GLYCOGENOLYSIS AND GLYCOLYSIS IN MUSCLE
... other species, and the ability of mitochondria to take up and oxidize lactate directly. As will be described in the following section, since the 1920s, it has been believed that lactate is produced in muscle and other cells as the result of insufficient oxygen. However, it is now clear that lactate i ...
... other species, and the ability of mitochondria to take up and oxidize lactate directly. As will be described in the following section, since the 1920s, it has been believed that lactate is produced in muscle and other cells as the result of insufficient oxygen. However, it is now clear that lactate i ...
Enoyl acyl carrier protein reductase inhibitors: a patent review (2006
... multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) [4] have become troublesome due to the ineffectiveness of existing therapeutics. In the case of TB, the WHO estimates that a third of the world’s population is infected with the latent form of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and that > 0.5 million people worldwid ...
... multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) [4] have become troublesome due to the ineffectiveness of existing therapeutics. In the case of TB, the WHO estimates that a third of the world’s population is infected with the latent form of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and that > 0.5 million people worldwid ...
PDQ Physiology
... lated with metabolic activity and rate of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production. The two mitochondrial membranes differ greatly in their properties: 1. The inner bilayer has a much larger surface area because it forms cristae that project into the mitochondrial matrix. • It contains the carnitine ...
... lated with metabolic activity and rate of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production. The two mitochondrial membranes differ greatly in their properties: 1. The inner bilayer has a much larger surface area because it forms cristae that project into the mitochondrial matrix. • It contains the carnitine ...
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting
... compound pyruvate can be catabolized in the citric acid cycle. First, however, the pyruvate 1) loses a carbon, which is given off as a molecule of CO2, 2) is oxidized to form a two-carbon compound called acetate, and 3) is bonded to coenzyme A. These three steps result in the formation of A) acetyl ...
... compound pyruvate can be catabolized in the citric acid cycle. First, however, the pyruvate 1) loses a carbon, which is given off as a molecule of CO2, 2) is oxidized to form a two-carbon compound called acetate, and 3) is bonded to coenzyme A. These three steps result in the formation of A) acetyl ...
Ketone Body Metabolism Preserves Hepatic Function during
... ketone body metabolism during a classically ketogenic period, the transition to birth, and in a classically ‘non-ketogenic’ state, overnutrition, using novel genetic mouse models, high-resolution measures of dynamic metabolism using ...
... ketone body metabolism during a classically ketogenic period, the transition to birth, and in a classically ‘non-ketogenic’ state, overnutrition, using novel genetic mouse models, high-resolution measures of dynamic metabolism using ...
Divergent evolution of the thiolase superfamily and chalcone
... (b-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase (KAS) I and KAS II and the condensing domain of polyketide synthase) have invariant Cys and two His residues (CHH triad), while a Cys–His–Asn (CHN) triad is found in initiation enzymes (KAS III, 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase (KCS) and the chalcone synthase (CHS) f ...
... (b-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase (KAS) I and KAS II and the condensing domain of polyketide synthase) have invariant Cys and two His residues (CHH triad), while a Cys–His–Asn (CHN) triad is found in initiation enzymes (KAS III, 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase (KCS) and the chalcone synthase (CHS) f ...
Physiological implications of class IIa bacteriocin resistance in
... cells an advantage in the absence of glucose. An example of such an up-regulation exists for two enzymes associated with b-glucoside-specific PTSs in class IIa-resistant L. monocytogenes strains (Gravesen et al., 2002b). Such an up-regulation can explain that the specific growth rate of EGDe-mptA is ...
... cells an advantage in the absence of glucose. An example of such an up-regulation exists for two enzymes associated with b-glucoside-specific PTSs in class IIa-resistant L. monocytogenes strains (Gravesen et al., 2002b). Such an up-regulation can explain that the specific growth rate of EGDe-mptA is ...
De novo production of resveratrol from glucose or
... S. cerevisiae CEN.PK102-5B (MATa ura3-52 his3Δ1 leu2-3/112 MAL2-8c SUC2) (Entian and Kötter, 2007) was used for construction of resveratrol-producing strains. All the yeast strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. Yeast cells transformed with integrative plasmids were selected on synthetic ...
... S. cerevisiae CEN.PK102-5B (MATa ura3-52 his3Δ1 leu2-3/112 MAL2-8c SUC2) (Entian and Kötter, 2007) was used for construction of resveratrol-producing strains. All the yeast strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. Yeast cells transformed with integrative plasmids were selected on synthetic ...
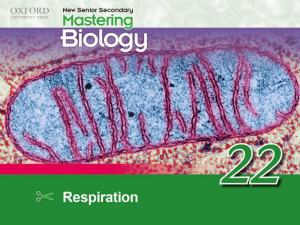
respiration_DSE_revi..
