Fulltext - Jultika
... enzymatically active, reducing 2E-enoyl-CoAs to acyl-CoAs in an NADPH-dependent manner. Altogether, our data showed that NRBF-1 is a mitochondrial 2-enoyl-CoA reductase/2-enoyl thioester reductase (MECR/ETR1), the human functional counterpart of yeast Etr1p. In addition, MECR was also isolated from ...
... enzymatically active, reducing 2E-enoyl-CoAs to acyl-CoAs in an NADPH-dependent manner. Altogether, our data showed that NRBF-1 is a mitochondrial 2-enoyl-CoA reductase/2-enoyl thioester reductase (MECR/ETR1), the human functional counterpart of yeast Etr1p. In addition, MECR was also isolated from ...
Enzymes
... ATP is released by the process of hydrolysis The reaction is controlled by the enzyme "ATP-ase" ...
... ATP is released by the process of hydrolysis The reaction is controlled by the enzyme "ATP-ase" ...
Citric acid cycle - Issaquah Connect
... • Mitochondria have a double membrane that allows compartmentalization within the mitochondria and is important to its function • The outer membrane is smooth, but the inner membrane is highly convoluted, forming folds called cristae • Cristae contain enzymes important to ATP production; cristae als ...
... • Mitochondria have a double membrane that allows compartmentalization within the mitochondria and is important to its function • The outer membrane is smooth, but the inner membrane is highly convoluted, forming folds called cristae • Cristae contain enzymes important to ATP production; cristae als ...
3 AnAtomy for nutrition`s sAke
... amount of food until the food can be processed; forms a mixture of food and gastric secretions, which becomes a semiliquid blend called chyme (KIME); and controls movement of the chyme into the small intestine at a rate suitable for proper digestion and absorption by the small intestine. An empty ...
... amount of food until the food can be processed; forms a mixture of food and gastric secretions, which becomes a semiliquid blend called chyme (KIME); and controls movement of the chyme into the small intestine at a rate suitable for proper digestion and absorption by the small intestine. An empty ...
Natural Carbon Isotope Abundance of Plasma
... (mainly from ingestion of C3 and C4 metabolism plants) and to the discrimination between ‘light’ and ‘heavy’ isotopes during biochemical reactions (isotope effects and isotopic fractionation). Methodology/Principal Findings: Carbon isotopic abundance was measured in ZDF (fa/+) and ZDF (fa/fa), (lean ...
... (mainly from ingestion of C3 and C4 metabolism plants) and to the discrimination between ‘light’ and ‘heavy’ isotopes during biochemical reactions (isotope effects and isotopic fractionation). Methodology/Principal Findings: Carbon isotopic abundance was measured in ZDF (fa/+) and ZDF (fa/fa), (lean ...
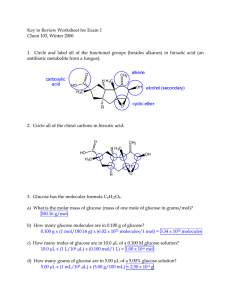
103 Rev Ex1 key Win06
... Unsaturated fatty acids have cis double bonds that make it hard for them to stack well together, while saturated fatty acids can stack closely together. So, the unsaturated fatty acids experience weaker intermolecular forces (dispersion forces) than the saturated fatty acids, making them liquid at r ...
... Unsaturated fatty acids have cis double bonds that make it hard for them to stack well together, while saturated fatty acids can stack closely together. So, the unsaturated fatty acids experience weaker intermolecular forces (dispersion forces) than the saturated fatty acids, making them liquid at r ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY - Illinois State University
... • Graph illustrates glucose utilization after 100g glucose consumption then 40 day fast ...
... • Graph illustrates glucose utilization after 100g glucose consumption then 40 day fast ...
Isotope fractionations in the biosynthesis of cell components by
... of fungi closely followed that of the substrates. Palmitic acid (C16:0), derived from phospholipids, did not display a large carbon isotope fractionation against the substrate. Stearic acid (C18:0), however, was depleted in 13 C against C16:0 in all strains. The desaturation of C18:0 to oleic acid ( ...
... of fungi closely followed that of the substrates. Palmitic acid (C16:0), derived from phospholipids, did not display a large carbon isotope fractionation against the substrate. Stearic acid (C18:0), however, was depleted in 13 C against C16:0 in all strains. The desaturation of C18:0 to oleic acid ( ...
Cellular Respiration - Parkway C-2
... glucose is broken into 2 glyceraldehyde 3-phosphates (a 3-carbon compound) “investing” 2 ATP. These are converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid and the ‘investment’ pays out a total of 4 ATP and 2 NADH. The process of glycolysis produces and then captures two pairs of high-energy electrons usin ...
... glucose is broken into 2 glyceraldehyde 3-phosphates (a 3-carbon compound) “investing” 2 ATP. These are converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid and the ‘investment’ pays out a total of 4 ATP and 2 NADH. The process of glycolysis produces and then captures two pairs of high-energy electrons usin ...
Physiology 4 Endocrinology
... Which of the following proteins has largest capacity to bind with thyroxine? a) albumin b) globulin c) TBG (thyroxine binding globulin) d) transferrin e) ferritin ...
... Which of the following proteins has largest capacity to bind with thyroxine? a) albumin b) globulin c) TBG (thyroxine binding globulin) d) transferrin e) ferritin ...
Bio 6 – Fermentation & Cellular Respiration Lab INTRODUCTION
... and inorganic phosphate (Pi) is exergonic and thus releases energy which cells can use to do any number of things. Once hydrolyzed, ATP can be regenerated from ADP and Pi, though this is endergonic and thus requires energy. The energy needed to regenerate ATP is obtained from “food”, whatever that m ...
