EOC Review All Content
... • Evidence includes mitochondria and chloroplast have prokaryotic type DNA ...
... • Evidence includes mitochondria and chloroplast have prokaryotic type DNA ...
Cellular Neuroanatomy I
... The neuronal membrane serves as a barrier to enclose the cytoplasm and to exclude certain substances that float in the fluid that bathes the neuron. The membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Phospholipids have a polar phosphate group at one end that is hydrophilic (“ ...
... The neuronal membrane serves as a barrier to enclose the cytoplasm and to exclude certain substances that float in the fluid that bathes the neuron. The membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Phospholipids have a polar phosphate group at one end that is hydrophilic (“ ...
Fluid mechanics and cell transport in immunotherapeutics and
... Despite its broad utility, with billions of administrations each year, drug delivery with the needle and syringe has many limitations. Perhaps most importantly, is the inability to deliver genes and drugs to immunologically-sensitive antigen presenting cells—called Langerhans cells)—resident just be ...
... Despite its broad utility, with billions of administrations each year, drug delivery with the needle and syringe has many limitations. Perhaps most importantly, is the inability to deliver genes and drugs to immunologically-sensitive antigen presenting cells—called Langerhans cells)—resident just be ...
Biology II Chapter 5 The Working Cell Notes Outline MEMBRANE
... a. It is crucial for cells that ________________ moves across their membrane – Water moves across membranes in response to solute concentration inside and outside of the cell by a process called ______________________ – Osmosis will move water across a membrane _________________ its concentration gr ...
... a. It is crucial for cells that ________________ moves across their membrane – Water moves across membranes in response to solute concentration inside and outside of the cell by a process called ______________________ – Osmosis will move water across a membrane _________________ its concentration gr ...
Chapter 1
... c) Building blocks of proteins are the amino acids, each of which has a carboxyl group, an amino group and a side chain called the R group. d) Proteins have complex shapes held together by hydrogen bonds. e) Protein shapes, which determine how proteins function, can be altered (denatured) by pH, tem ...
... c) Building blocks of proteins are the amino acids, each of which has a carboxyl group, an amino group and a side chain called the R group. d) Proteins have complex shapes held together by hydrogen bonds. e) Protein shapes, which determine how proteins function, can be altered (denatured) by pH, tem ...
Document
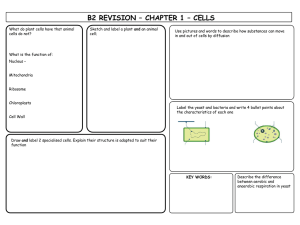
... Specialised Cells Cells are specialised to carry out a specific function. The structure gives a clue to its function. ...
... Specialised Cells Cells are specialised to carry out a specific function. The structure gives a clue to its function. ...
Chapter 1
... c) Building blocks of proteins are the amino acids, each of which has a carboxyl group, an amino group and a side chain called the R group. d) Proteins have complex shapes held together by hydrogen bonds. e) Protein shapes, which determine how proteins function, can be altered (denatured) by pH, tem ...
... c) Building blocks of proteins are the amino acids, each of which has a carboxyl group, an amino group and a side chain called the R group. d) Proteins have complex shapes held together by hydrogen bonds. e) Protein shapes, which determine how proteins function, can be altered (denatured) by pH, tem ...
Standard 1 answer key. SB1a. Cell theory: states all cells come from
... B) proteins-monomer is amino acid, polymer is a folded polypeptide chain, major functions-biological catalysts, hormones, strong muscles C)nucleic acids-monomer is nucleotides (5 carbon sugar, phosphate and nitrogen base), polymer-chains of nucleotides joined together forming nucleic acid, function- ...
... B) proteins-monomer is amino acid, polymer is a folded polypeptide chain, major functions-biological catalysts, hormones, strong muscles C)nucleic acids-monomer is nucleotides (5 carbon sugar, phosphate and nitrogen base), polymer-chains of nucleotides joined together forming nucleic acid, function- ...
- thevignanam
... • If a protein is made up of more than one polypeptide chain it is said to have quaternary structure. • This refers to the spatial arrangement of the polypeptide subunits and the nature of the interactions between them. ...
... • If a protein is made up of more than one polypeptide chain it is said to have quaternary structure. • This refers to the spatial arrangement of the polypeptide subunits and the nature of the interactions between them. ...
A look at macromolecules (Text pages 38
... secondary structure • Quaternary: more than one polypeptide chain Structure determined by order of amino acids • Degree of hydrogen bonding • Structure can be ‘denatured’ • Gentle vs. harsh ...
