Biology 4 Matching Quiz Chapter 19 Match the following terms on
... Chapter 19 Match the following terms on the left to their descriptions on the right. 1. _______ hemoglobin ...
... Chapter 19 Match the following terms on the left to their descriptions on the right. 1. _______ hemoglobin ...
3 Treating disease
... A specific antigen is injected into the animal, stimulating the production of plasma cells. The plasma cells are removed from the animal and fused with cancerous myeloma cells from normal mice. These form immortal hybridoma cells, which can produce a single type of antibody indefinitely. ...
... A specific antigen is injected into the animal, stimulating the production of plasma cells. The plasma cells are removed from the animal and fused with cancerous myeloma cells from normal mice. These form immortal hybridoma cells, which can produce a single type of antibody indefinitely. ...
Forensic Biology by Richard Li
... binding to the subsequently produced antibodies. Antigens are generally proteins or polysaccharides, but other substances such as nucleic acids can also be antigens. ...
... binding to the subsequently produced antibodies. Antigens are generally proteins or polysaccharides, but other substances such as nucleic acids can also be antigens. ...
12.2 Review Questions What happens when serum containing B
... 1. What happens when serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells carrying the B antigen? Will the same thing happen if serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells containing A antigen? Explain your answer. 2. What is serology and what is its most widespread application? I ...
... 1. What happens when serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells carrying the B antigen? Will the same thing happen if serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells containing A antigen? Explain your answer. 2. What is serology and what is its most widespread application? I ...
Purification of Antibodies
... In addition, the immunoglobulins in antisera may bind with low avidity to molecules that are not true target antigens. For these and other reasons, antisera can manifest a level of background reactivity that is unacceptably high. There are three ways to deal with this problem. 1) An innocuous blocki ...
... In addition, the immunoglobulins in antisera may bind with low avidity to molecules that are not true target antigens. For these and other reasons, antisera can manifest a level of background reactivity that is unacceptably high. There are three ways to deal with this problem. 1) An innocuous blocki ...
ELISA Pre and Post Test
... a. first line defenses; b. nonspecific immunities; c. specific immunities; d. both a and b. 3. An antigen is: a. a protein or other molecule that can be separate or found on a pathogen and is foreign to your body; b. a protein made in response to a specific pathogen used to limit pathogen’s growth; ...
... a. first line defenses; b. nonspecific immunities; c. specific immunities; d. both a and b. 3. An antigen is: a. a protein or other molecule that can be separate or found on a pathogen and is foreign to your body; b. a protein made in response to a specific pathogen used to limit pathogen’s growth; ...
antibody antigen interaction
... Antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules. Biological Aspects of Antibody- ...
... Antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules. Biological Aspects of Antibody- ...
1Mono Clonal Antibodies (reviewed)
... Discovery The idea of a "magic bullet" was first proposed by Paul Ehrlich who at the beginning of the 20th century postulated that if a compound could be made that selectively targeted a disease-causing organism, then a toxin for that organism could be delivered along with the agent of selectivity. ...
... Discovery The idea of a "magic bullet" was first proposed by Paul Ehrlich who at the beginning of the 20th century postulated that if a compound could be made that selectively targeted a disease-causing organism, then a toxin for that organism could be delivered along with the agent of selectivity. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 7. Adverse blood transfusion reaction are classified as Type ______ hypersensitivity. 8. The organ donor has to be fully HLA-compatible for successful transplantation. 9. Hybridoma cells cannot grow in the absence of thymidine in the medium. 10. TMB/H2O2 can be used as a substrate in ELISA. III. Com ...
... 7. Adverse blood transfusion reaction are classified as Type ______ hypersensitivity. 8. The organ donor has to be fully HLA-compatible for successful transplantation. 9. Hybridoma cells cannot grow in the absence of thymidine in the medium. 10. TMB/H2O2 can be used as a substrate in ELISA. III. Com ...
Monoclonal Antibodies
... Chimeric antibodies – human-mouse hybrid antibodies with mouse CDR fused with human constant regions Splicing mouse CDR into human antibody gene regions Transgenic mice ...
