Chapter 14: Human Heredity Thomas Hunt Morgan: studied
... Sex-linked Trait: a trait carried on the X sex chromosome. Because males only get one X, any X chromosome linked gene a male inherits is expressed. If female has only one X with trait, she is a carrier. Females usually get carrier status from father’s X. Ex: color-blindness – normal color vision is ...
... Sex-linked Trait: a trait carried on the X sex chromosome. Because males only get one X, any X chromosome linked gene a male inherits is expressed. If female has only one X with trait, she is a carrier. Females usually get carrier status from father’s X. Ex: color-blindness – normal color vision is ...
Comp 5a Packet
... 2. Proteins are made of 20 different ________________. 3. Long chains of amino acids make up _________________. 4. Fred Griffith worked with what type of bacteria? 5. What did he find to be true after his experiments with the S and R strains of bacteria? 6. This process of picking up DNA from the en ...
... 2. Proteins are made of 20 different ________________. 3. Long chains of amino acids make up _________________. 4. Fred Griffith worked with what type of bacteria? 5. What did he find to be true after his experiments with the S and R strains of bacteria? 6. This process of picking up DNA from the en ...
Chapter 13
... MicroRNAs regulate gene expression by base pairing with complementary sequences in target mRNAs. ...
... MicroRNAs regulate gene expression by base pairing with complementary sequences in target mRNAs. ...
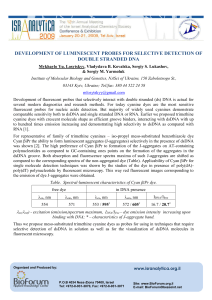
Development of luminescent probes for selective detection of double
... several modern diagnostics and research methods. For today cyanine dyes are the most sensitive fluorescent probes for nucleic acids detection. But majority of widely used cyanines demonstrate comparable sensitivity both to dsDNA and single stranded DNA or RNA. Earlier we proposed trimethine cyanine ...
... several modern diagnostics and research methods. For today cyanine dyes are the most sensitive fluorescent probes for nucleic acids detection. But majority of widely used cyanines demonstrate comparable sensitivity both to dsDNA and single stranded DNA or RNA. Earlier we proposed trimethine cyanine ...
During the last years we have observed a rapid development of
... diagnostic services. An increasing number of laboratories replace their “in-house” developed techniques by the commercial diagnostic assays, but they often modify manufacturer's instructions. Therefore, it is necessary to validate and verify all methods and techniques before their implementation int ...
... diagnostic services. An increasing number of laboratories replace their “in-house” developed techniques by the commercial diagnostic assays, but they often modify manufacturer's instructions. Therefore, it is necessary to validate and verify all methods and techniques before their implementation int ...
chapter 12 - TeacherWeb
... b. is the enzyme that creates hydrogen bonds between nucleotides on the DNA template strand and their complementary RNA nucleotides. c. is the enzyme that transcribes exons, but does not transcribe introns. d. is a ribozyme composed of snRNPs. e. begins transcription at a promoter sequence and moves ...
... b. is the enzyme that creates hydrogen bonds between nucleotides on the DNA template strand and their complementary RNA nucleotides. c. is the enzyme that transcribes exons, but does not transcribe introns. d. is a ribozyme composed of snRNPs. e. begins transcription at a promoter sequence and moves ...
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE
... one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. The gene-enzyme relationship has since been revised to the Example: In hemoglobin, each polypeptide chain is specified by a separate gene. Other genes code for RNA are not translated to polypeptides; some genes are involved in controlling other genes. THE CENT ...
... one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. The gene-enzyme relationship has since been revised to the Example: In hemoglobin, each polypeptide chain is specified by a separate gene. Other genes code for RNA are not translated to polypeptides; some genes are involved in controlling other genes. THE CENT ...
Biotechnology Notes
... • Recombinant DNA DNA that has been genetically modified by connecting DNA fragments from multiple sources • Host organism you are obtaining the gene from • Vector organism such as a bacteria, you are going to use to put the recombinant DNA into the organism you are trying to change • Plasmid DN ...
... • Recombinant DNA DNA that has been genetically modified by connecting DNA fragments from multiple sources • Host organism you are obtaining the gene from • Vector organism such as a bacteria, you are going to use to put the recombinant DNA into the organism you are trying to change • Plasmid DN ...
Ultimate AP BIOLOGY REVIE
... caused by interactions among the various R groups of the amino acids involved. › Quaternary structure: The arrangement of separate polypeptide “subunits” into a single protein ...
... caused by interactions among the various R groups of the amino acids involved. › Quaternary structure: The arrangement of separate polypeptide “subunits” into a single protein ...
3 macromolecules no pics pdf
... • Where the DNA strand is unzipped is known as the replication fork – From this fork, each of the original strands acts as a template for replication • The leading strand allows the new strand synthesized complementary to it, to be synthesized 5' to 3' in the same direction as the movement of the re ...
... • Where the DNA strand is unzipped is known as the replication fork – From this fork, each of the original strands acts as a template for replication • The leading strand allows the new strand synthesized complementary to it, to be synthesized 5' to 3' in the same direction as the movement of the re ...
