13.3_Mutations
... 1 Explain What is a frameshift mutation and give an example Infer The effects of a mutation are not always visible. Choose a species and explain how a biologist might determine whether a mutation has occurred and, if so, what type of mutation it is 2 Review List four effect mutations can have on gen ...
... 1 Explain What is a frameshift mutation and give an example Infer The effects of a mutation are not always visible. Choose a species and explain how a biologist might determine whether a mutation has occurred and, if so, what type of mutation it is 2 Review List four effect mutations can have on gen ...
The ATM repair pathway inhibits RNA polymerase I transcription in
... •Responding to the environment •Replacement of damaged/worn-out parts ...
... •Responding to the environment •Replacement of damaged/worn-out parts ...
Gene Technology Study Guide
... animals are selected and passed on to their future generations. o Produces organisms with desired traits o Increasing the frequency of certain alleles in a population is the essence of genetic technology. o Through the processes of hybridization and inbreeding, desired traits can be passed on to fut ...
... animals are selected and passed on to their future generations. o Produces organisms with desired traits o Increasing the frequency of certain alleles in a population is the essence of genetic technology. o Through the processes of hybridization and inbreeding, desired traits can be passed on to fut ...
Brouwer_791H_Proposal - University of New Hampshire
... encoding for the amino acid sequence of every protein in the body. It is also this pattern that is determined during sequencing using the STEM technique (Robinson). The full sequence of these bases is unique to the individual and is the true “fingerprint” for organisms that can provide insight into ...
... encoding for the amino acid sequence of every protein in the body. It is also this pattern that is determined during sequencing using the STEM technique (Robinson). The full sequence of these bases is unique to the individual and is the true “fingerprint” for organisms that can provide insight into ...
What is your DNA Alias - mychandlerschools.org
... similar molecule to DNA called mRNA or messenger RNA. mRNA is single standed, unlike the double stranded DNA, so it is able to get through the tiny pores in the nucleus to carry the message to the ribosome. This process is called transcription. Another difference between DNA and RNA is that RNA does ...
... similar molecule to DNA called mRNA or messenger RNA. mRNA is single standed, unlike the double stranded DNA, so it is able to get through the tiny pores in the nucleus to carry the message to the ribosome. This process is called transcription. Another difference between DNA and RNA is that RNA does ...
Chapter 16 - Human Ancestry
... Modern Humans Cave art from about 14,000 years ago indicates that by that time our ancestors had achieved milestones in cultural evolution - Fine hand coordination; use of symbols A preserved man, frozen in ice from about 5,200 years ago, is genetically like us - Ötzi, the Ice Man ...
... Modern Humans Cave art from about 14,000 years ago indicates that by that time our ancestors had achieved milestones in cultural evolution - Fine hand coordination; use of symbols A preserved man, frozen in ice from about 5,200 years ago, is genetically like us - Ötzi, the Ice Man ...
Chapter 2 – The Chemical Basis of Life
... intracellular signaling proteins) g) Catalysts (enzymes both free and membrane bound) 2. Enzymes – protein that serves as a chemical catalyst – increases the rate of specific reactions without being used up (hammer and nails analogy) ****does not make a reaction happen that normally wouldn’t ...
... intracellular signaling proteins) g) Catalysts (enzymes both free and membrane bound) 2. Enzymes – protein that serves as a chemical catalyst – increases the rate of specific reactions without being used up (hammer and nails analogy) ****does not make a reaction happen that normally wouldn’t ...
Test #4: Biomolecule Foldable
... subunits called nucleotides has which of these functions in the cell? F ...
... subunits called nucleotides has which of these functions in the cell? F ...
Lecture 2
... Is a 4-chambered heart an homologous or analogous character between mammals & birds? Homologous ...
... Is a 4-chambered heart an homologous or analogous character between mammals & birds? Homologous ...
Prokaryotic Gene Expression
... • Prokaryotes continue to play a central role as tools for biotechnology and for research on eukaryotes. • Prokaryotes play important ecological roles, including the cycling of elements. • Many prokaryotes and viruses are pathogens. ...
... • Prokaryotes continue to play a central role as tools for biotechnology and for research on eukaryotes. • Prokaryotes play important ecological roles, including the cycling of elements. • Many prokaryotes and viruses are pathogens. ...
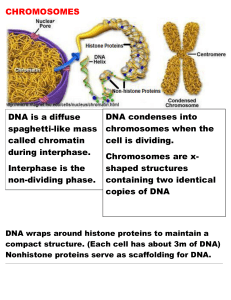
Chromosomes Notes
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of
... All four of the histones that make up the core of the nucleosome are relatively small proteins (102-135 amino acids), and they share a structural motif, known as the histone fold, formed from three alpha helices connected by two loops. ...
... All four of the histones that make up the core of the nucleosome are relatively small proteins (102-135 amino acids), and they share a structural motif, known as the histone fold, formed from three alpha helices connected by two loops. ...
Genetics
... molecules, the DNA is usually found attached to the cell membrane at some point or points. Although bacteria do not possess a nucleus, the DNA is localized in a distinct area with in the cell called the nucleoid region. There is no membrane around the nucleoid region and lies free in the cytoplasm o ...
