Some Amino Acids
... pancreas to produce enough insulin. • Insulin is a protein needed to promote the adsorption of glucose into the cells. • Animal insulin was used as a treatment. • Now human insulin can be synthesized and manufactured because Sanger was able to determine the exact structure of human insulin. © 2014 P ...
... pancreas to produce enough insulin. • Insulin is a protein needed to promote the adsorption of glucose into the cells. • Animal insulin was used as a treatment. • Now human insulin can be synthesized and manufactured because Sanger was able to determine the exact structure of human insulin. © 2014 P ...
Muscle Metabolism - White Plains Public Schools
... Muscle glycogen provides the major source of glucose followed by blood glucose and then fats. ...
... Muscle glycogen provides the major source of glucose followed by blood glucose and then fats. ...
Exam 4 key fall 2010
... (5) 15. Explain why NADH produced in glycolysis in eukaryotes typically causes a problem. ...
... (5) 15. Explain why NADH produced in glycolysis in eukaryotes typically causes a problem. ...
O A RIGINAL RTICLE
... as the primary molecular target of the frontline antitubercular drug isoniazid (INH) [4]. Recent studies demonstrated that InhA is also the target for the second line antitubercular drug ethionamide (ETA) [5]. InhA catalyzes the reduction of long-chain trans-2-enoyl-ACP in the type II fatty acid bio ...
... as the primary molecular target of the frontline antitubercular drug isoniazid (INH) [4]. Recent studies demonstrated that InhA is also the target for the second line antitubercular drug ethionamide (ETA) [5]. InhA catalyzes the reduction of long-chain trans-2-enoyl-ACP in the type II fatty acid bio ...
Photosynthesis_Cell Resp_Jeopardy
... # of carbon dioxide molecules produced by 5 turns of the Kreb’s cycle. ...
... # of carbon dioxide molecules produced by 5 turns of the Kreb’s cycle. ...
Biological Molecules - Napa Valley College
... What are the types of carbohydrates What is the function of each of the carbohydrate Know what types of organisms the complex carbohydrates are found in, the digestibility of the different complex carbohydrates. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... What are the types of carbohydrates What is the function of each of the carbohydrate Know what types of organisms the complex carbohydrates are found in, the digestibility of the different complex carbohydrates. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
PDF w
... These include CO, olefins, aromatic hydrocarbons, and the like. The other auxiliary criterion is that if a given acid depends strongly on basicity and little on polarizability as far as rates of nucleophilic displacements are concerned, then i t will depend even less on polarizability as far as equi ...
... These include CO, olefins, aromatic hydrocarbons, and the like. The other auxiliary criterion is that if a given acid depends strongly on basicity and little on polarizability as far as rates of nucleophilic displacements are concerned, then i t will depend even less on polarizability as far as equi ...
Phosphofructokinase (PFK) Exercise
... muscle cramps. Patients with this genetic disorder are advised not to exercise vigorously. Explain why reduced physical activity can help these patients. ...
... muscle cramps. Patients with this genetic disorder are advised not to exercise vigorously. Explain why reduced physical activity can help these patients. ...
Phenyllactic Acid: A Potential Antimicrobial Compound in Lactic acid
... ά-ketoglutarate. The phenylalanine is first transaminated to phenylpyruvic acid (PPA) and PPA is further reduced to PhLA [28,29,30]. The transamination reaction is mediated by aromatic amino acid transferase (AAT) which has broad substrate specificity including leucine, tyrosine and methionine [31]. ...
... ά-ketoglutarate. The phenylalanine is first transaminated to phenylpyruvic acid (PPA) and PPA is further reduced to PhLA [28,29,30]. The transamination reaction is mediated by aromatic amino acid transferase (AAT) which has broad substrate specificity including leucine, tyrosine and methionine [31]. ...
Metabolism of Leukotrienes: The Linear Biosynthetic Pathway
... been comprehensively reviewed (11). 5-LO pools may be cytosolic or nuclear depending upon cell type and are translocated to the nuclear envelope where the reaction occurs (12), with 5-LO in complex with a required 5lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP)(11,13). The 5-LO reactions are the determining ...
... been comprehensively reviewed (11). 5-LO pools may be cytosolic or nuclear depending upon cell type and are translocated to the nuclear envelope where the reaction occurs (12), with 5-LO in complex with a required 5lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP)(11,13). The 5-LO reactions are the determining ...
Document
... Proteins perform biological functions such as structural support, catalysis of chemical reactions, immune response to foreign substances, transport of molecules across membranes, and control of genetic expression. The three-dimensional structure and function of a protein is determined by the sequenc ...
... Proteins perform biological functions such as structural support, catalysis of chemical reactions, immune response to foreign substances, transport of molecules across membranes, and control of genetic expression. The three-dimensional structure and function of a protein is determined by the sequenc ...
Polar amino acids with negative charge
... Nonetheless, it is called an amino acid. The primary amine on the α carbon of glutamate semialdehyde forms a Schiff base with the aldehyde which is then reduced, yielding proline. • When proline is in a peptide bond, it does not have a hydrogen on the α amino group, so it cannot donate a hydrogen bo ...
