PDF
... over non-fluorescent ectodermal cells. The researchers find that those cells in contact with the ectoderm immediately after the EMT migrate dorsolaterally as a group, but are sometimes overtaken by cells not in contact with the ectoderm. Murray and Saint conclude that mesodermal cells use a combinat ...
... over non-fluorescent ectodermal cells. The researchers find that those cells in contact with the ectoderm immediately after the EMT migrate dorsolaterally as a group, but are sometimes overtaken by cells not in contact with the ectoderm. Murray and Saint conclude that mesodermal cells use a combinat ...
PDF
... over non-fluorescent ectodermal cells. The researchers find that those cells in contact with the ectoderm immediately after the EMT migrate dorsolaterally as a group, but are sometimes overtaken by cells not in contact with the ectoderm. Murray and Saint conclude that mesodermal cells use a combinat ...
... over non-fluorescent ectodermal cells. The researchers find that those cells in contact with the ectoderm immediately after the EMT migrate dorsolaterally as a group, but are sometimes overtaken by cells not in contact with the ectoderm. Murray and Saint conclude that mesodermal cells use a combinat ...
Hair cells
... sour, salty, bitter, & amino acids (umami) Taste receptor cells are modified epithelial cells ...
... sour, salty, bitter, & amino acids (umami) Taste receptor cells are modified epithelial cells ...
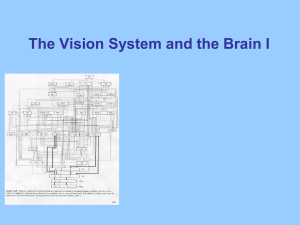
retina, primary visual pathway and primary
... nucleus of the thalamus. The secondary visual cortex (association, extrastriate, or prestriate areas) (V2 Brodmann’s area 18) and tertiary visual cortex (V3 (form) and V5 (motion) Brodmann’s area 19) Visual area V4 (color) is located in the inferior occipitotemporal area The primary visual cortex se ...
... nucleus of the thalamus. The secondary visual cortex (association, extrastriate, or prestriate areas) (V2 Brodmann’s area 18) and tertiary visual cortex (V3 (form) and V5 (motion) Brodmann’s area 19) Visual area V4 (color) is located in the inferior occipitotemporal area The primary visual cortex se ...
Pipecleaner Neuron Guide - spectrUM Discovery Area
... Parts of a neuron Cell body (soma)–where the cell’s nucleus and may other organelles are found. The nucleus is the control center of the cell containing DNA which is the code or recipe to make all our body’s parts. • Axon–axons send information received from the cell body to the next neuron in its ...
... Parts of a neuron Cell body (soma)–where the cell’s nucleus and may other organelles are found. The nucleus is the control center of the cell containing DNA which is the code or recipe to make all our body’s parts. • Axon–axons send information received from the cell body to the next neuron in its ...
doc Chapter 15 Notes
... - most common and best know of the metabolism disorders - a lot of phenylalanine in the blood interferes with the myelinisation of neurons in the CNS and because this myelination take place after birth and so if infants with PKU consume food containing phenylalanine they’ll develop severe mental ret ...
... - most common and best know of the metabolism disorders - a lot of phenylalanine in the blood interferes with the myelinisation of neurons in the CNS and because this myelination take place after birth and so if infants with PKU consume food containing phenylalanine they’ll develop severe mental ret ...
Endocrine_Lecture
... The Primary Portal Plexus (capillary bed) resides in the hypothalamus and is impinged upon by hypothalamic neurons. These neurons release neurohormones into the bloodstream within the capillaries. The portal vasculature carries the neurohormones to the Anterior lobe (pars distalis) of the pituitary ...
... The Primary Portal Plexus (capillary bed) resides in the hypothalamus and is impinged upon by hypothalamic neurons. These neurons release neurohormones into the bloodstream within the capillaries. The portal vasculature carries the neurohormones to the Anterior lobe (pars distalis) of the pituitary ...
Lectures for 5th week: Visual System I
... occurs within brain regions (retina, LGN, V1) occurs between brain regions (V4, IT, MT, PPC) occurs between brain circuits (ventral, dorsal) Visual system also exemplifies concurrent processing ...
... occurs within brain regions (retina, LGN, V1) occurs between brain regions (V4, IT, MT, PPC) occurs between brain circuits (ventral, dorsal) Visual system also exemplifies concurrent processing ...
Focus On Vocabulary Chapter 02
... by the astounding complexity and intricate activity of the brain and nervous system. Most signals are excitatory, somewhat like pushing a neuron’s accelerator. Some are inhibitory, more like pushing its brake. Myers is making a comparison between the effect of a neuron firing and the effect of speed ...
... by the astounding complexity and intricate activity of the brain and nervous system. Most signals are excitatory, somewhat like pushing a neuron’s accelerator. Some are inhibitory, more like pushing its brake. Myers is making a comparison between the effect of a neuron firing and the effect of speed ...
Overview of Tissues
... Have a free surface and a basal surface – Lumen – the hollow space in an organ or tube ...
... Have a free surface and a basal surface – Lumen – the hollow space in an organ or tube ...
