target activities, is likely to produce undesirable side effects for the patient. As such, it is critical to develop selective inhibitors. Differences in the ...
... discovering small molecule inhibitors of bacterial ACC with clinical potential. Inhibition of the human homologues ACC1 and ACC2, or other off target activities, is likely to produce undesirable side effects for the patient. As such, it is critical to develop selective inhibitors. Differences in the ...
basic chemistry of atoms and molecules
... called monomers. Monomers are the basic building blocks used to create even larger molecules called polymers. Some common monomers are glucose, glycerol and fatty acids, amino acids, and nucleotides. These monomers can be used to build the four biologically important polymers, which are carbo ...
... called monomers. Monomers are the basic building blocks used to create even larger molecules called polymers. Some common monomers are glucose, glycerol and fatty acids, amino acids, and nucleotides. These monomers can be used to build the four biologically important polymers, which are carbo ...
Effect of Zinc on Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Intermediates and
... 1966; Gupta & Venkitasubramanian, 1975;Maggon, Gopal & Venkitasubramanian, 1g73), but the mechanism of this stimulatory action is not understood at present. The effect of zinc on the metabolism of A. pdrdsiticus has not been reported. It has been shown that soybean is a poor substrate for aflatoxin ...
... 1966; Gupta & Venkitasubramanian, 1975;Maggon, Gopal & Venkitasubramanian, 1g73), but the mechanism of this stimulatory action is not understood at present. The effect of zinc on the metabolism of A. pdrdsiticus has not been reported. It has been shown that soybean is a poor substrate for aflatoxin ...
Lecture 15 (Parker) - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... This is the first of four oxidative reduction reactions of the citric acid cycle generating NADH ...
... This is the first of four oxidative reduction reactions of the citric acid cycle generating NADH ...
Oxidation
... • Light strikes the Photosystem II causing it to transfer e to primary electron acceptor at the reaction centre. • Excited e travel down the ETC electron transport chain (plastoquinone to cytochrome complex), electron loses energy at each exchange. • Electrons are replaced by splitting water molecul ...
... • Light strikes the Photosystem II causing it to transfer e to primary electron acceptor at the reaction centre. • Excited e travel down the ETC electron transport chain (plastoquinone to cytochrome complex), electron loses energy at each exchange. • Electrons are replaced by splitting water molecul ...