Roles of the Methylcitrate and Methylmalonyl
... mankind, but we are only now beginning to understand how it is able to survive and persist indefinitely in the host. Understanding carbon metabolism of the pathogen during infection is key, not only as a source of potential drug targets, but also for elucidating the environment in vivo, so that drug ...
... mankind, but we are only now beginning to understand how it is able to survive and persist indefinitely in the host. Understanding carbon metabolism of the pathogen during infection is key, not only as a source of potential drug targets, but also for elucidating the environment in vivo, so that drug ...
Cellular Respiration: Supplying Energy to Metabolic Reactions
... ATP also provides the necessary activation energy to * Synthesise organic compounds (endergonic, anabolic reactions) * Speed up many exergonic, catabolic reactions. You use HEAPS of ATP. Here are some estimates * 10 million molecules per muscle cell per second! * The average vertebrate consumes its ...
... ATP also provides the necessary activation energy to * Synthesise organic compounds (endergonic, anabolic reactions) * Speed up many exergonic, catabolic reactions. You use HEAPS of ATP. Here are some estimates * 10 million molecules per muscle cell per second! * The average vertebrate consumes its ...
WO 2012/149481 Al
... (GI) tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system (CNS) of animals including humans. ...
... (GI) tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system (CNS) of animals including humans. ...
Three-Dimensional Algebraic Models of the tRNA Code and 12
... beginning with purines (R) are always of only one kind for one amino acid; this is usually G, sometimes a modified purine, rarely A [17]. This salient wobbling feature allows two or more neighboring codon triplets to share a common anticodon, which is the reverse complementary of one of them. In the ...
... beginning with purines (R) are always of only one kind for one amino acid; this is usually G, sometimes a modified purine, rarely A [17]. This salient wobbling feature allows two or more neighboring codon triplets to share a common anticodon, which is the reverse complementary of one of them. In the ...
20 Insulin Secretion and Action
... 3–6) are characterized by insufficient β-cell mass. Genetic defects are also responsible for several clinical diabetes syndromes and diabetes in some animal models. Defective expression of β-cell mitochondrial protein frataxin, a gene that is deficient in Friedreich ataxia, results in decreased β-ce ...
... 3–6) are characterized by insufficient β-cell mass. Genetic defects are also responsible for several clinical diabetes syndromes and diabetes in some animal models. Defective expression of β-cell mitochondrial protein frataxin, a gene that is deficient in Friedreich ataxia, results in decreased β-ce ...
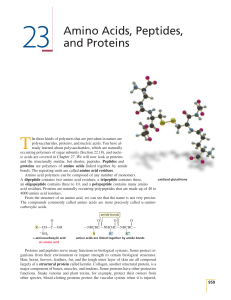
23 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. You have already learned about polysaccharides, which are naturally occurring polymers of sugar subunits (Section 22.18), and nucleic acids are covered in Chapter 27. We will now look at proteins and the structurally similar, but shorter, peptides. Pepti ...
... polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. You have already learned about polysaccharides, which are naturally occurring polymers of sugar subunits (Section 22.18), and nucleic acids are covered in Chapter 27. We will now look at proteins and the structurally similar, but shorter, peptides. Pepti ...
Chapter 1 – Title of Chapter
... d. Low blood pressure. e. Liver damage. 4. Upper level for adults: 3500 mg/day. c. Choline food sources – Milk, liver, eggs, and peanuts. 2. Inositol and Carnitine a. Inositol is made from glucose and is part of the cell membrane structure. b. Carnitine is made from lysine and transports long-chain ...
... d. Low blood pressure. e. Liver damage. 4. Upper level for adults: 3500 mg/day. c. Choline food sources – Milk, liver, eggs, and peanuts. 2. Inositol and Carnitine a. Inositol is made from glucose and is part of the cell membrane structure. b. Carnitine is made from lysine and transports long-chain ...
for growth. fermentation end products and genes required growth of
... anaerobically by fermenting sugars. In fermentation, NADH generated by glycolysis cannot be reoxidized by electron transport systems. Instead, NAD1 is generated with endogenous electron acceptors produced during metabolism of pyruvate, while ATP is generated by substrate-level phosphorylation, unlik ...
... anaerobically by fermenting sugars. In fermentation, NADH generated by glycolysis cannot be reoxidized by electron transport systems. Instead, NAD1 is generated with endogenous electron acceptors produced during metabolism of pyruvate, while ATP is generated by substrate-level phosphorylation, unlik ...
