7nQ Jj I f NO "7^07 - UNT Digital Library
... During the course of my thesis work, I was required to read a genetics textbook, with which I had not previously read. As I read this book, I realized that there was still much information to which I had not previously been exposed. My thesis work offered a new way for me obtain knowledge that I di ...
... During the course of my thesis work, I was required to read a genetics textbook, with which I had not previously read. As I read this book, I realized that there was still much information to which I had not previously been exposed. My thesis work offered a new way for me obtain knowledge that I di ...
TAP Express® Kit
... This step generates the TAP Primary® fragment, a DNA fragment that contains the gene-ofinterest with the added 5’- and 3’-TAP Ends sequences. These 5’- and 3’-TAP Ends sequences are necessary for adding the TAP Express® promoter and terminator fragments in the second PCR step. The conditions recomme ...
... This step generates the TAP Primary® fragment, a DNA fragment that contains the gene-ofinterest with the added 5’- and 3’-TAP Ends sequences. These 5’- and 3’-TAP Ends sequences are necessary for adding the TAP Express® promoter and terminator fragments in the second PCR step. The conditions recomme ...
MacVector 14.0 Getting Started Guide
... can be selected from the keyword list when editing the features of protein or nucleic acid sequences. ...
... can be selected from the keyword list when editing the features of protein or nucleic acid sequences. ...
OLSON LAB PROTOCOL: Agarose Gel Electrophoresis using GelRed
... samples, such as those resulting from PCR • As DNA molecules are negatively charged, a current can be applied to a gel to draw the fragments toward the cathode (positive pole) • Larger fragments move more slowly through the agarose gel matrix than small fragments and hence the fragments are size fra ...
... samples, such as those resulting from PCR • As DNA molecules are negatively charged, a current can be applied to a gel to draw the fragments toward the cathode (positive pole) • Larger fragments move more slowly through the agarose gel matrix than small fragments and hence the fragments are size fra ...
Population genetics and the modern synthesis of evolutionary theory
... − since most DNA is unused “junk DNA”, most mutations have no effect − mutations that do affect a working gene are usually harmful − just as randomly changing a part in a complex machine is much more likely to prevent it from working than to make it work better − but on very rare occasions, a change ...
... − since most DNA is unused “junk DNA”, most mutations have no effect − mutations that do affect a working gene are usually harmful − just as randomly changing a part in a complex machine is much more likely to prevent it from working than to make it work better − but on very rare occasions, a change ...
Biochem Jeopardy
... Explain how an enzyme works using the terms substrate and active site (correctly) in your explanation. A: What is “a substrate bonds to the active site of the enzyme causing a ...
... Explain how an enzyme works using the terms substrate and active site (correctly) in your explanation. A: What is “a substrate bonds to the active site of the enzyme causing a ...
Discriminating Between Annual and Perennial
... Currently, the Fluorescence test is used to determine seed purity Problem Fluorescence test is less effective as a result of the two species intermingling and tends to overestimate the annual types. i.e It docks the farmer’s pay more than necessary ...
... Currently, the Fluorescence test is used to determine seed purity Problem Fluorescence test is less effective as a result of the two species intermingling and tends to overestimate the annual types. i.e It docks the farmer’s pay more than necessary ...
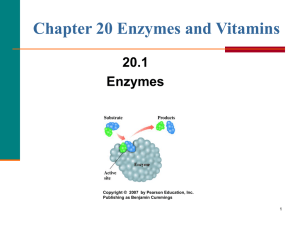
Enzymes
... This increased activity with temperature is only true up to a point. Remember that enzymes are proteins. Many of these proteins are large molecules and can withstand a moderate rise in temperature, but at some point temperature will DENATURE proteins. This means that the enzyme will begin to "unrave ...
... This increased activity with temperature is only true up to a point. Remember that enzymes are proteins. Many of these proteins are large molecules and can withstand a moderate rise in temperature, but at some point temperature will DENATURE proteins. This means that the enzyme will begin to "unrave ...
Global and Local Sequence Alignment
... Multiplying all substitution and gap scores by a positive constant does not change the optimal alignment. Why? Adding a constant < to all substitution scores, and
... Multiplying all substitution and gap scores by a positive constant does not change the optimal alignment. Why? Adding a constant < to all substitution scores, and
pcr (polymerase chain reaction)
... If you had glowing colonies on your #1A plate with IPTG, then you do not need to do colony PCR because your circuit has been assembled correctly and it is already in the host strain of interest (those expressing lacI). Instead of colony PCR, just make an overnight culture in 6 mL LB+Amp media of at ...
... If you had glowing colonies on your #1A plate with IPTG, then you do not need to do colony PCR because your circuit has been assembled correctly and it is already in the host strain of interest (those expressing lacI). Instead of colony PCR, just make an overnight culture in 6 mL LB+Amp media of at ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... The proper fit of a substrate (S) in an active site forms an enzyme-substrate (ES) complex. E+S ES Within the ES complex, the reaction occurs to convert substrate to product (P). ES E+P The products, which are no longer attracted to the active site, are released. Overall, substrate is conver ...
