Chapter 4
... Primary cell cultures are established from animal tissues Most cells removed from an animal grow and divide for a limited period of time (about 50 doublings), then eventually die Certain “transformed cells” may arise that are immortal and can be used to form a cell line Transformed cells may be deri ...
... Primary cell cultures are established from animal tissues Most cells removed from an animal grow and divide for a limited period of time (about 50 doublings), then eventually die Certain “transformed cells” may arise that are immortal and can be used to form a cell line Transformed cells may be deri ...
Chapt 5 - Workforce Solutions
... What is facilitated diffusion? Carrier proteins bind to the molecule that they transport across the membrane. Facilitated diffusion is movement of a molecule from high to low concentration with the help of a carrier protein. -is specific -is passive -saturates when all carriers are occupied ...
... What is facilitated diffusion? Carrier proteins bind to the molecule that they transport across the membrane. Facilitated diffusion is movement of a molecule from high to low concentration with the help of a carrier protein. -is specific -is passive -saturates when all carriers are occupied ...
doc CHEE_370_HW_1_
... 7. (10 points) Cells of Escherichia coli take up lactose via the Lac permease system, glucose via the phosphotransferase system, and maltose via an ABC-type transporter. For each of these sugars describe: (i) the components of their transport system, and (ii) the source of energy that drives the tra ...
... 7. (10 points) Cells of Escherichia coli take up lactose via the Lac permease system, glucose via the phosphotransferase system, and maltose via an ABC-type transporter. For each of these sugars describe: (i) the components of their transport system, and (ii) the source of energy that drives the tra ...
BIO109 Survey of Biology - Cape Cod Community College
... 3. Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, students are able to do the following. • Explain the properties required for life by recognizing the levels of scientific organization • Classify the variety of life forms that have evolved • Assemble lab specimens into taxonom ...
... 3. Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, students are able to do the following. • Explain the properties required for life by recognizing the levels of scientific organization • Classify the variety of life forms that have evolved • Assemble lab specimens into taxonom ...
CELL SNAP - YourGenome.org
... known as cisternae. It extends out from the nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm of the cell and is involved in the production, folding and transport of proteins produced by the ribosomes on its surface. Rod- or sausage-shaped organelles found inside cells. They are the power stations of the cell pro ...
... known as cisternae. It extends out from the nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm of the cell and is involved in the production, folding and transport of proteins produced by the ribosomes on its surface. Rod- or sausage-shaped organelles found inside cells. They are the power stations of the cell pro ...
glossary of terms - Personal Genome Diagnostics
... Important class of molecules found in all living cells. A protein is composed of one or more long chains of amino acids, the sequence of which corresponds to the DNA sequence of the gene that encodes it. Proteins play a variety of roles in the cell, including structural (cytoskeleton), mechanical (m ...
... Important class of molecules found in all living cells. A protein is composed of one or more long chains of amino acids, the sequence of which corresponds to the DNA sequence of the gene that encodes it. Proteins play a variety of roles in the cell, including structural (cytoskeleton), mechanical (m ...
Dev Biol L1
... This course aims to provide a broad look at development integrating. We will explore the basic body plan of the embryo and how organs are formed, with special emphasis on vertebrate models. Embryonic and Adult Stem Cells will also be covered ...
... This course aims to provide a broad look at development integrating. We will explore the basic body plan of the embryo and how organs are formed, with special emphasis on vertebrate models. Embryonic and Adult Stem Cells will also be covered ...
DNA-notes
... *Nucleotides: repeating units of DNA *Nucleotides are composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphorus containing molecule, (called the backbone) and a nitrogen containing molecule called a base. *Four types of bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. *Bases pair A to T and G to C (compleme ...
... *Nucleotides: repeating units of DNA *Nucleotides are composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphorus containing molecule, (called the backbone) and a nitrogen containing molecule called a base. *Four types of bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. *Bases pair A to T and G to C (compleme ...
glucocerebrosidease
... • White blood cells have a type of lipid called glucocerebroside in their cell membranes. (Glucocerebroside is involved in cell to cell signaling.) ...
... • White blood cells have a type of lipid called glucocerebroside in their cell membranes. (Glucocerebroside is involved in cell to cell signaling.) ...
Organelles File
... in coordination with each other and help the organism to survive. The functions of animal cell is carried out by the different cell organelles. The organelles of the cell function as a unit and regulate the activities of the cell. The different cell organelles and their functions are as follows: Cel ...
... in coordination with each other and help the organism to survive. The functions of animal cell is carried out by the different cell organelles. The organelles of the cell function as a unit and regulate the activities of the cell. The different cell organelles and their functions are as follows: Cel ...
ANIMAL TISSUE CULTURE PRESENTATION
... and cell concentration. Total protein content and specific enzyme activity levels measured on a per cell basis vary substantially over the course of a culture due to changes in the growth rate and composition of the culture medium. Protein and enzyme content will be high during exponential growth bu ...
... and cell concentration. Total protein content and specific enzyme activity levels measured on a per cell basis vary substantially over the course of a culture due to changes in the growth rate and composition of the culture medium. Protein and enzyme content will be high during exponential growth bu ...
Ch8 sec4Life with Carbon
... Nucleic Acids • Nucleic acids are very large organic molecules made up of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorous. The two types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. – Nucleotides are the building blocks of Nucleic acids. There are only four kinds of Nucleotides. – DNA and Proteins: The di ...
... Nucleic Acids • Nucleic acids are very large organic molecules made up of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorous. The two types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. – Nucleotides are the building blocks of Nucleic acids. There are only four kinds of Nucleotides. – DNA and Proteins: The di ...
New Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentation
... The twenty amino acids (that make up proteins)each have assigned to them both three-letter (can be upper or lower case) and one-letter codes (upper case). ...
... The twenty amino acids (that make up proteins)each have assigned to them both three-letter (can be upper or lower case) and one-letter codes (upper case). ...
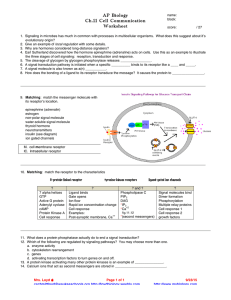
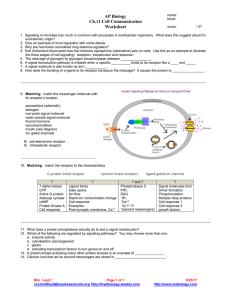
AP Biology Ch.11 Cell Communication Worksheet
... Rapid ion concentration change Cell response Examples: Post-synaptic membrane, Ca++ ...
... Rapid ion concentration change Cell response Examples: Post-synaptic membrane, Ca++ ...
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... Centrioles - Centrioles are selfreplicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the ...
... Centrioles - Centrioles are selfreplicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the ...
Types of Cells
... Centrioles - Centrioles are selfreplicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the ...
... Centrioles - Centrioles are selfreplicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the ...
RED &WHITE BLOOD CELLS
... A very simple cell. Major function is to transport oxygen to the tissues . And disposal of carbon dioxide and protons formed by the tissue metabolism. Is composed of a membrane surrounding the hemoglobin. Hb forms about 95% of the intracellular protein of the red cell. ...
... A very simple cell. Major function is to transport oxygen to the tissues . And disposal of carbon dioxide and protons formed by the tissue metabolism. Is composed of a membrane surrounding the hemoglobin. Hb forms about 95% of the intracellular protein of the red cell. ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.