if on the Internet, Press on your browser to
... with T in what is called Watson-Crick base-pairing. A compound that binds with a stretch of doublehelical DNA having a characteristic base sequence would therefore be one that acts on any gene containing that particular sequence of bases on one of its strands. The task of recognition is relatively e ...
... with T in what is called Watson-Crick base-pairing. A compound that binds with a stretch of doublehelical DNA having a characteristic base sequence would therefore be one that acts on any gene containing that particular sequence of bases on one of its strands. The task of recognition is relatively e ...
midterm 2 asnwer scheme
... Three-dimensional structure of a single protein molecules The α-helices and β-pleated sheets are folded into compact globule. Protein folding occurs as consequence of interactions between the side chains in their primary structure Question 2 a) ...
... Three-dimensional structure of a single protein molecules The α-helices and β-pleated sheets are folded into compact globule. Protein folding occurs as consequence of interactions between the side chains in their primary structure Question 2 a) ...
DNA replication limits…
... instance, in the lower half of Figure 2, the original strand has a C-G pair; then, during replication, cytosine (C) is incorrectly matched to adenine (A) because of wobble. In this example, wobble occurs because A has an extra hydrogen atom. In the next round of cell division, the double strand with ...
... instance, in the lower half of Figure 2, the original strand has a C-G pair; then, during replication, cytosine (C) is incorrectly matched to adenine (A) because of wobble. In this example, wobble occurs because A has an extra hydrogen atom. In the next round of cell division, the double strand with ...
Name Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological
... 3. Anabolic enzymes catalyze reactions called dehydration synthesis; catabolic enzymes catalyze reactions called hydrolysis. Compare the outcomes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis, with an example for each. 4. How is it possible to construct millions of different macromolecules from only a few ...
... 3. Anabolic enzymes catalyze reactions called dehydration synthesis; catabolic enzymes catalyze reactions called hydrolysis. Compare the outcomes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis, with an example for each. 4. How is it possible to construct millions of different macromolecules from only a few ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... BAC is a DNA construct, based on a fertility plasmid (or F-plasmid), used for transforming and cloning in bacteria, usually E. coli. F-plasmids play a crucial role because they contain partition genes that promote the even distribution of plasmids after bacterial cell division. BAC's usual insert si ...
... BAC is a DNA construct, based on a fertility plasmid (or F-plasmid), used for transforming and cloning in bacteria, usually E. coli. F-plasmids play a crucial role because they contain partition genes that promote the even distribution of plasmids after bacterial cell division. BAC's usual insert si ...
genetic concepts
... genetic information one gene of male and one of female origin give rise to a particular feature ...
... genetic information one gene of male and one of female origin give rise to a particular feature ...
CHAPTER 13
... to disease & deformities Golden retrievers - epilepsy Dalmations - hereditary deafness ...
... to disease & deformities Golden retrievers - epilepsy Dalmations - hereditary deafness ...
Cell Building Blocks
... The term is more-specifically used to refer to fatty-acids and their derivatives (including tn-, di-, and mono-glyccrides and phospholipids) as well as other fatsoluble sterol-containing metabolites such as cholesterol. Lipids serve many functions in living organisms including energy storage, serve ...
... The term is more-specifically used to refer to fatty-acids and their derivatives (including tn-, di-, and mono-glyccrides and phospholipids) as well as other fatsoluble sterol-containing metabolites such as cholesterol. Lipids serve many functions in living organisms including energy storage, serve ...
PowerPoint
... with restriction enzymes. Electrical current pulls DNA fragments through a gel. Smaller fragments move faster and travel farther than larger fragments. Fragments of different sizes appear as bands on the gel ...
... with restriction enzymes. Electrical current pulls DNA fragments through a gel. Smaller fragments move faster and travel farther than larger fragments. Fragments of different sizes appear as bands on the gel ...
Document
... The information in very similar (homologous) DNA molecules can be exchanged by homologous recombination systems. Non-homologous recombination systems also exist. Recombination takes place in all organisms. ...
... The information in very similar (homologous) DNA molecules can be exchanged by homologous recombination systems. Non-homologous recombination systems also exist. Recombination takes place in all organisms. ...
