Supplementary Information (doc 63K)
... defective developmental process in the ercc-1 mixed stage populations, which had a great influence on the transcriptomic data. Rather, in UV irradiated cultured mammalian cells similar changes in gene expression occur as in naturally aged tissues, which is reverted when UV-photolesions are removed(4 ...
... defective developmental process in the ercc-1 mixed stage populations, which had a great influence on the transcriptomic data. Rather, in UV irradiated cultured mammalian cells similar changes in gene expression occur as in naturally aged tissues, which is reverted when UV-photolesions are removed(4 ...
Lecture 5 The chemical nature of the Gene
... Arguments in favour of genes being made of DNA • All cells of a given species contain a constant amount of DNA but the types and amounts of proteins differ in different cells • The amount of DNA doubles in every cell just before it divides and an exactly equal amount is distributed to the two dau ...
... Arguments in favour of genes being made of DNA • All cells of a given species contain a constant amount of DNA but the types and amounts of proteins differ in different cells • The amount of DNA doubles in every cell just before it divides and an exactly equal amount is distributed to the two dau ...
Chalmers_Bioinformatics
... Next Generation Sequencing • Next generation sequencing refers to methods newer than the Sanger approach • A variety of techniques developed by different companies • DNA is generally immobilized on a solid support • Very large numbers of small reads • Multiple reads of a each section of genomic DNA ...
... Next Generation Sequencing • Next generation sequencing refers to methods newer than the Sanger approach • A variety of techniques developed by different companies • DNA is generally immobilized on a solid support • Very large numbers of small reads • Multiple reads of a each section of genomic DNA ...
DNA Structure and history10
... • DNA composition: “Chargaff’s rules” – varies from species to species – all 4 bases not in equal quantity – bases present in characteristic ratio • humans: A = 30.9% T = 29.4% G = 19.9% C = 19.8% ...
... • DNA composition: “Chargaff’s rules” – varies from species to species – all 4 bases not in equal quantity – bases present in characteristic ratio • humans: A = 30.9% T = 29.4% G = 19.9% C = 19.8% ...
Review questions to go with the powerpoint
... 56.DNA put together from 2 different species is called _________________ DNA. 57.A ________ is an organism made from one cell of another organism and is a genetically ______________ copy. 58.What technique can separate DNA molecules of different length based on the size of the molecules? 59.A ______ ...
... 56.DNA put together from 2 different species is called _________________ DNA. 57.A ________ is an organism made from one cell of another organism and is a genetically ______________ copy. 58.What technique can separate DNA molecules of different length based on the size of the molecules? 59.A ______ ...
Biotechnology Labs Makeup Assignment
... 2) Write a one page paper (one page per lab you’re making up) describing the following: DNA Extraction Only: -describe the technique used to purify and extract DNA from cells. What reagents (i.e. chemicals) are needed and what is the function of each reagent? (1 page) Dye/Indicator Lab Only: -how do ...
... 2) Write a one page paper (one page per lab you’re making up) describing the following: DNA Extraction Only: -describe the technique used to purify and extract DNA from cells. What reagents (i.e. chemicals) are needed and what is the function of each reagent? (1 page) Dye/Indicator Lab Only: -how do ...
Lab 5 minipreps
... There are a number of techniques for isolating plasmid DNA. Most labs have adopted one of the spin column kits on the market. These are fast and reliable. For DNA purification, we will use anion-exchange resin/ spin column technique available through Qiagen (Santa Clarita, CA). It is based on the al ...
... There are a number of techniques for isolating plasmid DNA. Most labs have adopted one of the spin column kits on the market. These are fast and reliable. For DNA purification, we will use anion-exchange resin/ spin column technique available through Qiagen (Santa Clarita, CA). It is based on the al ...
Molecular Genetics
... The portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins are called exons. parts of the mRNA that are kept and expressed ...
... The portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins are called exons. parts of the mRNA that are kept and expressed ...
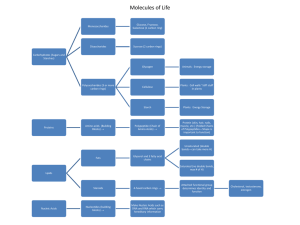
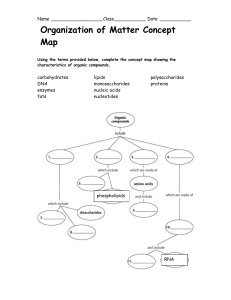
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... 8-18. Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. ...
