Filed Pursuant to Rule 424(b)(2) Registration Statement No. 333
... significantly less liquidity in the secondary market. In such a case, the price at which the notes could be sold likely would be lower than if an active market existed. Many economic and other factors will impact the market value of the notes. The market for, and the market value of, the notes may b ...
... significantly less liquidity in the secondary market. In such a case, the price at which the notes could be sold likely would be lower than if an active market existed. Many economic and other factors will impact the market value of the notes. The market for, and the market value of, the notes may b ...
Austrian Business Cycle Theory: An Application to New Zealand`s
... as instigating the ‘marginal revolution’ in economics, or as would be a more correct terminology; the ‘subjective value revolution’ (Salerno, 2010). In Principles of Economics, Menger sets forth his theory of price based on the subjective valuations of individual actors, that price is determined at ...
... as instigating the ‘marginal revolution’ in economics, or as would be a more correct terminology; the ‘subjective value revolution’ (Salerno, 2010). In Principles of Economics, Menger sets forth his theory of price based on the subjective valuations of individual actors, that price is determined at ...
Engineering Economics - Inside Mines
... The acceptance or rejection of a project based on the IRR criterion is made by comparing the calculated rate with the required rate of return, or cutoff rate established by the firm. If the IRR exceeds the required rate the project should be accepted; if not, it should be rejected. If the required r ...
... The acceptance or rejection of a project based on the IRR criterion is made by comparing the calculated rate with the required rate of return, or cutoff rate established by the firm. If the IRR exceeds the required rate the project should be accepted; if not, it should be rejected. If the required r ...
Shifts from Deposits into Currency
... moving funds from lenders to borrowers. Indeed, financial intermediaries are a far more important source of financing for corporations than securities markets are. Why are financial intermediaries and indirect finance so important in financial markets? To answer this question, we need to understand ...
... moving funds from lenders to borrowers. Indeed, financial intermediaries are a far more important source of financing for corporations than securities markets are. Why are financial intermediaries and indirect finance so important in financial markets? To answer this question, we need to understand ...
the role of central bank rate on commercial banks profitability in
... Interest rate is the price a borrower pays for the use of money they borrow from a lender/financial institutions or fee paid on borrowed assets (Crowley, 2007). Interest can be thought of as "rent of money". Interest rates are fundamental to a ‘capitalist society’ and are normally expressed as a per ...
... Interest rate is the price a borrower pays for the use of money they borrow from a lender/financial institutions or fee paid on borrowed assets (Crowley, 2007). Interest can be thought of as "rent of money". Interest rates are fundamental to a ‘capitalist society’ and are normally expressed as a per ...
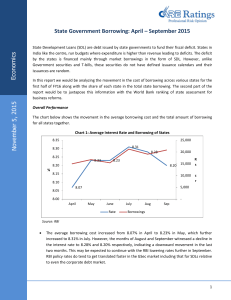
State Government Borrowing
... This report is prepared by Credit Analysis &Research Limited (CARE Ratings). CARE Ratings has taken utmost care to ensure accuracy and objectivity while developing this report based on information available in public domain. However, neither the accuracy nor completeness of information contained in ...
... This report is prepared by Credit Analysis &Research Limited (CARE Ratings). CARE Ratings has taken utmost care to ensure accuracy and objectivity while developing this report based on information available in public domain. However, neither the accuracy nor completeness of information contained in ...
mmi14-Hoffmann 19104742 en
... have preferential access to international finance through the state-owned banking system. As a result of this financial repression, savings decisions by private households and firms should be driven by variation in the domestic (financially repressed) interest rate and firm savings should predict future ...
... have preferential access to international finance through the state-owned banking system. As a result of this financial repression, savings decisions by private households and firms should be driven by variation in the domestic (financially repressed) interest rate and firm savings should predict future ...
Interest Rates and Real Business Cycles in Emerging Markets S. Tolga TİRYAKİ
... in developing country business cycles, we observe that real interest rates are also strongly countercyclical in developing countries compared to the weakly procyclical relationship in developed countries. Lastly, it is widely documented that developing countries are subject to sudden stops in capita ...
... in developing country business cycles, we observe that real interest rates are also strongly countercyclical in developing countries compared to the weakly procyclical relationship in developed countries. Lastly, it is widely documented that developing countries are subject to sudden stops in capita ...
Regime Switching Interest Rates and Fluctuations in
... small open economies: they are characterized by (1) a higher volatility of macroeconomic variables, (2) a strongly countercyclical trade balance, (3) consumption volatility exceeding output volatility, and (4) a real interest rate that is much more volatile in emerging economies, strongly countercyc ...
... small open economies: they are characterized by (1) a higher volatility of macroeconomic variables, (2) a strongly countercyclical trade balance, (3) consumption volatility exceeding output volatility, and (4) a real interest rate that is much more volatile in emerging economies, strongly countercyc ...
The Macroeconomic Transition to High Household Debt Jeffrey R. Campbell Zvi Hercowitz
... The model’s equilibrium resembles this in an extreme way. The borrower owes all the debt to the saver. With the model calibrated to the period prior to 1982, we compute the transition to a new steady state following a financial reform calibrated to the actual reduction of equity requirements on hou ...