Answered copy of exam 3
... IX. In cattle C_ animals are normal and cc develop cataracts. A DNA based polymorphism detected by PCR is just 4 map units from the cataracts gene. It’s alleles are designated A35 or A50 for the size of the amplified product. Suppose a bull has the genotype ...
... IX. In cattle C_ animals are normal and cc develop cataracts. A DNA based polymorphism detected by PCR is just 4 map units from the cataracts gene. It’s alleles are designated A35 or A50 for the size of the amplified product. Suppose a bull has the genotype ...
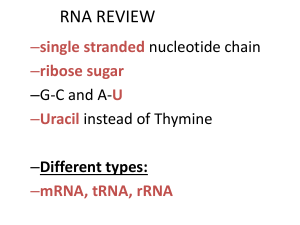
RNA and protein synthesis
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process where DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. Involves tRNA and rRNA DNA ...
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process where DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. Involves tRNA and rRNA DNA ...
Protein Synthesis - Overview
... tRNA delivers amino acids to the polypeptide building site (ribosome) tRNA is a small single stranded nucleic acid, resembles a cloverleaf one arm: anticodon (sequence of three bases complementary to mRNA) 3’ end has acceptor site for a particular amino acid • this recognition by tRNA of mRNA is fac ...
... tRNA delivers amino acids to the polypeptide building site (ribosome) tRNA is a small single stranded nucleic acid, resembles a cloverleaf one arm: anticodon (sequence of three bases complementary to mRNA) 3’ end has acceptor site for a particular amino acid • this recognition by tRNA of mRNA is fac ...
Prokaryotes, Viruses, and Protistans
... • May contain chloroplasts • May divide by mitosis and meiosis ...
... • May contain chloroplasts • May divide by mitosis and meiosis ...
Plant disease - Topic exploration pack
... 2. Liquidise the plant sample. 3. Add the plant sample to a plastic tube or ‘microtiter’ plate (96 well plate). 4. Leave for 5 minutes for all the proteins in the plant sample to bind to the plastic (including the disease antigen if present). 5. Wash the wells with a buffered salt solution to wash o ...
... 2. Liquidise the plant sample. 3. Add the plant sample to a plastic tube or ‘microtiter’ plate (96 well plate). 4. Leave for 5 minutes for all the proteins in the plant sample to bind to the plastic (including the disease antigen if present). 5. Wash the wells with a buffered salt solution to wash o ...
File
... Remember- ** There are two strands to DNA- The strand that is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction is called the leading strand and is described below: First the enzyme, helicase unwinds the two strands of DNA. Once the strands are separated, a replication fork is established. As the helicase unwin ...
... Remember- ** There are two strands to DNA- The strand that is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction is called the leading strand and is described below: First the enzyme, helicase unwinds the two strands of DNA. Once the strands are separated, a replication fork is established. As the helicase unwin ...
File
... monomers called? What are the parts of the monomer? How do they connect to make a polymer? What are they two types of polymers? The GATC code provides instructions for cell structure and function. ...
... monomers called? What are the parts of the monomer? How do they connect to make a polymer? What are they two types of polymers? The GATC code provides instructions for cell structure and function. ...
SI Practice exam 2
... 10. How does compartmentalization into organelles help eukaryotes solve a problem associated with the large size of eukaryotic cells? a. Compartmentalization reduces diffusion distance and concentrates molecules needed for specific reactions. ...
... 10. How does compartmentalization into organelles help eukaryotes solve a problem associated with the large size of eukaryotic cells? a. Compartmentalization reduces diffusion distance and concentrates molecules needed for specific reactions. ...
Document
... (translocates) 3 bases (a new codon: AUG) along the mRNA in the 5' ---> 3' direction. • Termination: tRNA recognizes release factors of nonsense codon. Newly completed polypeptide is released ...
... (translocates) 3 bases (a new codon: AUG) along the mRNA in the 5' ---> 3' direction. • Termination: tRNA recognizes release factors of nonsense codon. Newly completed polypeptide is released ...
CHAPTER 10
... releases both the DNA & the newly formed RNA. b. The newly formed RNA can be any type of RNA, free to perform it’s job within the cell. ...
... releases both the DNA & the newly formed RNA. b. The newly formed RNA can be any type of RNA, free to perform it’s job within the cell. ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.