... Nonetheless, it is called an amino acid. The primary amine on the α carbon of glutamate semialdehyde forms a Schiff base with the aldehyde which is then reduced, yielding proline. • When proline is in a peptide bond, it does not have a hydrogen on the α amino group, so it cannot donate a hydrogen bo ...
Karavay P.A1*, Leonid I. Nefyodov2
... turned out that the vast majority of the diagnostic values of the group have shifts in the level of functional and metabolic related amino acids and their derivatives, and as such no specific changes in the concentrations of individual compounds of this class is observed.
... turned out that the vast majority of the diagnostic values of the group have shifts in the level of functional and metabolic related amino acids and their derivatives, and as such no specific changes in the concentrations of individual compounds of this class is observed.
Cellular Respiration
... for cellular work • 6 CO2 are released • Raw materials for electron transport system: • 10 NADH • 2 FADH2 ...
... for cellular work • 6 CO2 are released • Raw materials for electron transport system: • 10 NADH • 2 FADH2 ...
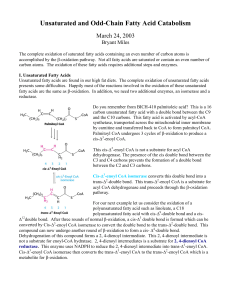
Unsaturated and Odd-Chain Fatty Acid Catabolism
... Most of the acetyl CoA produced by β-oxidation undergoes complete oxidation through the citric acid cycle. The entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate. Under fasting conditions or diabetes, gluconeogenisis depletes the concentration of oxaloacetate. ...
... Most of the acetyl CoA produced by β-oxidation undergoes complete oxidation through the citric acid cycle. The entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate. Under fasting conditions or diabetes, gluconeogenisis depletes the concentration of oxaloacetate. ...
Muscles
... CoA) and oxidative phosphorylation (which utilises the high energy compounds NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP). Glucose, fatty acids and proteins all lead to the formation of acetyl–CoA and therefore provide the initial fuel for the TCA cycle and accompanying oxidative phosphorylation. The advantage of ...
... CoA) and oxidative phosphorylation (which utilises the high energy compounds NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP). Glucose, fatty acids and proteins all lead to the formation of acetyl–CoA and therefore provide the initial fuel for the TCA cycle and accompanying oxidative phosphorylation. The advantage of ...
CK12 Homework Sections 1.27 to 1.30 Section 1.27 Glycolysis 1
... 1. What is fermentation? Fermentation is making ATP without oxygen, which involves glycolysis only. 2. Name two types of fermentation. Lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. 3. What is the main advantage of aerobic respiration? Of anaerobic respiration? Most living things use oxygen to ...
... 1. What is fermentation? Fermentation is making ATP without oxygen, which involves glycolysis only. 2. Name two types of fermentation. Lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. 3. What is the main advantage of aerobic respiration? Of anaerobic respiration? Most living things use oxygen to ...
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University
... large bowel by anaerobic bacteria. It has been shown that these compounds can have tumour-promoting capacities in animal experiments. In epidemiological studies, colonic cancer risk is related to the faecal bile acid concentration. In serum and bile of patients with colonic adenomas, more deoxycholi ...
... large bowel by anaerobic bacteria. It has been shown that these compounds can have tumour-promoting capacities in animal experiments. In epidemiological studies, colonic cancer risk is related to the faecal bile acid concentration. In serum and bile of patients with colonic adenomas, more deoxycholi ...
Peptide bonds, polypeptides and proteins printable pdf
... Water, polypeptide synthesis and folding: Were it not for the presence of hydrophobic R-groups, all polypeptides would assume an extended configuration in water. H-bond donors and acceptor groups in polypeptide backbone would form Hbonds with each other and with water molecules. More typical polypep ...
... Water, polypeptide synthesis and folding: Were it not for the presence of hydrophobic R-groups, all polypeptides would assume an extended configuration in water. H-bond donors and acceptor groups in polypeptide backbone would form Hbonds with each other and with water molecules. More typical polypep ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... Linear arrangement of n amino acid residues linked by peptide bonds. Polymers composed of two, three, a few, and many amino acid residues are called as dipeptides, tripeptides, oligopeptides and polypeptides. Proteins are molecules that consist of one or more polypeptide chains. ...
... Linear arrangement of n amino acid residues linked by peptide bonds. Polymers composed of two, three, a few, and many amino acid residues are called as dipeptides, tripeptides, oligopeptides and polypeptides. Proteins are molecules that consist of one or more polypeptide chains. ...
SYNTHESIS OF OXOQUINOLINE DERIVATIVES COUPLED TO DIFFERENT AMINO ACID ESTERS
... possess useful biological activity and used as antibacterial, antifungal and antitumor agents. These pharmacological properties of quinolines aroused our interest in synthesizing several new compounds featuring heterocyclic rings of the quinoline derivatives linked to amino acid ester side chains wi ...
... possess useful biological activity and used as antibacterial, antifungal and antitumor agents. These pharmacological properties of quinolines aroused our interest in synthesizing several new compounds featuring heterocyclic rings of the quinoline derivatives linked to amino acid ester side chains wi ...