... and inorganic phosphate (Pi) is exergonic and thus releases energy which cells can use to do any number of things. Once hydrolyzed, ATP can be regenerated from ADP and Pi, though this is endergonic and thus requires energy. The energy needed to regenerate ATP is obtained from “food”, whatever that m ...
Notes: Amino Acids and Proteins:
... Protein in our diets comes from both animal and vegetable sources. Most animal sources (meat, milk, eggs) provide what's called "complete protein," meaning that they contain all of the essential amino acids. Vegetable sources usually are low on or missing certain essential amino acids. For example, ...
... Protein in our diets comes from both animal and vegetable sources. Most animal sources (meat, milk, eggs) provide what's called "complete protein," meaning that they contain all of the essential amino acids. Vegetable sources usually are low on or missing certain essential amino acids. For example, ...
Cellular Respiration
... In the absence of oxygen, a cell will use fermentation to produce ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. Lactic Acid Fermentation converts glucose into lactic acid. This type of fermentation occurs in human muscle cells during strenuous exercise when breathing cannot supply the cells with enough ox ...
... In the absence of oxygen, a cell will use fermentation to produce ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. Lactic Acid Fermentation converts glucose into lactic acid. This type of fermentation occurs in human muscle cells during strenuous exercise when breathing cannot supply the cells with enough ox ...
Inherited metabolic disease - 15 December 2015
... • Many IEMs cause brain damage • May be progressive – regression ...
... • Many IEMs cause brain damage • May be progressive – regression ...
VITAMINS-6
... Vitamin B7 : What’s the role • Biotin is attached at the active site of five mammalian enzymes known as carboxylases • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase I and II catalyze the binding of bicarbonate to acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA • Malonyl-CoA is required for the synthesis of fatty acids • Pyruvate carboxyl ...
... Vitamin B7 : What’s the role • Biotin is attached at the active site of five mammalian enzymes known as carboxylases • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase I and II catalyze the binding of bicarbonate to acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA • Malonyl-CoA is required for the synthesis of fatty acids • Pyruvate carboxyl ...
De novo lipogenesis in the liver in health and disease: more than
... the substrate for the next round of elongation as it binds the thiol-group of the cysteine at the catalytic site of KS. The elongation ceases at the 16- or 18-carbon stage (Foster & Bloom, 1963; Carey, Dils & Hansen, 1970) with release of palmitic acid or stearic acid from ACP via activity of the th ...
... the substrate for the next round of elongation as it binds the thiol-group of the cysteine at the catalytic site of KS. The elongation ceases at the 16- or 18-carbon stage (Foster & Bloom, 1963; Carey, Dils & Hansen, 1970) with release of palmitic acid or stearic acid from ACP via activity of the th ...
Plant Respiration Exchange of Gases in Plants - E
... Answer: Aerobic respiration takes place within the mitochondria. Following are the main steps in aerobic respiration: Stepwise removal of all the hydrogen atoms leads to complete oxidation of pyruvate. This leaves three molecules of CO2. This step takes place in the matrix of mitochondria. Electrons ...
... Answer: Aerobic respiration takes place within the mitochondria. Following are the main steps in aerobic respiration: Stepwise removal of all the hydrogen atoms leads to complete oxidation of pyruvate. This leaves three molecules of CO2. This step takes place in the matrix of mitochondria. Electrons ...
(i) Enzymes are (1)
... A cells B hormones C proteins D sugars (ii) An enzyme is a biological catalyst that ...
... A cells B hormones C proteins D sugars (ii) An enzyme is a biological catalyst that ...
Section 2-3: Carbon Compounds (p. 44-48)
... Borg like me you would not need carbonbased molecules! ...
... Borg like me you would not need carbonbased molecules! ...
Glycogen Metabolism Gluconeogenesis
... Reverse Regulation of Phosphorylase and Synthase • The same kinase phosphorylates both phosphorylase and synthase • Synthase A (dephos.) is always active • Synthase D (phos.) is dependent on [G-6-P] • The same event that turns one on turns the other one off. ...
... Reverse Regulation of Phosphorylase and Synthase • The same kinase phosphorylates both phosphorylase and synthase • Synthase A (dephos.) is always active • Synthase D (phos.) is dependent on [G-6-P] • The same event that turns one on turns the other one off. ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration STAGE 1: Glycolysis
... reactions. Glycolysis begins with the addition of energy. Two highenergy phosphates from two molecules of ATP are added to the six-carbon molecule glucose, producing a six-carbon molecule with two phosphates. ...
... reactions. Glycolysis begins with the addition of energy. Two highenergy phosphates from two molecules of ATP are added to the six-carbon molecule glucose, producing a six-carbon molecule with two phosphates. ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 9
... atmosphere as waste ATP can be used directly to supply energy for the cell High energy electron carriers move into the ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN ...
... atmosphere as waste ATP can be used directly to supply energy for the cell High energy electron carriers move into the ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN ...
赣南医学院教案
... 3. Mix, incubate at room temperature for 10min, and then filter respectively. 4. Add chromogenic agent powders into three fossae of a white porcelain plate with a spoon. Drop 1-2 drops filtrate into fossae one by one. Observe the change of color in every fossa and analyze the results. Ketone bodies ...
... 3. Mix, incubate at room temperature for 10min, and then filter respectively. 4. Add chromogenic agent powders into three fossae of a white porcelain plate with a spoon. Drop 1-2 drops filtrate into fossae one by one. Observe the change of color in every fossa and analyze the results. Ketone bodies ...