The Liver - cloudfront.net
... pancreas. When glucagon is released, the processes begin. Gluconeogenesis occurs when energy sources are low, such as during fasting, administration of low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise.8 Because liver failure can affect these processes, affected patients may have decreased glucose levels. ...
... pancreas. When glucagon is released, the processes begin. Gluconeogenesis occurs when energy sources are low, such as during fasting, administration of low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise.8 Because liver failure can affect these processes, affected patients may have decreased glucose levels. ...
Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Production of Fermented
... and whiskies, sucrose-rich plants (molasses or sugar juice from sugarcane) in the case of rums, or from fruits (which do not require pre-hydrolysis) in the case of wines and brandies. In the presence of sugars, together with other essential nutrients such as amino acids, minerals and vitamins, S. ce ...
... and whiskies, sucrose-rich plants (molasses or sugar juice from sugarcane) in the case of rums, or from fruits (which do not require pre-hydrolysis) in the case of wines and brandies. In the presence of sugars, together with other essential nutrients such as amino acids, minerals and vitamins, S. ce ...
Nitrogen source governs the patterns of growth and
... (PII) are two different families of components of the complex antibiotic pristinamycin produced by ‘ Streptomyces pristinaespiralis ’, a filamentous, Gram-positive bacterium. PI and PII, and especially their main components, PIA, PIIA and PIIB (Fig. 1) are produced simultaneously during the culture ...
... (PII) are two different families of components of the complex antibiotic pristinamycin produced by ‘ Streptomyces pristinaespiralis ’, a filamentous, Gram-positive bacterium. PI and PII, and especially their main components, PIA, PIIA and PIIB (Fig. 1) are produced simultaneously during the culture ...
Different lipid A types in lipopolysaccharides of phototrophic and
... lipid A and lipopolysaccharide analyses do not only confirm the recently proposed taxonomical division, but also support the phylogenetical relationship proposed by the 16S rRNA catalogues. (2) Phylogenetical relatedness is also suggested between the phototrophic Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Rhodobacter ...
... lipid A and lipopolysaccharide analyses do not only confirm the recently proposed taxonomical division, but also support the phylogenetical relationship proposed by the 16S rRNA catalogues. (2) Phylogenetical relatedness is also suggested between the phototrophic Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Rhodobacter ...
Specialised training
... D. Competitive phase – refinement of skills/ maintenance of fitness levels/quality rather than quantity/relevant examples of training modifications E. Tapering/peaking – preparation for specific competition/mainly skill focus F. Transition phase – active rest/out of season recovery period ...
... D. Competitive phase – refinement of skills/ maintenance of fitness levels/quality rather than quantity/relevant examples of training modifications E. Tapering/peaking – preparation for specific competition/mainly skill focus F. Transition phase – active rest/out of season recovery period ...
Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Production of Fermented
... and whiskies, sucrose-rich plants (molasses or sugar juice from sugarcane) in the case of rums, or from fruits (which do not require pre-hydrolysis) in the case of wines and brandies. In the presence of sugars, together with other essential nutrients such as amino acids, minerals and vitamins, S. ce ...
... and whiskies, sucrose-rich plants (molasses or sugar juice from sugarcane) in the case of rums, or from fruits (which do not require pre-hydrolysis) in the case of wines and brandies. In the presence of sugars, together with other essential nutrients such as amino acids, minerals and vitamins, S. ce ...
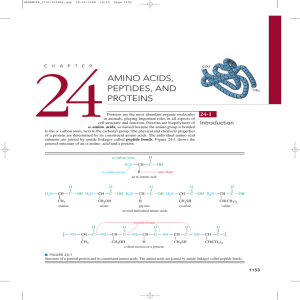
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... Proteins that provide all the essential amino acids in about the right proportions for human nutrition are called complete proteins. Examples of complete proteins are those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely ...
... Proteins that provide all the essential amino acids in about the right proportions for human nutrition are called complete proteins. Examples of complete proteins are those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely ...
Modulation of glucokinase by glucose, small
... potent and selective activator optimized for recognition by liver specific OATPs (organic anion transporting polypeptides). This activator has enhanced hepatic uptake, low hepatic oxidative metabolism and low passive permeability to minimize distribution into peripheral tissues that lack OATP transp ...