... molecules, the DNA is usually found attached to the cell membrane at some point or points. Although bacteria do not possess a nucleus, the DNA is localized in a distinct area with in the cell called the nucleoid region. There is no membrane around the nucleoid region and lies free in the cytoplasm o ...
1 Protein structure Protein folding
... Properties of proteins are determined by both the particular sequence of amino acids and by the conformation (fold) of the protein. Flexibility in the bonds around C: – (phi) – (psi) – sidechain ...
... Properties of proteins are determined by both the particular sequence of amino acids and by the conformation (fold) of the protein. Flexibility in the bonds around C: – (phi) – (psi) – sidechain ...
In this essay you should have written it as two
... 2 Molecules of ATP are required to start the process Net gain of 2 ATP are produced Diagram can be used to show the above points maximum of 3 Kreb's cycle is an aerobic process / needs oxygen in the cell and occurs in the central liquid matrix of the mitochondrion 3C Pyruvic acid is converted to 2C ...
... 2 Molecules of ATP are required to start the process Net gain of 2 ATP are produced Diagram can be used to show the above points maximum of 3 Kreb's cycle is an aerobic process / needs oxygen in the cell and occurs in the central liquid matrix of the mitochondrion 3C Pyruvic acid is converted to 2C ...
8/22/13 Comp 555 Fall 2013 1 - UNC Computational Systems Biology
... • In 1908, Thomas Hunt Morgan and Alfred H. Sturtevant showed that genes were located on chromosomes. Experimenting with Drosophila (fruit flies) they found sex chromosomes, sex-linked traits, and crossing-over. They were able to associate mutations to specific chromosomal regions, thus mapping ge ...
... • In 1908, Thomas Hunt Morgan and Alfred H. Sturtevant showed that genes were located on chromosomes. Experimenting with Drosophila (fruit flies) they found sex chromosomes, sex-linked traits, and crossing-over. They were able to associate mutations to specific chromosomal regions, thus mapping ge ...
Chapter 11 – What is DNA and how does it work?
... 20.) Put the steps of DNA replication in order: A.) New complementary nucleotides move in to match both halves of the DNA ladder. B.) Two identical DNA molecules are formed! C.) They form hydrogen bonds with the old nucleotides. D.) DNA unzips at the hydrogen bonds. ...
... 20.) Put the steps of DNA replication in order: A.) New complementary nucleotides move in to match both halves of the DNA ladder. B.) Two identical DNA molecules are formed! C.) They form hydrogen bonds with the old nucleotides. D.) DNA unzips at the hydrogen bonds. ...
Cell Membrane
... This structure explains how DNA can be copied Each half has the info needed to make the other half (complimentary strands) ...
... This structure explains how DNA can be copied Each half has the info needed to make the other half (complimentary strands) ...
DNA Repair & Recombination
... • All 3 genomes in plants constantly being damaged by UV and other forms of radiation, chemicals, and other stresses (e.g., oxidative, heat). • Some proteins involved in repair also function in recombination – e.g., recombination can be used to repair double-strand breaks. ...
... • All 3 genomes in plants constantly being damaged by UV and other forms of radiation, chemicals, and other stresses (e.g., oxidative, heat). • Some proteins involved in repair also function in recombination – e.g., recombination can be used to repair double-strand breaks. ...
Ch. 9: Presentation Slides
... Genomics and Proteomics • The field of genomics deals with the DNA sequence, organization, function, and evolution of genomes • Proteomics aims to identify all the proteins in a cell or organism including any posttranslationally modified forms, as well as their cellular localization, functions, and ...
... Genomics and Proteomics • The field of genomics deals with the DNA sequence, organization, function, and evolution of genomes • Proteomics aims to identify all the proteins in a cell or organism including any posttranslationally modified forms, as well as their cellular localization, functions, and ...
AP Biology - APBioKorzwiki
... Restriction enzymes restriction endonucleases discovered in 1960s evolved in bacteria to cut up foreign DNA (“restriction”) ...
... Restriction enzymes restriction endonucleases discovered in 1960s evolved in bacteria to cut up foreign DNA (“restriction”) ...
Conservation of Primary Structure in Bacterial Ribosomal Protein
... Functional (Higo et al., 1973), immunological (Isono et al., 1973) and sequence data (Yaguchi et al., 1973) on the ribosomal proteins from various bacterial sources suggest considerable conservation of protein structure during the evolutionary development of the bacterial ribosome. To determine the ...
... Functional (Higo et al., 1973), immunological (Isono et al., 1973) and sequence data (Yaguchi et al., 1973) on the ribosomal proteins from various bacterial sources suggest considerable conservation of protein structure during the evolutionary development of the bacterial ribosome. To determine the ...
DNA Structure & Function
... Erwin Chargaff: Adenine and thymine are always present in equal amounts, and cytosione & guanine are always present in equal amounts within a molecule of DNA Rosalind Franklin & Wilson: used X-ray crystallography to image DNA Watson & Crick: discovered that DNA is in the form of a double helix and t ...
... Erwin Chargaff: Adenine and thymine are always present in equal amounts, and cytosione & guanine are always present in equal amounts within a molecule of DNA Rosalind Franklin & Wilson: used X-ray crystallography to image DNA Watson & Crick: discovered that DNA is in the form of a double helix and t ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.