... When pyruvate enters a mitochondrion it is converted to acetylCoA. Coenzyme A (CoA) is a large molecule (and a vitamin) that acts as a coenzyme. The conversion of pyruvate to acetylCoA is an coupled oxidationreduction reaction in which high energy electrons are removed from pyruvate and end up in NA ...
... When pyruvate enters a mitochondrion it is converted to acetylCoA. Coenzyme A (CoA) is a large molecule (and a vitamin) that acts as a coenzyme. The conversion of pyruvate to acetylCoA is an coupled oxidationreduction reaction in which high energy electrons are removed from pyruvate and end up in NA ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell)
... C) often have "kinks" in their tails caused by the presence of a double bond between carbons. D) remain fluid because they are tightly packed against one another. E) form impermeable layers for cells . Answer: C الكولسترول المرتبط بأغشية الخاليا الحيوانية ...
... C) often have "kinks" in their tails caused by the presence of a double bond between carbons. D) remain fluid because they are tightly packed against one another. E) form impermeable layers for cells . Answer: C الكولسترول المرتبط بأغشية الخاليا الحيوانية ...
Full-Text PDF
... forms FFA and TG via de novo lipogenesis (DNL). Diacylglycerol (DAG), an active lipid intermediate, is produced during TG generation. Then TG is packed with apolipoprotein B100 (ApoB100), facilitating VLDL-TG production and secretion. Glyceraldehyde can also be converted to acetyl-CoA (consecutively ...
... forms FFA and TG via de novo lipogenesis (DNL). Diacylglycerol (DAG), an active lipid intermediate, is produced during TG generation. Then TG is packed with apolipoprotein B100 (ApoB100), facilitating VLDL-TG production and secretion. Glyceraldehyde can also be converted to acetyl-CoA (consecutively ...
... into Arg (WU, 1997) or released into the blood stream. Citrulline is captured by the kidney and converted into Arg, which is then sent to other tissues through specific transporters. A consequence of this metabolic dissimilarity between birds and mammals is that birds are dependent on exogenous sour ...
Oral free and dipeptide forms of glutamine supplementation
... injuries [10,11] or insults [12]. The mechanisms involved in the protective effects of L-glutamine supplementation include the antioxidant properties of the amino acid, mediated by glutathione (GSH) [4,13] and also specific molecular targets as transcription factors, mainly NF-kB [14]. The tripeptide ...
... injuries [10,11] or insults [12]. The mechanisms involved in the protective effects of L-glutamine supplementation include the antioxidant properties of the amino acid, mediated by glutathione (GSH) [4,13] and also specific molecular targets as transcription factors, mainly NF-kB [14]. The tripeptide ...
Cloning and functional characterization of a new subtype of the
... 33). Skeletal muscle expresses a subtype of system N, called Nm, which shows significantly weaker Li⫹ tolerance and pH sensitivity than the hepatic system N (1, 13). Two different types of system N have been described in the brain (21, 33). The system present in astrocytes is similar to the hepatic ...
... 33). Skeletal muscle expresses a subtype of system N, called Nm, which shows significantly weaker Li⫹ tolerance and pH sensitivity than the hepatic system N (1, 13). Two different types of system N have been described in the brain (21, 33). The system present in astrocytes is similar to the hepatic ...
LAP5 and LAP6 encode anther-specific proteins with similarity to
... long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase. In this study we describe the identification and characterization of two highly conserved anther-specific genes that are involved in pollen exine development, likely participate in sporopollenin biosynthesis, and similar to ACOS5, are related to, yet distinct fr ...
... long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase. In this study we describe the identification and characterization of two highly conserved anther-specific genes that are involved in pollen exine development, likely participate in sporopollenin biosynthesis, and similar to ACOS5, are related to, yet distinct fr ...
A1018 High oleic GM soybean AppR SD1 Safety Assess AMENDED
... desaturase gene (gm-fad2-1) using gene silencing. The genetic modification also results in a decreased level of linoleic acid. Soybean 305423 also contains a modified version of a soybean acetolactate synthase (als) gene (gm-hra). The GM-HRA enzyme can function in the presence of the ALS-inhibiting ...
... desaturase gene (gm-fad2-1) using gene silencing. The genetic modification also results in a decreased level of linoleic acid. Soybean 305423 also contains a modified version of a soybean acetolactate synthase (als) gene (gm-hra). The GM-HRA enzyme can function in the presence of the ALS-inhibiting ...
41 Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism
... As has been seen in previous chapters of this text, nucleotides serve numerous functions in different reaction pathways. For example, nucleotides are the activated precursors of DNA and RNA. Nucleotides form the structural moieties of many coenzymes (examples include NADH, FAD, and coenzyme A). Nucl ...