... The model’s equilibrium resembles this in an extreme way. The borrower owes all the debt to the saver. With the model calibrated to the period prior to 1982, we compute the transition to a new steady state following a financial reform calibrated to the actual reduction of equity requirements on hou ...
PDF
... their monthly repayment (for those with adjustable rate mortgages) and condition their ability to refinance (through their impact on housing prices). • Commercial banks, which traditionally engage in transformation, have recently increased their sensitivity to market conditions. First and arbitragin ...
... their monthly repayment (for those with adjustable rate mortgages) and condition their ability to refinance (through their impact on housing prices). • Commercial banks, which traditionally engage in transformation, have recently increased their sensitivity to market conditions. First and arbitragin ...
SIGNIFICANCE OF CREDIT RATIONING IN UKRAINE by Ivan
... credit rationing cannot exist. In the neoclassical framework, the loan has two characteristics: interest rate and maturity. The customer's risk is known, and, provided there are no information costs, the lenders may perfectly price discriminate amongst borrowers through setting interest rates on the ...
... credit rationing cannot exist. In the neoclassical framework, the loan has two characteristics: interest rate and maturity. The customer's risk is known, and, provided there are no information costs, the lenders may perfectly price discriminate amongst borrowers through setting interest rates on the ...
bondch11s
... incentive increases during periods of falling interest rates, with the greatest increases occurring when borrowers determine that rates have bottomed out. The refinancing incentive can be measured by the difference between the mortgage portfolio's weighted average rate, referred to as the weighted ...
... incentive increases during periods of falling interest rates, with the greatest increases occurring when borrowers determine that rates have bottomed out. The refinancing incentive can be measured by the difference between the mortgage portfolio's weighted average rate, referred to as the weighted ...
consolidated statement of financial position as at 31 march 2011
... construction services have been estimated to be equal to the construction costs plus margin of 17.5% and the effective interest rate of 12.5% for lending by the grantor. The construction industry margins range between 15-20% and management has determined that a margin of 17.5% is both conservative a ...
... construction services have been estimated to be equal to the construction costs plus margin of 17.5% and the effective interest rate of 12.5% for lending by the grantor. The construction industry margins range between 15-20% and management has determined that a margin of 17.5% is both conservative a ...
Case Objectives - Trinity University
... valuable even if their intrinsic values are negative. The reason is the time value component equal to the difference between total value and intrinsic value. Time value tends to decrease as options approach expiration dates. The farther away the expiration date, the more time the option has to event ...
... valuable even if their intrinsic values are negative. The reason is the time value component equal to the difference between total value and intrinsic value. Time value tends to decrease as options approach expiration dates. The farther away the expiration date, the more time the option has to event ...
Mankiw 6e PowerPoints
... Y/Y depends on growth in the factors of production and on technological progress (all of which we take as given, for now). Hence, the quantity theory predicts a one-for-one relation between changes in the money growth rate and changes in the inflation rate. ...
... Y/Y depends on growth in the factors of production and on technological progress (all of which we take as given, for now). Hence, the quantity theory predicts a one-for-one relation between changes in the money growth rate and changes in the inflation rate. ...
Chapter 22 Credit Risk
... 51.88Q Total 345.33Q The bond pays a coupon of 3.5 every six months and has a continuously compounded yield of 5% per year. Its market price is 105.3289. The risk-free value of the bond is obtained by discounting the promised cash flows at 4%. It is 108.2837. The total loss from defaults should ther ...
... 51.88Q Total 345.33Q The bond pays a coupon of 3.5 every six months and has a continuously compounded yield of 5% per year. Its market price is 105.3289. The risk-free value of the bond is obtained by discounting the promised cash flows at 4%. It is 108.2837. The total loss from defaults should ther ...
Financing Growth in the WAEMU Through the Regional
... Securities’ issuance procedures depend on the type of security. Although regional regulations require that government bills and bonds be auctioned on the primary market, some T-bonds are still issued by syndication. T-bill and T-bond auctions are carried out for each member country at the national b ...
... Securities’ issuance procedures depend on the type of security. Although regional regulations require that government bills and bonds be auctioned on the primary market, some T-bonds are still issued by syndication. T-bill and T-bond auctions are carried out for each member country at the national b ...
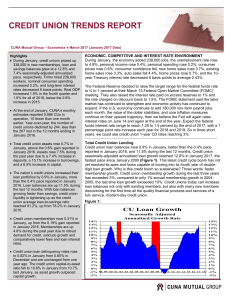
Interest

Interest is money paid by a borrower to a lender for a credit or a similar liability. Important examples are bond yields, interest paid for bank loans, and returns on savings. Interest differs from profit in that it is paid to a lender, whereas profit is paid to an owner. In economics, the various forms of credit are also referred to as loanable funds.When money is borrowed, interest is typically calculated as a percentage of the principal, the amount owed to the lender. The percentage of the principal that is paid over a certain period of time (typically a year) is called the interest rate. Interest rates are market prices which are determined by supply and demand. They are generally positive because loanable funds are scarce.Interest is often compounded, which means that interest is earned on prior interest in addition to the principal. The total amount of debt grows exponentially, and its mathematical study led to the discovery of the number e. In practice, interest is most often calculated on a daily, monthly, or yearly basis, and its impact is influenced greatly by its compounding rate.