• Physiological functions of the liver. • Describe the major functions
... Bile secretion: ( bile salts&acids formation) Detoxification & protective Immunity –kupffer cells,Miscellaneous Synthesis ...
... Bile secretion: ( bile salts&acids formation) Detoxification & protective Immunity –kupffer cells,Miscellaneous Synthesis ...
Uncoupling effect of polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency in isolated
... difficult because there is no accumulation of ATP, as in experiments with isolated mitochondria. The cellular energy status can only be assessed from the steady-state concentrations of adenine nucleotides. These values are shown in Table 2 for both the cytosolic and mitochondrial compartments. The P ...
... difficult because there is no accumulation of ATP, as in experiments with isolated mitochondria. The cellular energy status can only be assessed from the steady-state concentrations of adenine nucleotides. These values are shown in Table 2 for both the cytosolic and mitochondrial compartments. The P ...
2nd Phase of Glycolysis
... In addition to the allosteric effectors, pyruvate kinase is regulated by covalent modification. Hormones such as glucagon activate a cAMP-dependent protein kinase which transfers the γphosphate of ATP to the pyruvate kinase. The phosphorylated pyruvate kinase is more strongly inhibited by ATP and a ...
... In addition to the allosteric effectors, pyruvate kinase is regulated by covalent modification. Hormones such as glucagon activate a cAMP-dependent protein kinase which transfers the γphosphate of ATP to the pyruvate kinase. The phosphorylated pyruvate kinase is more strongly inhibited by ATP and a ...
Table 4–2. SOURCES, FUNCTIONS, AND EFFECTS OF VITAMINS
... Tendency to bleed Deficiency: Bleeding due to deficiency of prothrombin and other factors, osteopenia ...
... Tendency to bleed Deficiency: Bleeding due to deficiency of prothrombin and other factors, osteopenia ...
Respiration ppt - mleonessciencepage
... • can survive and make use of the energy released from glycolysis itself • Two forms of anaerobes are: – Facultative anaerobes – these can survive in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. – Obligate anaerobes – Survive only as anaerobes. ...
... • can survive and make use of the energy released from glycolysis itself • Two forms of anaerobes are: – Facultative anaerobes – these can survive in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. – Obligate anaerobes – Survive only as anaerobes. ...
MusselsAlive Report
... and, therefore, the contribution in fat is very low. The recommended adequate intake (AI) for ω3 ...
... and, therefore, the contribution in fat is very low. The recommended adequate intake (AI) for ω3 ...
Amino Acids, Amino Sugars and Sugars Present in the Cell Wall of
... 24 (NCTC 8305), 25, 27,30. The type strain 12 was isolated from a case of nephritis. Strains identified by the presence of T antigen: types 2 (NCTC 8322, glossy), 3/13, 5/27; a strain-carrying type 1 2 M antigen and a type 10 T antigen (designated 12/10);a strain-carrying type 1 4 M antigen alone (1 ...
... 24 (NCTC 8305), 25, 27,30. The type strain 12 was isolated from a case of nephritis. Strains identified by the presence of T antigen: types 2 (NCTC 8322, glossy), 3/13, 5/27; a strain-carrying type 1 2 M antigen and a type 10 T antigen (designated 12/10);a strain-carrying type 1 4 M antigen alone (1 ...
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ
... -classification, structure, biological role and metabolic pathways of main biomolecules included in the animal and plant cells, methods for storing and transmitting genetic information, the principles of energy transformation in biological systems, the main methods for the synthesis of biologically ...
... -classification, structure, biological role and metabolic pathways of main biomolecules included in the animal and plant cells, methods for storing and transmitting genetic information, the principles of energy transformation in biological systems, the main methods for the synthesis of biologically ...
Amino Acids, Amino Sugars and Sugars Present in
... 24 (NCTC 8305), 25, 27,30. The type strain 12 was isolated from a case of nephritis. Strains identified by the presence of T antigen: types 2 (NCTC 8322, glossy), 3/13, 5/27; a strain-carrying type 1 2 M antigen and a type 10 T antigen (designated 12/10);a strain-carrying type 1 4 M antigen alone (1 ...
... 24 (NCTC 8305), 25, 27,30. The type strain 12 was isolated from a case of nephritis. Strains identified by the presence of T antigen: types 2 (NCTC 8322, glossy), 3/13, 5/27; a strain-carrying type 1 2 M antigen and a type 10 T antigen (designated 12/10);a strain-carrying type 1 4 M antigen alone (1 ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
... • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
Muscle Energy and Metabolism
... aerobic respiration produces 36-38 ATP per glucose – efficient means of meeting the ATP demands of prolonged exercise – one’s rate of oxygen consumption rises for 3 to 4 minutes and levels off to a steady state in which ...