... potent and selective activator optimized for recognition by liver specific OATPs (organic anion transporting polypeptides). This activator has enhanced hepatic uptake, low hepatic oxidative metabolism and low passive permeability to minimize distribution into peripheral tissues that lack OATP transp ...
On the mechanism of action of the antifungal agent propionate
... Sodium propionate is widely used as a preservative due to its ability to inhibit fungal growth. Furthermore, this shortchain fatty acid (pion ¼ fat) prevents the biosynthesis of polyketides such as ochratoxin A by Aspergillus sulphureus and Penicillium viridicatum [1]. On the other hand, many fungi ...
... Sodium propionate is widely used as a preservative due to its ability to inhibit fungal growth. Furthermore, this shortchain fatty acid (pion ¼ fat) prevents the biosynthesis of polyketides such as ochratoxin A by Aspergillus sulphureus and Penicillium viridicatum [1]. On the other hand, many fungi ...
Major roles of isocitrate lyase and malate synthase in
... is probably involved in processes other than lipid utilization or gluconeogenesis, since an ICL-deficient mutant is unable to utilize acetate, ethanol, citrate, glycerol, oleate, lactate, pyruvate, peptone, glutamate or alanine for growth, unlike the parental strain (Ramı́rez & Lorenz, 2007; Piekars ...
... is probably involved in processes other than lipid utilization or gluconeogenesis, since an ICL-deficient mutant is unable to utilize acetate, ethanol, citrate, glycerol, oleate, lactate, pyruvate, peptone, glutamate or alanine for growth, unlike the parental strain (Ramı́rez & Lorenz, 2007; Piekars ...
1. 1. Overview of Bioorganic Chemistry
... models, showed that the cleavage was accompanied by simultaneous isomerization of the natural 3',5'-linked RNA to its 2',5'-linked isomer. It is also established that ribonucleosides are converted to deoxyribonucleosides by a biochemical process that removes the 2'-hydroxyl group, and that could hav ...
... models, showed that the cleavage was accompanied by simultaneous isomerization of the natural 3',5'-linked RNA to its 2',5'-linked isomer. It is also established that ribonucleosides are converted to deoxyribonucleosides by a biochemical process that removes the 2'-hydroxyl group, and that could hav ...
Basic Science for Clinicians
... How does AMP work as a molecular signal? AMP directly regulates a limited number of enzymes that are involved in metabolic pathways responsible for cellular energy generation (Figure 1). For instance, AMP activates glycogen phosphorylase, which releases stored glucose from glycogen, an important sou ...
... How does AMP work as a molecular signal? AMP directly regulates a limited number of enzymes that are involved in metabolic pathways responsible for cellular energy generation (Figure 1). For instance, AMP activates glycogen phosphorylase, which releases stored glucose from glycogen, an important sou ...
Cellular Respiration
... 9.2 Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate • Glycolysis can occur whether or not O2 is present. o If O2 is present, the chemical energy stored in pyruvate and NADH can be extracted by the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation o More than 75% of the original e ...
... 9.2 Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate • Glycolysis can occur whether or not O2 is present. o If O2 is present, the chemical energy stored in pyruvate and NADH can be extracted by the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation o More than 75% of the original e ...
inclusion of a glycogen regulation mathematical model into a
... biology point of view through mathematical modeling is daunting but very important as there has been a drastic increase in the prevalence of obesity, diabetes and other concerns relating to metabolism. By obtaining a better understanding of metabolic processes, especially during transitional feeding ...
... biology point of view through mathematical modeling is daunting but very important as there has been a drastic increase in the prevalence of obesity, diabetes and other concerns relating to metabolism. By obtaining a better understanding of metabolic processes, especially during transitional feeding ...
Chapter 11- Looking for the Edge
... • “Additive,” or, 1+1=2. This suggests that when two supplements are combined, the effect is equal to the sum of the individual effects. An example of this concept might include calcium and vitamin D. • “Antagonize,” or, 1+1=0. In this case, the effects of one supplement may actually negate the ef ...
... • “Additive,” or, 1+1=2. This suggests that when two supplements are combined, the effect is equal to the sum of the individual effects. An example of this concept might include calcium and vitamin D. • “Antagonize,” or, 1+1=0. In this case, the effects of one supplement may actually negate the ef ...