... As has been seen in previous chapters of this text, nucleotides serve numerous functions in different reaction pathways. For example, nucleotides are the activated precursors of DNA and RNA. Nucleotides form the structural moieties of many coenzymes (examples include NADH, FAD, and coenzyme A). Nucl ...
URIC ACID
... Hypoxanthine and guanine can be metabolised directly to xanthine, but AMP/adenosine have to be converted to IMP/inosine first. Xanthine is metabolised to uric acid by the enzyme xanthine oxidase, also responsible for conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine. Because de novo synthesis is an energy requ ...
... Hypoxanthine and guanine can be metabolised directly to xanthine, but AMP/adenosine have to be converted to IMP/inosine first. Xanthine is metabolised to uric acid by the enzyme xanthine oxidase, also responsible for conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine. Because de novo synthesis is an energy requ ...
Malic acid production by Aspergillus oryzae
... Citric acid is a well-known organic acid that is extensively used in the food and beverage industry as it combines a pleasant taste with low toxicity and palatability. It serves several functions in the food formulation, like sterilization, flavor fixation and enhancement, bacterial stabilization, a ...
... Citric acid is a well-known organic acid that is extensively used in the food and beverage industry as it combines a pleasant taste with low toxicity and palatability. It serves several functions in the food formulation, like sterilization, flavor fixation and enhancement, bacterial stabilization, a ...
Facultative Anaerobiosis in the Invertebrates: Pathways and Control
... that mammalian tissues utilize PEP rapidly in the presence of ADP to form pyruvate and ATP (reaction 1). This reaction is catalyzed by pyruvate kinase. Once pyruvate is formed it may be converted anaerobically (as in rapidly contracting muscle) to lactate, or aerobically to CO2 and water via the tri ...
... that mammalian tissues utilize PEP rapidly in the presence of ADP to form pyruvate and ATP (reaction 1). This reaction is catalyzed by pyruvate kinase. Once pyruvate is formed it may be converted anaerobically (as in rapidly contracting muscle) to lactate, or aerobically to CO2 and water via the tri ...
Analysis of the Role of Mitochondria of Sake in Fermentation Technologies
... As described above, genes involved in oxidative respiration are repressed in the presence of fermentable sugars and in the absence of oxygen. Similar to this regulation, several genes are known to be induced in response to hypoxia. In contrast to upregulation of the mitochondrial genes in response t ...
... As described above, genes involved in oxidative respiration are repressed in the presence of fermentable sugars and in the absence of oxygen. Similar to this regulation, several genes are known to be induced in response to hypoxia. In contrast to upregulation of the mitochondrial genes in response t ...
Acute hibernation decreases myocardial pyruvate carboxylation and
... (Millar; Houston, TX) was positioned in the left ventricle via the carotid artery. The animal was then heparinized (300 U/kg bolus ⫹ 150 U 䡠 kg⫺1 䡠 h⫺1 iv) and infused with a 20% triglyceride emulsion (Intralipid 20%, 0.3 ml 䡠 kg⫺1 䡠 h⫺1 iv) to increase plasma free fatty acids (FFA) to 0.6 mM (32). ...
... (Millar; Houston, TX) was positioned in the left ventricle via the carotid artery. The animal was then heparinized (300 U/kg bolus ⫹ 150 U 䡠 kg⫺1 䡠 h⫺1 iv) and infused with a 20% triglyceride emulsion (Intralipid 20%, 0.3 ml 䡠 kg⫺1 䡠 h⫺1 iv) to increase plasma free fatty acids (FFA) to 0.6 mM (32). ...
Rectal drug delivery: A promising route for enhancing drug absorption
... of insulin was known to be very poor due to its extensive degradation by various peptidase and digestive enzymes and poor membrane permeability characteristics. Acyl derivatives of insulin were synthesized to improve the gastrointestinal absorption of insulin. The acyl derivatives of insulin were sy ...
... of insulin was known to be very poor due to its extensive degradation by various peptidase and digestive enzymes and poor membrane permeability characteristics. Acyl derivatives of insulin were synthesized to improve the gastrointestinal absorption of insulin. The acyl derivatives of insulin were sy ...
thyroid synthesis, mode of action, metabolic functions and disorders
... Deiodination of Iodothronines • During digestion of thyroglobulin, iodothyronins are also freed but not released in to the blood • Enzyme Deiodinase cleaves Iodine from them making it available for more and more thyroid hormone synthesis inside the gland Thyroid Hormone Secretion • About 93 per cent ...
... Deiodination of Iodothronines • During digestion of thyroglobulin, iodothyronins are also freed but not released in to the blood • Enzyme Deiodinase cleaves Iodine from them making it available for more and more thyroid hormone synthesis inside the gland Thyroid Hormone Secretion • About 93 per cent ...