... aerobic respiration produces 36-38 ATP per glucose – efficient means of meeting the ATP demands of prolonged exercise – one’s rate of oxygen consumption rises for 3 to 4 minutes and levels off to a steady state in which ...
J24077086
... and broad substrate specificity (i.e., several amino acids share the same transport system). Functional criteria such as the type of amino acid (e.g., basic, acidic) or thermodynamic properties(energy dependence of transport) were used to classify amino acid transporters. This classification has bee ...
... and broad substrate specificity (i.e., several amino acids share the same transport system). Functional criteria such as the type of amino acid (e.g., basic, acidic) or thermodynamic properties(energy dependence of transport) were used to classify amino acid transporters. This classification has bee ...
Aphelenchoides besseyi
... these metabolites from their hosts and the environment through the lipid binding proteins (LBPs) [4,5]. Nematodes have been found to produce a series of unusual proteins that exhibit high affinity binding to lipid, and these proteins can be divided into two different classes according to their molec ...
... these metabolites from their hosts and the environment through the lipid binding proteins (LBPs) [4,5]. Nematodes have been found to produce a series of unusual proteins that exhibit high affinity binding to lipid, and these proteins can be divided into two different classes according to their molec ...
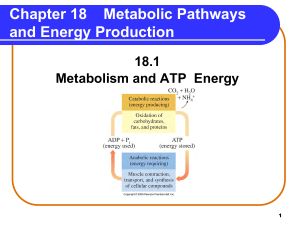
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... • NADH (Complex I) oxidation for 3 ATPs. NADH + 3 ADP + 3Pi NAD+ + 3 ATP • FADH2 (Complex II) oxidation for 2 ATPs. FADH2 + 2 ADP + 2Pi FAD + 2 ATP ...
... • NADH (Complex I) oxidation for 3 ATPs. NADH + 3 ADP + 3Pi NAD+ + 3 ATP • FADH2 (Complex II) oxidation for 2 ATPs. FADH2 + 2 ADP + 2Pi FAD + 2 ATP ...
89. Carboxylic Acids as a Traceless Activation Group for Conjugate Additions: A Three-�Step Synthesis of (�)-�Lyrica
... conditions followed by treatment with acid promoted decarboxylation to afford racemic pregabalin in only three steps. In conclusion, we have demonstrated the utility of carboxylic acids as a traceless activation group for radical conjugate addition via visible light-mediated photoredox catalysis. The ...
... conditions followed by treatment with acid promoted decarboxylation to afford racemic pregabalin in only three steps. In conclusion, we have demonstrated the utility of carboxylic acids as a traceless activation group for radical conjugate addition via visible light-mediated photoredox catalysis. The ...
Proteins - Winona State University
... 1. They can supply energy for processes such as growth, movement, electrical signalling, metabolism 2. They can regulate body processes such as metabolism, growth, membrane transport, cellular communication 3. They can provide the building blocks for making the structures of our cells and our bodies ...
... 1. They can supply energy for processes such as growth, movement, electrical signalling, metabolism 2. They can regulate body processes such as metabolism, growth, membrane transport, cellular communication 3. They can provide the building blocks for making the structures of our cells and our bodies ...
Chapter 6
... Cells can use the energy in fats and proteins as well. – Fats are digested into fatty acids and glycerol. – Proteins are digested into amino acids. Cells must convert fats and proteins into molecules that can enter and be metabolized by the enzymes of glycolysis or the Kreb’s cycle. Copyright © The ...
... Cells can use the energy in fats and proteins as well. – Fats are digested into fatty acids and glycerol. – Proteins are digested into amino acids. Cells must convert fats and proteins into molecules that can enter and be metabolized by the enzymes of glycolysis or the Kreb’s cycle. Copyright © The ...
الشريحة 1
... • Glucose is a reducing monosaccharide that serves as the principal fuel of all the tissues. It enters the cell through the influence of insulin and undergoes a series of chemical reactions to produce energy. • The glucose level in the blood is maintained within a narrow range under diverse conditio ...
... • Glucose is a reducing monosaccharide that serves as the principal fuel of all the tissues. It enters the cell through the influence of insulin and undergoes a series of chemical reactions to produce energy. • The glucose level in the blood is maintained within a narrow range under diverse conditio ...
Lactic Acid Bacteria: Characteristics
... • Low pH also inhibits growth of other bacteria • Give tart taste to fermented milks • Growth is self-limiting (build up of waste products) • Used in probiotics (presence in livestock feed inhibits ...
... • Low pH also inhibits growth of other bacteria • Give tart taste to fermented milks • Growth is self-limiting (build up of waste products) • Used in probiotics (presence in livestock feed inhibits ...