Genetic Control of Cell Function and Inheritance
... • Long, double-stranded helical structure composed of nucleotides, which consist of phosphoric acid, deoxyribose, and one of four nitrogenous bases (T,C,A or G) • Spiral staircase with paired bases representing the steps • Nitrogenous bases carry the genetic information ...
... • Long, double-stranded helical structure composed of nucleotides, which consist of phosphoric acid, deoxyribose, and one of four nitrogenous bases (T,C,A or G) • Spiral staircase with paired bases representing the steps • Nitrogenous bases carry the genetic information ...
Chromosomal Structure HWK
... 1. (a) A histone is a positively charged protein that DNA is bound to in a chromosome; a nucleosome is a complex of eight histones enveloped by DNA (b) A telomere is a long sequence of repetitive, noncoding DNA that is found at the end of chromosomes, while a centromere is a constricted region of a ...
... 1. (a) A histone is a positively charged protein that DNA is bound to in a chromosome; a nucleosome is a complex of eight histones enveloped by DNA (b) A telomere is a long sequence of repetitive, noncoding DNA that is found at the end of chromosomes, while a centromere is a constricted region of a ...
Bio4751signaltransductionTechniques
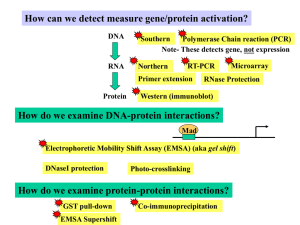
... 1. Southern- Detect DNA only 2. Northern- Detect RNA 3. Microarray- Detect RNA of 100s of expressed genes 4. RT-PCR ( Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction- to detect RNA) 5. Western (Immunoblot)- Detect protein 6. Immunostaining- Detect proteins in situ 7. EMSA- protein-DNA interactions 8 ...
... 1. Southern- Detect DNA only 2. Northern- Detect RNA 3. Microarray- Detect RNA of 100s of expressed genes 4. RT-PCR ( Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction- to detect RNA) 5. Western (Immunoblot)- Detect protein 6. Immunostaining- Detect proteins in situ 7. EMSA- protein-DNA interactions 8 ...
4 1. agribiotechnology 2. genetically modified organisms
... 33. The biochemical property of lectins that is the basis for most of their biological effects is their ability to bind to: (A) amphipathic molecules. (B) hydrophobic molecules. (C) specific lipids. (D) specific oligosaccharides. (E) specific peptides. 34. Inhibitors against this viral enzyme have ...
... 33. The biochemical property of lectins that is the basis for most of their biological effects is their ability to bind to: (A) amphipathic molecules. (B) hydrophobic molecules. (C) specific lipids. (D) specific oligosaccharides. (E) specific peptides. 34. Inhibitors against this viral enzyme have ...
DNA and Protein Synthesisx
... They all have the same basic structure: a coiled chain of nucleotides with a triplet of exposed nitrogen bases at one end and an attachment site for an amino acid at the other end. The triplet of exposed nitrogen bases is called an anticodon. When the anticodon binds with a messenger RNA codon insid ...
... They all have the same basic structure: a coiled chain of nucleotides with a triplet of exposed nitrogen bases at one end and an attachment site for an amino acid at the other end. The triplet of exposed nitrogen bases is called an anticodon. When the anticodon binds with a messenger RNA codon insid ...
Cornell Notes Template
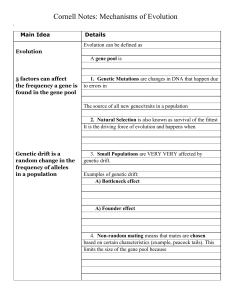
... The source of all new genes/traits in a population 2. Natural Selection is also known as survival of the fittest It is the driving force of evolution and happens when ...
... The source of all new genes/traits in a population 2. Natural Selection is also known as survival of the fittest It is the driving force of evolution and happens when ...
Transcription Regulation (Prof. Fridoon)
... Many genes also have enhancer (1000 nucleotide away) where specific activators only made by certain cells can bind. ...
... Many genes also have enhancer (1000 nucleotide away) where specific activators only made by certain cells can bind. ...
DNA Mutations - U
... Radiation Cells have the ability to repair damages, but as an organism ages, DNA repair does not work as effectively; thus changes occur in the DNA ...
... Radiation Cells have the ability to repair damages, but as an organism ages, DNA repair does not work as effectively; thus changes occur in the DNA ...
Transcription to Translation Scavenger Hunt
... 2. (2-5 min) Transcription: Instruct students that they will only be able to take their mRNA strip, their nucleotides and their strip of paper into and out of the nucleus (hallway outside of class). Instruct students NOT to write directly onto the mRNA and protein strips (otherwise you will have to ...
... 2. (2-5 min) Transcription: Instruct students that they will only be able to take their mRNA strip, their nucleotides and their strip of paper into and out of the nucleus (hallway outside of class). Instruct students NOT to write directly onto the mRNA and protein strips (otherwise you will have to ...
Unit 2 Terms
... the presence of certain chemicals or defective fetal cells in the amniotic fluid, obtained by aspiration from a needle inserted into the uterus To be capable of combining with complementary nucleic acid by a process of heating and cooling Indiscriminate examination of members of a population to dete ...
