Example - Solon City Schools
... directly to the olfactory cortex in the brain bypassing the thalamus – Olfactory cortex – receives information from the olfactory bulb • Conscious awareness of odors • Identification of odors ...
... directly to the olfactory cortex in the brain bypassing the thalamus – Olfactory cortex – receives information from the olfactory bulb • Conscious awareness of odors • Identification of odors ...
This newsletter is for your information only and is not a substitute for
... experiences). The brain's programmed genetic development and our environmental life experiences interplay causing brain cells (neurons) to grow, to die, to form new connections, to lose connections, to turn on, and to turn off. These changes are most pronounced in the womb and during the first three ...
... experiences). The brain's programmed genetic development and our environmental life experiences interplay causing brain cells (neurons) to grow, to die, to form new connections, to lose connections, to turn on, and to turn off. These changes are most pronounced in the womb and during the first three ...
Chapter 27 Lecture notes
... B. Neurons are found with supporting cells or glia. There may be as many as 50 supporting cells for every neuron. These cells protect, insulate, or reinforce the neurons. NOTE: These supporting cells are also called neuroglia (or glial cells). There are six major types of neuroglia. For example, ast ...
... B. Neurons are found with supporting cells or glia. There may be as many as 50 supporting cells for every neuron. These cells protect, insulate, or reinforce the neurons. NOTE: These supporting cells are also called neuroglia (or glial cells). There are six major types of neuroglia. For example, ast ...
Chapter Objectives - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Know that the local inhibitory interneurons, excited by glutamate, released by 1A afferents, release glycine. Know that many other inhibitory interneurons in the spinal cord release glycine, and that some release the inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA. Glycine released in ventral horn and binds to mo ...
... Know that the local inhibitory interneurons, excited by glutamate, released by 1A afferents, release glycine. Know that many other inhibitory interneurons in the spinal cord release glycine, and that some release the inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA. Glycine released in ventral horn and binds to mo ...
Viktor`s Notes * Visual Pathways and Cortex
... dorsal (parietal) pathway - concerned primarily with spatial orientation ("where"), motion; extension of magnocellular pathway; parietal lobe is devoted to directed attention. ventral (temporal) pathway - concerned with object recognition ("what") - shape and recognition of forms and faces; represen ...
... dorsal (parietal) pathway - concerned primarily with spatial orientation ("where"), motion; extension of magnocellular pathway; parietal lobe is devoted to directed attention. ventral (temporal) pathway - concerned with object recognition ("what") - shape and recognition of forms and faces; represen ...
Questions and Answers
... 3. How does Microglia repair neurons? And what kind of potential has that mechanism in Neuroscience? A: Microglia seem to be responsble for cleaning the brain tissue of dead neurons and other uncleanliness. The details and other functions are beyond my current knowledge. Macroglial cells produce mye ...
... 3. How does Microglia repair neurons? And what kind of potential has that mechanism in Neuroscience? A: Microglia seem to be responsble for cleaning the brain tissue of dead neurons and other uncleanliness. The details and other functions are beyond my current knowledge. Macroglial cells produce mye ...
Term - k20 learn
... This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 8. We have separated terms into categories to make it easier to remember them, but many terms could fit into more than one category. ...
... This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 8. We have separated terms into categories to make it easier to remember them, but many terms could fit into more than one category. ...
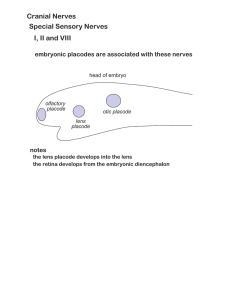
Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII
... Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...
... Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...
neuron-neuroglia
... What Functional type is it mostly? Sensory or Afferent What direction does it go? PNS to CNS ...
... What Functional type is it mostly? Sensory or Afferent What direction does it go? PNS to CNS ...
mspn12a
... Output layers: sends projections to the LGN and other areas of the brain, contain primarily stellate (interneuron)/pyramidal cells that make local/far-reaching projections (circle one). Circle pyramidal and ...
... Output layers: sends projections to the LGN and other areas of the brain, contain primarily stellate (interneuron)/pyramidal cells that make local/far-reaching projections (circle one). Circle pyramidal and ...