... secondary structure • Quaternary: more than one polypeptide chain Structure determined by order of amino acids • Degree of hydrogen bonding • Structure can be ‘denatured’ • Gentle vs. harsh ...
Application of Imaging Flow Cytometry to Monitor Life Cycle
... not. Therefore, the introduction of nontoxic cells into the marine environment could be an effective means of mitigating toxic A. tamarense blooms. Before such a strategy can be pursued, a more complete understanding of the factors governing sexuality is needed. In general, light microscopy is used ...
... not. Therefore, the introduction of nontoxic cells into the marine environment could be an effective means of mitigating toxic A. tamarense blooms. Before such a strategy can be pursued, a more complete understanding of the factors governing sexuality is needed. In general, light microscopy is used ...
to the PDF file.
... •Each DNA codon codes for a separate amino acids •Amino acids have the same basic form including the peptide bond •Variation occurs by having different ‘R’ groups ...
... •Each DNA codon codes for a separate amino acids •Amino acids have the same basic form including the peptide bond •Variation occurs by having different ‘R’ groups ...
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living
... specific metabolic activities take place. Most important among these is a cell nucleus that houses the DNA. This nucleus gives the eukaryote its name, which means "true nucleus". Other differences include: ...
... specific metabolic activities take place. Most important among these is a cell nucleus that houses the DNA. This nucleus gives the eukaryote its name, which means "true nucleus". Other differences include: ...
protein synthesis (simplified)
... It is the Sequence of bases that act like a code The sequence (order) of bases tells the cell what proteins to make. The sequence of bases dictates the sequence of amino acids, which determines the shape of a protein. ...
... It is the Sequence of bases that act like a code The sequence (order) of bases tells the cell what proteins to make. The sequence of bases dictates the sequence of amino acids, which determines the shape of a protein. ...
Structure of Macromolecules Dr. Nakhshab
... • There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins • peptide linkages form by condensation reactions between the carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent amino acids. ...
... • There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins • peptide linkages form by condensation reactions between the carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent amino acids. ...
Midterm Studyguide Avery L
... B. Vocab: Isomers- Molecules that have the same molecular formula, but different structures. For example, butane and isobutane. Monomer- A single molecule that can be binded to other monomers to form polymers. Example: Amino Acids Polymers- Chains of more than one monomer. Example: Polypeptides pH- ...
... B. Vocab: Isomers- Molecules that have the same molecular formula, but different structures. For example, butane and isobutane. Monomer- A single molecule that can be binded to other monomers to form polymers. Example: Amino Acids Polymers- Chains of more than one monomer. Example: Polypeptides pH- ...
./ ` . `.`4 Body Tissues 13. Figure 3-6: A. Simple squamous epLthelium
... (which causes the bubbling). ...
... (which causes the bubbling). ...
Folic acid
... • Toxicity primarily nephro- and neurotoxicity – Expected to have low selective toxicity because of detergent effects on cell membranes. ...
... • Toxicity primarily nephro- and neurotoxicity – Expected to have low selective toxicity because of detergent effects on cell membranes. ...
Chapter 6.4 The Building Blocks of Life
... In plants, a carbohydrate called cellulose provides structural support in cell walls Chitin, a polysaccharide, is the main component in the hard outer shell of shrimp, lobsters, and ...
... In plants, a carbohydrate called cellulose provides structural support in cell walls Chitin, a polysaccharide, is the main component in the hard outer shell of shrimp, lobsters, and ...
Method and System for Delivering Nucleic Acid into a Target Cell
... approach to enable spatial and temporal control over the transfection of stem cells. Oligonucleotide “handles” are covalently attached to a supporting substrate, which may be a solid surface or a two- or three-dimensional semi-solid structure, such as a hydrogel network. The oligonucleotides sequest ...
... approach to enable spatial and temporal control over the transfection of stem cells. Oligonucleotide “handles” are covalently attached to a supporting substrate, which may be a solid surface or a two- or three-dimensional semi-solid structure, such as a hydrogel network. The oligonucleotides sequest ...
Chapter 1 - Introduction
... particularly confocal microscopy, to directly visualize specific parts of a cell. This strategy makes use of fluorescent molecules that interact with specific proteins or membranes within the cell. For example, a fluorescent probe called MitoTrackerTM localizes to mitochondrial membranes, thus showi ...
... particularly confocal microscopy, to directly visualize specific parts of a cell. This strategy makes use of fluorescent molecules that interact with specific proteins or membranes within the cell. For example, a fluorescent probe called MitoTrackerTM localizes to mitochondrial membranes, thus showi ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.