... Chimeric antibodies – human-mouse hybrid antibodies with mouse CDR fused with human constant regions Splicing mouse CDR into human antibody gene regions Transgenic mice ...
Immunological Techniques in Research and Clinical Medicine
... • Antibodies can be “tagged” with small fluorescent molecules and still retain their binding specificity • These “tagged” antibodies can be used as probes to visualize specific molecules in tissues, cells, or anywhere ...
... • Antibodies can be “tagged” with small fluorescent molecules and still retain their binding specificity • These “tagged” antibodies can be used as probes to visualize specific molecules in tissues, cells, or anywhere ...
I. Immunity
... B. Lymphatic System: produces white blood cells and antibodies 1. White blood cells: two types-T cells and B cells 2. Antibody—protein that disables antigens 3. B cells—makes antibodies 4. T cells—helps make antibodies, kills infected cells 5. Memory B cells—used if attacked again by same antigen -D ...
... B. Lymphatic System: produces white blood cells and antibodies 1. White blood cells: two types-T cells and B cells 2. Antibody—protein that disables antigens 3. B cells—makes antibodies 4. T cells—helps make antibodies, kills infected cells 5. Memory B cells—used if attacked again by same antigen -D ...
Review on Immunostimulatory monoclonal antibodies for cancer
... Immunostimulatory monoclonal antibodies lead to development of immune-receptor molecules as new design for cancer therapy. These agents function on key receptors, either by antagonizing those that suppress immune responses or by triggering others that enhance immune responses. Complexities such as a ...
... Immunostimulatory monoclonal antibodies lead to development of immune-receptor molecules as new design for cancer therapy. These agents function on key receptors, either by antagonizing those that suppress immune responses or by triggering others that enhance immune responses. Complexities such as a ...
Antibodies - blobs.org
... The body has a number of ways of fighting off invaders like bacteria and viruses. Sometimes it uses chemicals that kill them off randomly. However, a really clever system has been designed to target them very specifically. Antibodies are the body’s clever labels for marking out these invaders. ...
... The body has a number of ways of fighting off invaders like bacteria and viruses. Sometimes it uses chemicals that kill them off randomly. However, a really clever system has been designed to target them very specifically. Antibodies are the body’s clever labels for marking out these invaders. ...
Protection against Disease
... Antibodies are molecules synthesises by animals in response to the presence of a foreign substance (antigen) They are made by B lymphocytes Antibodies are proteins found in plasma, tissue fluid and milk They are also called Immunoglobins ...
... Antibodies are molecules synthesises by animals in response to the presence of a foreign substance (antigen) They are made by B lymphocytes Antibodies are proteins found in plasma, tissue fluid and milk They are also called Immunoglobins ...
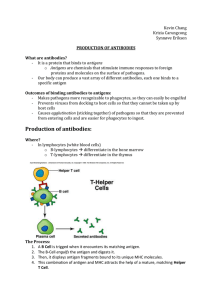
BLOCK F – Krizia,Kevin,Synnove – Production of Antibodies
... matching antigens. 7. Antibodies are made up of white blood cells, called B lymphocytes or B Cells. Each B Cell carries a different membrane-bound antibody molecule on its surface that serves as a receptor for recognizing a specific antigen. When antigen binds to this receptor, the B cell is stimula ...
... matching antigens. 7. Antibodies are made up of white blood cells, called B lymphocytes or B Cells. Each B Cell carries a different membrane-bound antibody molecule on its surface that serves as a receptor for recognizing a specific antigen. When antigen binds to this receptor, the B cell is stimula ...
Publication JournalArticle (Originalarbeit in einer wissenschaftlichen
... Four commonly used blocking agents, i.e., fetal calf serum, mammalian gelatin-Nonidet-P40, fish gelatinNonidet-P40, and defatted powdered milk were compared with respect to their efficiency to block the nonspecific background and to promote maximal immunoreactivity of monoclonal antibodies against h ...