... The proper fit of a substrate (S) in an active site forms an enzyme-substrate (ES) complex. E+S ES Within the ES complex, the reaction occurs to convert substrate to product (P). ES E+P The products, which are no longer attracted to the active site, are released. Overall, substrate is conver ...
biomolecules Feb 16 17.notebook
... Polypeptides are polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Peptide bonds are polar covalent bonds, allowing hydrogen bonding between amino acids. This influences the three dimensional shape of proteins. ...
... Polypeptides are polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Peptide bonds are polar covalent bonds, allowing hydrogen bonding between amino acids. This influences the three dimensional shape of proteins. ...
A dynamic deterministic model to optimize a multiple
... The deterministic model described above allows global optimization of the selection scheme to maximize the frequency of the desired genotype for a monogenic trait, while minimizing the loss of genetic progress on a polygenic trait. These objectives may be achieved by taking into account the whole po ...
... The deterministic model described above allows global optimization of the selection scheme to maximize the frequency of the desired genotype for a monogenic trait, while minimizing the loss of genetic progress on a polygenic trait. These objectives may be achieved by taking into account the whole po ...
Improvement of poly-γ-glutamic acid (PGA)
... of a total 147 mutant isolates. Consequently, screened PGA-producing mutants were spotted on fermentation PGA agar and the slime diameter (mm.) of nine isolates was higher than that of the wild type Strain improvement (P<0.05). Those of nine mutant isolates were quantified for PGA production in PGA ...
... of a total 147 mutant isolates. Consequently, screened PGA-producing mutants were spotted on fermentation PGA agar and the slime diameter (mm.) of nine isolates was higher than that of the wild type Strain improvement (P<0.05). Those of nine mutant isolates were quantified for PGA production in PGA ...
structure and function of bio- molecules - Aditya K Panda, PhD
... The molecules that form the building blocks of living organisms obey the same laws of nature as all other “chemical molecules”. However, such molecules are different in a sense that they have a function. They can be seen as highly efficient “tools” and/or “machines” or as dedicated “building materia ...
... The molecules that form the building blocks of living organisms obey the same laws of nature as all other “chemical molecules”. However, such molecules are different in a sense that they have a function. They can be seen as highly efficient “tools” and/or “machines” or as dedicated “building materia ...
Factors affecting enzyme activity ppt - Mr. Lesiuk
... A change in pH can alter the ionization of the R groups of the amino acids. When the charges on the amino acids change, hydrogen bonding within the protein molecule change and the molecule changes shape. The new shape may not be effective. The diagram shows that pepsin functions best in an acid envi ...
... A change in pH can alter the ionization of the R groups of the amino acids. When the charges on the amino acids change, hydrogen bonding within the protein molecule change and the molecule changes shape. The new shape may not be effective. The diagram shows that pepsin functions best in an acid envi ...
Document
... A change in pH can alter the ionization of the R groups of the amino acids. When the charges on the amino acids change, hydrogen bonding within the protein molecule change and the molecule changes shape. The new shape may not be effective. The diagram shows that pepsin functions best in an acid envi ...
... A change in pH can alter the ionization of the R groups of the amino acids. When the charges on the amino acids change, hydrogen bonding within the protein molecule change and the molecule changes shape. The new shape may not be effective. The diagram shows that pepsin functions best in an acid envi ...
Green Fluorescent Protein: A Reporter Molecule
... 238 amino acids Cylindrical fold Very stable structure that is resistant to denaturing ...
... 238 amino acids Cylindrical fold Very stable structure that is resistant to denaturing ...
Higher Human Biology unit 1 section 5 ENZYMES
... there as more active sites become occupied by substrates. This is only until the point where all active sites are filled and so rate of reaction levels off. As there are no more enzymes to react with more substrates, enzyme concentration becomes the limiting factor. ...
... there as more active sites become occupied by substrates. This is only until the point where all active sites are filled and so rate of reaction levels off. As there are no more enzymes to react with more substrates, enzyme concentration becomes the limiting factor. ...
1 Natural Selection 2 Mutation
... The allele frequencies in each generation are pu (1), pu (2), . . ., where pu (t + 1) is a function (given above) of pu (t) for all t > 0. Then, the likelihood for the fitness model is YY L ({wuv , pu (1)}) ∝ [pu (t)]nu (t) . t ...
... The allele frequencies in each generation are pu (1), pu (2), . . ., where pu (t + 1) is a function (given above) of pu (t) for all t > 0. Then, the likelihood for the fitness model is YY L ({wuv , pu (1)}) ∝ [pu (t)]nu (t) . t ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.