DNA replication - Understanding Evolution
... Students will understand that 1) molecular mechanisms that preserve the fidelity of the genetic sequence have been favored by natural selection, 2) some entities, such as HIV, lack some of these mechanisms and so have a higher rate of mutation and evolution, and 3) many challenges posed to medical s ...
... Students will understand that 1) molecular mechanisms that preserve the fidelity of the genetic sequence have been favored by natural selection, 2) some entities, such as HIV, lack some of these mechanisms and so have a higher rate of mutation and evolution, and 3) many challenges posed to medical s ...
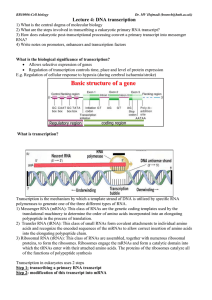
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... 3) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): This class of RNAs are assembled, together with numerous ribosomal proteins, to form the ribosomes. Ribosomes engage the mRNAs and form a catalytic domain into which the tRNAs enter with their attached amino acids. The proteins of the ribosomes catalyze all of the functions ...
... 3) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): This class of RNAs are assembled, together with numerous ribosomal proteins, to form the ribosomes. Ribosomes engage the mRNAs and form a catalytic domain into which the tRNAs enter with their attached amino acids. The proteins of the ribosomes catalyze all of the functions ...
DNA—From Genes to Proteins
... produces carbon dioxide and water. ribosome An organelle in the cytoplasm of all cells and the site of protein synthesis. sugar A molecule that links with a phosphate molecule via a chemical bond to form the backbone of the DNA double helix. template The strand of bases on DNA that serves as the bas ...
... produces carbon dioxide and water. ribosome An organelle in the cytoplasm of all cells and the site of protein synthesis. sugar A molecule that links with a phosphate molecule via a chemical bond to form the backbone of the DNA double helix. template The strand of bases on DNA that serves as the bas ...
amino acid
... to their complementary nucleotides through base pairing. 3. Another enzyme called DNA polymerase bonds these new nucleotides into a chain. 4. When the whole process is complete, there will be 2 copies of the DNA. ...
... to their complementary nucleotides through base pairing. 3. Another enzyme called DNA polymerase bonds these new nucleotides into a chain. 4. When the whole process is complete, there will be 2 copies of the DNA. ...
DNA - BiologyProvidence
... every single amino-acid molecule in the chain AND the order of the amino-acid molecules ...
... every single amino-acid molecule in the chain AND the order of the amino-acid molecules ...
Big Idea #3
... expressed in eukaryotic cells. Some areas of DNA are so tightly condensed around histone proteins that they can not unwind and be expressed (heterochromatin) DNA methylation: methyl groups can be added to nucleotides. These will block RNA polymerase from binding and make the genes inactive. (pla ...
... expressed in eukaryotic cells. Some areas of DNA are so tightly condensed around histone proteins that they can not unwind and be expressed (heterochromatin) DNA methylation: methyl groups can be added to nucleotides. These will block RNA polymerase from binding and make the genes inactive. (pla ...
Final Exam - brownscience
... 34. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, individuals who survive are the ones best adapted for their environment. The survival is due to 35. An adaptation is an inherited characteristics that can be 36. The hypothesis that species change over time by natural selection was proposed by 3 ...
... 34. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, individuals who survive are the ones best adapted for their environment. The survival is due to 35. An adaptation is an inherited characteristics that can be 36. The hypothesis that species change over time by natural selection was proposed by 3 ...
Strawberry DNA PowerPoint
... Add lysis mixture – detergent containing lauryl sulfate and salt, NaCl Add papain mixture to denature proteins( DNAses) Mix by rocking and rolling ...
... Add lysis mixture – detergent containing lauryl sulfate and salt, NaCl Add papain mixture to denature proteins( DNAses) Mix by rocking and rolling ...
2012/2013 AP Biology Midterm Review Sheet
... Explain the steps in semiconservative DNA replication/ (know the enzymes!) template DNA strand, DNA polymerase, leading strand, lagging strand, helicase, replication fork, single stranded binding proteins, DNA ligase, Okazaki fragments, RNA primase, RNA primer, new DNA made 5’ 3, new nucleotides a ...
... Explain the steps in semiconservative DNA replication/ (know the enzymes!) template DNA strand, DNA polymerase, leading strand, lagging strand, helicase, replication fork, single stranded binding proteins, DNA ligase, Okazaki fragments, RNA primase, RNA primer, new DNA made 5’ 3, new nucleotides a ...
File
... Check your Understanding 1. True or False: DNA replication and RNA synthesis both use the same polymerase to copy the DNA 2. True or False: Transcription takes places in the nucleus, while translation occurs in the cytoplasm 3. True or False: Transfer RNA (tRNA) carries the copied DNA out of the nu ...