... 8-18. Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. ...
deciphering macromolecules
... Lipids: Look for a 1:2 ratio of C:H and only very small amounts of O. Most will contain no S. Phospholipids can contain P and N (as part of the choline group; see Figure 5.13). Proteins Look for amino and carboxyl groups. Some contain S. All proteins can be identified by the presence of peptide bond ...
... Lipids: Look for a 1:2 ratio of C:H and only very small amounts of O. Most will contain no S. Phospholipids can contain P and N (as part of the choline group; see Figure 5.13). Proteins Look for amino and carboxyl groups. Some contain S. All proteins can be identified by the presence of peptide bond ...
The Biological Basis of Life
... Protein Synthesis • The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide is determined by the sequence of nitrogenous bases in the DNA unit (or gene) coding for that polypeptide. • Protein synthesis is a two-step process: – Transcription: copying the DNA to RNA – Translation: using the RNA to assemble the p ...
... Protein Synthesis • The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide is determined by the sequence of nitrogenous bases in the DNA unit (or gene) coding for that polypeptide. • Protein synthesis is a two-step process: – Transcription: copying the DNA to RNA – Translation: using the RNA to assemble the p ...
Mutated - Olympic High School
... is variation within that trait as a result of small sequence differences (DNA Amino Acids) ...
... is variation within that trait as a result of small sequence differences (DNA Amino Acids) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... Each mRNA may be translated thousands of times. tRNA molecules can be re-used after recharging, and ribosomal subunits are recycled for use translating another mRNA. ...
... Each mRNA may be translated thousands of times. tRNA molecules can be re-used after recharging, and ribosomal subunits are recycled for use translating another mRNA. ...
Topic 4.1: Chromosomes, genes, alleles, and mutations
... A mutation is a random, rare change in genetic materials › One type involves a change of the sequence ...
... A mutation is a random, rare change in genetic materials › One type involves a change of the sequence ...
Genetically Modified Food
... vector into a host cell (transformation) and Cloning the DNA Step 1) Adding the plasmid vector into a flask containing culture of a host cell Step 2) Generating temporary pores on the surface of the host cell Step 3) Allowing the plasmid vector to enter the host cell Step 4) Placing the host ...
... vector into a host cell (transformation) and Cloning the DNA Step 1) Adding the plasmid vector into a flask containing culture of a host cell Step 2) Generating temporary pores on the surface of the host cell Step 3) Allowing the plasmid vector to enter the host cell Step 4) Placing the host ...
Exam 3
... 2. Spontaneous tautomerization and addition of base analogues both cause mutations in the DNA by a common mechanism. BRIEFLY explain how these events cause mutations to occur? Spontaneous tautomerization is a transient shift in a proton on a nitrogenous base from one atom to another. This shift alte ...
... 2. Spontaneous tautomerization and addition of base analogues both cause mutations in the DNA by a common mechanism. BRIEFLY explain how these events cause mutations to occur? Spontaneous tautomerization is a transient shift in a proton on a nitrogenous base from one atom to another. This shift alte ...
CHAPTER 14
... such as homogenization or sonication. This would release the RNAs and other cellular macromolecules. The large cellular structures (organelles, membranes, etc.) could be removed from the cell extract by a centrifugation step. The large cellular structures would be found in the pellet, while soluble ...
... such as homogenization or sonication. This would release the RNAs and other cellular macromolecules. The large cellular structures (organelles, membranes, etc.) could be removed from the cell extract by a centrifugation step. The large cellular structures would be found in the pellet, while soluble ...
3 " ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ - 1 - G 2 ¢ 2 2 – 1. Biological catalysts are (A
... 41. A cell in an active metabolic state has (A) a high (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD+) ratio (B) a high (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD+) ratio (C) a low (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD+) ratio (D) a low (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD+) ratio 42. Which of the following is a source of NADPH? (A) the pen ...
... 41. A cell in an active metabolic state has (A) a high (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD+) ratio (B) a high (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD+) ratio (C) a low (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD+) ratio (D) a low (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD+) ratio 42. Which of the following is a source of NADPH? (A) the pen ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.