Glia Ç more than just brain glue
... and release of neurotransmitters; binding of the released neurotransmitters to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane of another neuron; and the sub sequent depolarization of this second neuron, propagating the signal further. Glia do not fire action potentials, but instead surround and ensheath neu ...
... and release of neurotransmitters; binding of the released neurotransmitters to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane of another neuron; and the sub sequent depolarization of this second neuron, propagating the signal further. Glia do not fire action potentials, but instead surround and ensheath neu ...
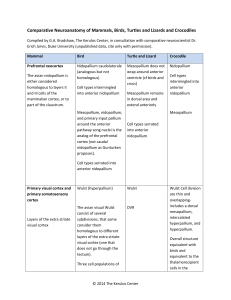
Comparative Neuroanatomy of Mammals, Birds, Turtles and Lizards
... subdivisions, that some consider them homologous to different layers of the extra striate visual cortex (one that does not go through the tectum). ...
... subdivisions, that some consider them homologous to different layers of the extra striate visual cortex (one that does not go through the tectum). ...
APPLICATION FOR MRC STUDENTSHIPS TO COMMENCE 2009
... This studentship will investigate how dopamine neurons are specified during development and how its dysfunction is associated with neurodevelopmental disorders including ADHD and Schizophrenia. The study will focus on the function of a transcription factor in the specification and function of a grou ...
... This studentship will investigate how dopamine neurons are specified during development and how its dysfunction is associated with neurodevelopmental disorders including ADHD and Schizophrenia. The study will focus on the function of a transcription factor in the specification and function of a grou ...
Document
... hyperchromatic tissue is the cortex, and the light stained tissue in the deep part is the medulla. Cortex is composed of all kinds of nerve cells, and can divide into 6 layers. To distinguish the 6 layers is not easy in this section, but you can distinguish the shape of the pyramidal cell, with a ti ...
... hyperchromatic tissue is the cortex, and the light stained tissue in the deep part is the medulla. Cortex is composed of all kinds of nerve cells, and can divide into 6 layers. To distinguish the 6 layers is not easy in this section, but you can distinguish the shape of the pyramidal cell, with a ti ...
Types of Receptors
... fluid surrounding the cells to be detected • Olfactory cells undergo adaptation rapidly for ...
... fluid surrounding the cells to be detected • Olfactory cells undergo adaptation rapidly for ...
BIOL241NSintro12aJUL2012
... Neuroglia • Half the volume of the nervous system • Many types of neuroglia in CNS and PNS ...
... Neuroglia • Half the volume of the nervous system • Many types of neuroglia in CNS and PNS ...
BIOL241NSintro12aJUL2012
... Neuroglia • Half the volume of the nervous system • Many types of neuroglia in CNS and PNS ...
... Neuroglia • Half the volume of the nervous system • Many types of neuroglia in CNS and PNS ...
Understanding Glial Differentiation in Vertebrate Nervous - J
... It has long been believed that astrocytes and oligodendrocytes are derived from a common glial precursor cell (0-2A progenitor), suggested by in vitro culture experiments (see text books, such as Jacobson 1991). Recent studies, however, have revealed that these glial cells differentiate from distinc ...
... It has long been believed that astrocytes and oligodendrocytes are derived from a common glial precursor cell (0-2A progenitor), suggested by in vitro culture experiments (see text books, such as Jacobson 1991). Recent studies, however, have revealed that these glial cells differentiate from distinc ...
Nervous System - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... – Long-lived, amitotic (non-divisible), and have a high metabolic rate ...
... – Long-lived, amitotic (non-divisible), and have a high metabolic rate ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Cranial nerves – 12 pairs of nerves originate from the brain to innervate the head and neck. Most cranial nerves are mixed, but some are sensory. Only the vagus nerve extends to thoracic and abdominal cavities. (Cranial nerves are listed in table 7.1.) Spinal nerves – 31 pairs of mixed nerves are fo ...
... Cranial nerves – 12 pairs of nerves originate from the brain to innervate the head and neck. Most cranial nerves are mixed, but some are sensory. Only the vagus nerve extends to thoracic and abdominal cavities. (Cranial nerves are listed in table 7.1.) Spinal nerves – 31 pairs of mixed nerves are fo ...
Supplementary material 4 – Unified probability of spike
... Taken together, this means that the frequency distribution of spikes from each neuron can be modelled as a bivariate Gaussian with a covariance matrix, the off-diagonal terms of which are zero. Furthermore, the combined frequency distribution in amplitude shape space can be represented by summing al ...
... Taken together, this means that the frequency distribution of spikes from each neuron can be modelled as a bivariate Gaussian with a covariance matrix, the off-diagonal terms of which are zero. Furthermore, the combined frequency distribution in amplitude shape space can be represented by summing al ...
Subventricular zone

The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a paired brain structure situated throughout the lateral walls of the lateral ventricles. It is composed of four distinct layers of variable thickness and cell density, as well as cellular composition. Along with the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the SVZ is one of two places where neurogenesis has been found to occur in the adult mammalian brain.