... Four commonly used blocking agents, i.e., fetal calf serum, mammalian gelatin-Nonidet-P40, fish gelatinNonidet-P40, and defatted powdered milk were compared with respect to their efficiency to block the nonspecific background and to promote maximal immunoreactivity of monoclonal antibodies against h ...
Monoclonal Antibodies Treatment for Various Diseases www
... Herceptin is specific for destroying cancer cells in the breast. Treatment procedure that involves Rituxan is very much effective in treating various types of lymphomas, especially Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. ...
... Herceptin is specific for destroying cancer cells in the breast. Treatment procedure that involves Rituxan is very much effective in treating various types of lymphomas, especially Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. ...
Powerpoint Presentation: The Monoclonal Antibodies
... The uses of monoclonal antibodies Diagnosing and identifying molecules • Preparations can be made to identify tissue types with a high degree of accuracy • The preparation of pregnancy testing kits using anti HCG antibody linked to a coloured indicator • The identification and localisation of molec ...
... The uses of monoclonal antibodies Diagnosing and identifying molecules • Preparations can be made to identify tissue types with a high degree of accuracy • The preparation of pregnancy testing kits using anti HCG antibody linked to a coloured indicator • The identification and localisation of molec ...
Monoclonal Antibodies
... Medical use of Antibodies Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are pure, single antibody types that are industrially produced. Clones of one type of immune cell.Typical production: Monoclonal antibodies = Tumour (cancer) cells + antigen immunized mouse spleen cells. Monoclonal antibodies can be used fo ...
... Medical use of Antibodies Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are pure, single antibody types that are industrially produced. Clones of one type of immune cell.Typical production: Monoclonal antibodies = Tumour (cancer) cells + antigen immunized mouse spleen cells. Monoclonal antibodies can be used fo ...
A1987H656200002
... even though the anti-Lyt-1 and anti-Lyt-2 MAbs detected non-polymorphic epitopes on glycoproteins known to be polymorphic and previously studied using alloantisera against the polymorphic epitopes, the biochemical analysis allowed us to demonstrate that the MAbs recognized these same molecules. This ...
... even though the anti-Lyt-1 and anti-Lyt-2 MAbs detected non-polymorphic epitopes on glycoproteins known to be polymorphic and previously studied using alloantisera against the polymorphic epitopes, the biochemical analysis allowed us to demonstrate that the MAbs recognized these same molecules. This ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II. State true or false; if false, give reasons. ...
... II. State true or false; if false, give reasons. ...
Monoclonal Antibodies
... inhibiting growth, or interfering with a key function. B. mAbs was modified for delivery of a toxin, radioisotope, cytokine or other active conjugates. C. it is also possible to design bispecific antibodies that can bind with their Fab regions both to target ...
... inhibiting growth, or interfering with a key function. B. mAbs was modified for delivery of a toxin, radioisotope, cytokine or other active conjugates. C. it is also possible to design bispecific antibodies that can bind with their Fab regions both to target ...
36-1577: Monoclonal Antibody to UACA / Nucling (Nuclear
... UACA (Uveal Autoantigen with Coiled-coil domains and Ankyrin repeats) is a 1,416 amino acid nuclear membrane protein. It was originally identified as an autoantigen in patients with panuveitis, a characteristic of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease, and in patients with Graves' disease. UACA was also late ...
... UACA (Uveal Autoantigen with Coiled-coil domains and Ankyrin repeats) is a 1,416 amino acid nuclear membrane protein. It was originally identified as an autoantigen in patients with panuveitis, a characteristic of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease, and in patients with Graves' disease. UACA was also late ...
HA4 c19 INVESTIGATOR Name Dr. Ann Hubbard
... ACKNOWLEDGMENTS STATEMENT We have been asked by NICHD to ensure that all investigators include an acknowledgment in publications that benefit from the use of the DSHB's products. We suggest that the following statement be used: “The (select: hybridoma, monoclonal antibody, or protein capture reagen ...
... ACKNOWLEDGMENTS STATEMENT We have been asked by NICHD to ensure that all investigators include an acknowledgment in publications that benefit from the use of the DSHB's products. We suggest that the following statement be used: “The (select: hybridoma, monoclonal antibody, or protein capture reagen ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.