Main Notes
... – ex. Lactase catalyzes (speed up) the breakdown of lactose into glucose and galactose – ex. Catalase speeds up the breakdown of hydrogen ...
... – ex. Lactase catalyzes (speed up) the breakdown of lactose into glucose and galactose – ex. Catalase speeds up the breakdown of hydrogen ...
Genetics Test 2
... 29) The Clydesdale is a large breed of horse that was used for specific farming purposes, such as plowing and pulling wagons. The biggest and most muscular male horses were crossed with the biggest and most muscular females to produce the strongest offspring possible. This is an example of SELECTIV ...
... 29) The Clydesdale is a large breed of horse that was used for specific farming purposes, such as plowing and pulling wagons. The biggest and most muscular male horses were crossed with the biggest and most muscular females to produce the strongest offspring possible. This is an example of SELECTIV ...
Artificial Selection Artificial Selection is the process of selecting and
... to produce offspring with the desired traits. The selection process is simple. Only those individuals, with the desired trait, will be allowed to reproduce. ...
... to produce offspring with the desired traits. The selection process is simple. Only those individuals, with the desired trait, will be allowed to reproduce. ...
Heidi Sleister
... – A search led to 5 people with strawberries. – Do any of these strawberries match the strawberries from the garden? ...
... – A search led to 5 people with strawberries. – Do any of these strawberries match the strawberries from the garden? ...
Cloning Genes
... Digest DNA with restriction enzymes Load DNA into wells of agarose gel Apply electric current to fractionate DNA fragments by size In electric field with positive and negative poles, which pole will DNA be attracted to? Why? ...
... Digest DNA with restriction enzymes Load DNA into wells of agarose gel Apply electric current to fractionate DNA fragments by size In electric field with positive and negative poles, which pole will DNA be attracted to? Why? ...
Restriction Enzymes
... The different sized bands can arise from different cut sites and/or different number of nucleotides between the cut sites. Sequence 1 ...
... The different sized bands can arise from different cut sites and/or different number of nucleotides between the cut sites. Sequence 1 ...
Supporting Methods Cells and SV40 infection BSC40 and U2OS
... ATRi treated SV40-infected or mock infected cells compared to SV40-infected cells in the presence of DMSO (Viability (% of DMSO), the OD of mock or SV40-infected cells in the presence/ absence of ATRi was divided by the OD generated from SV40 infected cells in the presence of DMSO. Plasmids and tran ...
... ATRi treated SV40-infected or mock infected cells compared to SV40-infected cells in the presence of DMSO (Viability (% of DMSO), the OD of mock or SV40-infected cells in the presence/ absence of ATRi was divided by the OD generated from SV40 infected cells in the presence of DMSO. Plasmids and tran ...
Biotechnology
... One major discovery that propelled the biotechnology science and industry was the discovery of restriction enzymes Restriction enzymes: enzymes that cut DNA at specific recognition nucleotide sequences known as restriction sites They were discovered in bacteria & are thought to have evolved to provi ...
... One major discovery that propelled the biotechnology science and industry was the discovery of restriction enzymes Restriction enzymes: enzymes that cut DNA at specific recognition nucleotide sequences known as restriction sites They were discovered in bacteria & are thought to have evolved to provi ...
Applied Genetics
... Toxic effects Pathogenic effects Allergic reactions Resistance to antibiotics ...
... Toxic effects Pathogenic effects Allergic reactions Resistance to antibiotics ...
Test Your Knowledge – Chapter 3 Name
... e. DNA and RNA. c. fatty acids. 13. Citric acid makes lemons taste sour. Which of the following is a functional group that would cause a molecule such as citric acid to be acidic? a. hydroxyl b. hydrocarbon c. amino d. carbonyl e. carboxyl 14. Which of the following ranks the molecules in the correc ...
... e. DNA and RNA. c. fatty acids. 13. Citric acid makes lemons taste sour. Which of the following is a functional group that would cause a molecule such as citric acid to be acidic? a. hydroxyl b. hydrocarbon c. amino d. carbonyl e. carboxyl 14. Which of the following ranks the molecules in the correc ...
document
... restriction digest, of DNA according to their size (length in base pairs). • DNA fragments are separated into bands containing fragments of the same length by electrical separation in a gel matrix. • DNA molecules migrate to the positive electrode, when an electric field is applied to the gel matrix ...
... restriction digest, of DNA according to their size (length in base pairs). • DNA fragments are separated into bands containing fragments of the same length by electrical separation in a gel matrix. • DNA molecules migrate to the positive electrode, when an electric field is applied to the gel matrix ...
1, 2, 5, 6, 7 Time: 08:00
... adaptations resulting from natural and artificial selection that may cause changes in populations over time (e.g., antibiotic-resistant bacteria, beak types, peppered moths, pestresistant crops). 16. Analyze scientific evidence (e.g., DNA, fossil records, cladograms, biogeography) to support hypothe ...
... adaptations resulting from natural and artificial selection that may cause changes in populations over time (e.g., antibiotic-resistant bacteria, beak types, peppered moths, pestresistant crops). 16. Analyze scientific evidence (e.g., DNA, fossil records, cladograms, biogeography) to support hypothe ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.