... the presence of certain chemicals or defective fetal cells in the amniotic fluid, obtained by aspiration from a needle inserted into the uterus To be capable of combining with complementary nucleic acid by a process of heating and cooling Indiscriminate examination of members of a population to dete ...
DNA analysis - Madeira City Schools
... A. Most common uses are: 1. analyze a person’s genes (looking for diseases) 2. compare the sequence of nitrogen bases among individuals (paternity and crime scenes) B. Use restriction enzymes 1. A restriction enzyme is an enzyme that cuts DNA at specific “recognition sites” 2. In nature restriction ...
... A. Most common uses are: 1. analyze a person’s genes (looking for diseases) 2. compare the sequence of nitrogen bases among individuals (paternity and crime scenes) B. Use restriction enzymes 1. A restriction enzyme is an enzyme that cuts DNA at specific “recognition sites” 2. In nature restriction ...
Some words to think about
... • To replace dead or damaged cells • To grow and develop • To form a new life- fertilization birth ...
... • To replace dead or damaged cells • To grow and develop • To form a new life- fertilization birth ...
university of oslo
... Example: the use of glucose and lactose by E. coli. Glucose indirectly prevents binding of the catabolite activator protein (CAP) to the DNA upstream of the lac operon by causing dephosphorylation of protein IIAGlc. Dephosphorylated IIAGlc inhibits adenylate cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the fo ...
... Example: the use of glucose and lactose by E. coli. Glucose indirectly prevents binding of the catabolite activator protein (CAP) to the DNA upstream of the lac operon by causing dephosphorylation of protein IIAGlc. Dephosphorylated IIAGlc inhibits adenylate cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the fo ...
Exam V2002 - English
... Example: the use of glucose and lactose by E. coli. Glucose indirectly prevents binding of the catabolite activator protein (CAP) to the DNA upstream of the lac operon by causing dephosphorylation of protein IIAGlc. Dephosphorylated IIAGlc inhibits adenylate cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the fo ...
... Example: the use of glucose and lactose by E. coli. Glucose indirectly prevents binding of the catabolite activator protein (CAP) to the DNA upstream of the lac operon by causing dephosphorylation of protein IIAGlc. Dephosphorylated IIAGlc inhibits adenylate cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the fo ...
國立彰化師範大學100 學年度碩士班招生考試試題
... (A) the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter. (B) the DNA introns are removed from the template. (C) the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA. (D) several transcription factors have bound to the promoter. 25. Which of the following is not true of mRNA processing after tran ...
... (A) the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter. (B) the DNA introns are removed from the template. (C) the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA. (D) several transcription factors have bound to the promoter. 25. Which of the following is not true of mRNA processing after tran ...
Concept 18.3. How get genetic variation in prokaryotes: • E. coli is
... On either side are pair of noncoding DNA ( 20-40 bases) = inverted repeats. Enzyme molecules recognize these as boundaries of insertion sequences and bind inverted repeats and to target site and catalyze cutting and resealing. If sequence goes into coding region of a gene or region required for regu ...
... On either side are pair of noncoding DNA ( 20-40 bases) = inverted repeats. Enzyme molecules recognize these as boundaries of insertion sequences and bind inverted repeats and to target site and catalyze cutting and resealing. If sequence goes into coding region of a gene or region required for regu ...
14.3_222-225
... Manipulating DNA Since the 1970s, techniques have been developed that allow scientists to cut, separate, and replicate DNA base-by-base. Using these tools, scientists can read the base sequences in DNA from any cell. Restriction enzymes cut DNA into smaller pieces, called restriction fragments, whic ...
... Manipulating DNA Since the 1970s, techniques have been developed that allow scientists to cut, separate, and replicate DNA base-by-base. Using these tools, scientists can read the base sequences in DNA from any cell. Restriction enzymes cut DNA into smaller pieces, called restriction fragments, whic ...
Simulating Protein Synthesis
... List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
... List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
BiotechnologyPractice - juan-roldan
... A. Genetically altered crops require less pesticide. B. Genetically altered crops produce less carbon dioxide. C. Genetically altered crops are more delicious. D. Genetically altered crops are unable to reproduce. 3. The first commercial application of genetic engineering was the use of bacteria to ...
... A. Genetically altered crops require less pesticide. B. Genetically altered crops produce less carbon dioxide. C. Genetically altered crops are more delicious. D. Genetically altered crops are unable to reproduce. 3. The first commercial application of genetic engineering was the use of bacteria to ...
Genetics and Heredity
... •Mendel probably chose to work with peas because they are available in many varieties. ...
... •Mendel probably chose to work with peas because they are available in many varieties. ...
Cloning of genes from genomic DNA Part 1 and 2: DNA Isolation
... How does one isolate genomic DNA? There are several methods but almost all of them require separation of tissue into individual cells (or at least small clumps of cells) followed by lysis of the cells, often through addition of detergent and proteases. After lysis, protocols tend to vary but the ide ...
... How does one isolate genomic DNA? There are several methods but almost all of them require separation of tissue into individual cells (or at least small clumps of cells) followed by lysis of the cells, often through addition of detergent and proteases. After lysis, protocols tend to vary but the ide ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.