... Check your Understanding 1. True or False: DNA replication and RNA synthesis both use the same polymerase to copy the DNA 2. True or False: Transcription takes places in the nucleus, while translation occurs in the cytoplasm 3. True or False: Transfer RNA (tRNA) carries the copied DNA out of the nu ...
General
... biology is to “decipher” information contained in biological sequences Since the nucleotide sequence of a genome contains all information necessary to produce a functional organism, we should in theory be able to duplicate this decoding using computers ...
... biology is to “decipher” information contained in biological sequences Since the nucleotide sequence of a genome contains all information necessary to produce a functional organism, we should in theory be able to duplicate this decoding using computers ...
R N A & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... granular structures where protein synthesis takes place. Messenger RNA (mRNA) ~ “records" information from DNA in the cells nucleus and carry it to the ribosomes. They serve as messengers to the cell. Transfer RNA (tRNA)~ the function of transfer RNA is to deliver amino acids one by one to protein c ...
... granular structures where protein synthesis takes place. Messenger RNA (mRNA) ~ “records" information from DNA in the cells nucleus and carry it to the ribosomes. They serve as messengers to the cell. Transfer RNA (tRNA)~ the function of transfer RNA is to deliver amino acids one by one to protein c ...
IMPLICATIONS OF ANTHROPGENY FOR MEDICINE AND
... Homo erectus: An extinct hominin species with fossil evidence Population: A defined group of similar individuals among whom from 1.9 million (possibly earlier) to 70 thousand years ago and interbreeding occurs. found from Africa to Indonesia. May have been the first hominin Selection: Allele frequen ...
... Homo erectus: An extinct hominin species with fossil evidence Population: A defined group of similar individuals among whom from 1.9 million (possibly earlier) to 70 thousand years ago and interbreeding occurs. found from Africa to Indonesia. May have been the first hominin Selection: Allele frequen ...
Science - Mansfield ISD
... (College and Career Readiness Standards) 6B Recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms. (EOC Supporting Standard) ...
... (College and Career Readiness Standards) 6B Recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms. (EOC Supporting Standard) ...
Eukaryotes - Alice Pevyhouse
... • RNA can duplicate itself • Catalyze reactions that produce subunits of RNA (more building blocks!) • Catalyze chains of amino acids which can be used to produce proteins! ...
... • RNA can duplicate itself • Catalyze reactions that produce subunits of RNA (more building blocks!) • Catalyze chains of amino acids which can be used to produce proteins! ...
Chance and Necessity in the Selection of Nucleic Acid Catalysts
... substrate onto their own 5′-ends, with the incoming oligonucleotide displacing the pyrophosphate group from the 5′-triphosphate on the pool RNA to form a new phosphodiester linkage; the attached oligonucleotide acts to “tag” the catalytically active RNAs. Following the reaction, molecules that had p ...
... substrate onto their own 5′-ends, with the incoming oligonucleotide displacing the pyrophosphate group from the 5′-triphosphate on the pool RNA to form a new phosphodiester linkage; the attached oligonucleotide acts to “tag” the catalytically active RNAs. Following the reaction, molecules that had p ...
Nucleic Acid Chemistry
... • Leading strand – 3’ end of template – As opens up, DNA polymerase binds – Makes new DNA 5’ - 3’ • Same direction as opening of helix ...
... • Leading strand – 3’ end of template – As opens up, DNA polymerase binds – Makes new DNA 5’ - 3’ • Same direction as opening of helix ...
Chapter 2 DNA to end Extended Response
... uses information on the mRNA; mRNA carries the genetic information of DNA; mRNA binds to ribosome; mRNA contains series of codons/base triplets; tRNA binds with an amino acid and carries it to the ribosome; tRNA has the anticodon that is complementary to the codon on the mRNA; two tRNAs bind to a ri ...
... uses information on the mRNA; mRNA carries the genetic information of DNA; mRNA binds to ribosome; mRNA contains series of codons/base triplets; tRNA binds with an amino acid and carries it to the ribosome; tRNA has the anticodon that is complementary to the codon on the mRNA; two tRNAs bind to a ri ...
Biology 1 Notes Chapter 12 - DNA and RNA Prentice Hall pages
... 1) Transcription (occurs in the ...
... 1) Transcription (occurs in the ...
REVIEW for EXAM4-May 12th
... Furthermore, there is some control over the initiation, elongation, and termination of the polypeptide chain on the ribosome itself. IV. Post translational control are the final modifications to proteins that determine their folding. As proteins are folded, additional functional groups can be added ...
... Furthermore, there is some control over the initiation, elongation, and termination of the polypeptide chain on the ribosome itself. IV. Post translational control are the final modifications to proteins that determine their folding. As proteins are folded, additional functional groups can be added ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.