Lecture 12 - Websupport1
... Both equilibrium and hearing are provided by receptors of the inner ear Anatomy of the ear – External Ear • Auricle or pinnae surrounds the ear ...
... Both equilibrium and hearing are provided by receptors of the inner ear Anatomy of the ear – External Ear • Auricle or pinnae surrounds the ear ...
Sparse but not `Grandmother-cell` coding in the medial temporal lobe
... by a large set of studies in both humans and animals (see for example [18,36]. In line with this evidence, it is very likely that the responses of human MTL cells described in the previous section link visual (or other forms of) perception to memory. For example, the cell responding to pictures of S ...
... by a large set of studies in both humans and animals (see for example [18,36]. In line with this evidence, it is very likely that the responses of human MTL cells described in the previous section link visual (or other forms of) perception to memory. For example, the cell responding to pictures of S ...
Substrate Micropatterning as a New in Vitro Cell Culture System to
... inverted microscopy, permit live-cell imaging. In this context, the limited number of axons and myelinating cells in each Matrigel line would facilitate the characterization of morphological and biomechanical events that occur both during axonal ensheathment and myelin compaction. Such a live-cell s ...
... inverted microscopy, permit live-cell imaging. In this context, the limited number of axons and myelinating cells in each Matrigel line would facilitate the characterization of morphological and biomechanical events that occur both during axonal ensheathment and myelin compaction. Such a live-cell s ...
CHAPTER 4
... – Formed from the axons of ganglion cells which carries impulses towards brain – Optic Disk – blind spot where the optic nerve exits the eyeball (no photoreceptors) – Optic Chiasm – junction in brain where optic nerves converge & axons are rerouted so that a crossing over of visual ...
... – Formed from the axons of ganglion cells which carries impulses towards brain – Optic Disk – blind spot where the optic nerve exits the eyeball (no photoreceptors) – Optic Chiasm – junction in brain where optic nerves converge & axons are rerouted so that a crossing over of visual ...
Plasticity and nativism: Towards a resolution of
... neuron and connection in the to-be-born child’s brain would be placed. This “DNAas-blueprint” idea would fit nicely with nativism, but, alas, it clearly cannot be right. For one thing, there just is not enough information in the human genome to specify exact where each neuron and synapse will go [25 ...
... neuron and connection in the to-be-born child’s brain would be placed. This “DNAas-blueprint” idea would fit nicely with nativism, but, alas, it clearly cannot be right. For one thing, there just is not enough information in the human genome to specify exact where each neuron and synapse will go [25 ...
Plasticity and nativism: Towards a resolution of
... neuron and connection in the to-be-born child’s brain would be placed. This “DNAas-blueprint” idea would fit nicely with nativism, but, alas, it clearly cannot be right. For one thing, there just is not enough information in the human genome to specify exact where each neuron and synapse will go [25 ...
... neuron and connection in the to-be-born child’s brain would be placed. This “DNAas-blueprint” idea would fit nicely with nativism, but, alas, it clearly cannot be right. For one thing, there just is not enough information in the human genome to specify exact where each neuron and synapse will go [25 ...
Nervous tissue Nervous system
... The human nervous system contains more than 10 billion neurons. Although neurons show the greatest variation in size and shape of any group of cells in the body, they can be grouped into three general categories. • Sensory neurons convey impulses from receptors to the CNS. Processes of these neurons ...
... The human nervous system contains more than 10 billion neurons. Although neurons show the greatest variation in size and shape of any group of cells in the body, they can be grouped into three general categories. • Sensory neurons convey impulses from receptors to the CNS. Processes of these neurons ...
Structure of the Inner Ear
... intracellular fluid (high K+, low Na+). • Stria vascularis actively pumps ions against concentration gradients to maintain ion balance in endolymph. ...
... intracellular fluid (high K+, low Na+). • Stria vascularis actively pumps ions against concentration gradients to maintain ion balance in endolymph. ...
Subventricular zone

The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a paired brain structure situated throughout the lateral walls of the lateral ventricles. It is composed of four distinct layers of variable thickness and cell density, as well as cellular composition. Along with the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the SVZ is one of two places where neurogenesis has been found to occur in the adult mammalian brain.