DNA Technology and Genomics I.
... The bacterial clone will make the protein encoded by the foreign gene. The potential uses of cloned genes fall into two general categories. a. To produce a protein product. For example, bacteria carrying the gene for human growth hormone can produce large quantities of the hormone. b. To prepare man ...
... The bacterial clone will make the protein encoded by the foreign gene. The potential uses of cloned genes fall into two general categories. a. To produce a protein product. For example, bacteria carrying the gene for human growth hormone can produce large quantities of the hormone. b. To prepare man ...
Topic 18 revision notes - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... Describe evolution as the change in adaptive features of a population over time as the result of natural selection Define the process of adaptation - the process, resulting from natural selection, by which populations become more suited to their environment over many generations Describe the develop ...
... Describe evolution as the change in adaptive features of a population over time as the result of natural selection Define the process of adaptation - the process, resulting from natural selection, by which populations become more suited to their environment over many generations Describe the develop ...
Edward A. Birge: Bacterial and bacteriophage genetics, 4th edn
... genetics is really the study of the properties, synthesis and inheritance of nucleic acids. This chapter focuses on DNA (although some viruses have RNA as their genetic material, which is discussed in later chapters). It describes the main structural features of DNA, its replication process, and var ...
... genetics is really the study of the properties, synthesis and inheritance of nucleic acids. This chapter focuses on DNA (although some viruses have RNA as their genetic material, which is discussed in later chapters). It describes the main structural features of DNA, its replication process, and var ...
Introduction Kit components
... agorose gel and rapid PCR clean-up of DNA bands ranging from 100bp to 20kb. The GF-1 AmbiClean Kit ( Gel & PCR ) contains special buffers to provide the correct salt concentration and pH for efficient recovery (80 - 90%) of DNA from both PCR product and agarose gel from both TAE or TBE buffer. This ...
... agorose gel and rapid PCR clean-up of DNA bands ranging from 100bp to 20kb. The GF-1 AmbiClean Kit ( Gel & PCR ) contains special buffers to provide the correct salt concentration and pH for efficient recovery (80 - 90%) of DNA from both PCR product and agarose gel from both TAE or TBE buffer. This ...
Foundations of Biology
... The most highly packaged form of DNA is “heterochromatin” Heterochromatin cannot be transcribed, therefore expression of genes is prevented Chromosome puffs on some insect chomosomes illustrate where active gene expression is going on ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
... The most highly packaged form of DNA is “heterochromatin” Heterochromatin cannot be transcribed, therefore expression of genes is prevented Chromosome puffs on some insect chomosomes illustrate where active gene expression is going on ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
Types of Natural Selection
... Suppose termites in an area begin to build deeper nests. Anteaters with long tongues could more effectively prey on termites than those with short or average tongue length ...
... Suppose termites in an area begin to build deeper nests. Anteaters with long tongues could more effectively prey on termites than those with short or average tongue length ...
Biomolecules Review Worksheets 14 KEY
... Single‐ringed nitrogenous base; cytosine, thymine and uracil (uracil only in RNA) Bases that bond to each other by hydrogen bonding; A‐T and G‐C a ring‐shaped molecule containing C and N; aached to the 1' carbon in a nucleode ...
... Single‐ringed nitrogenous base; cytosine, thymine and uracil (uracil only in RNA) Bases that bond to each other by hydrogen bonding; A‐T and G‐C a ring‐shaped molecule containing C and N; aached to the 1' carbon in a nucleode ...
DNA ISOLATION FROM AGAROSE GELS WITH DEAE PAPER
... After the DNA bands have been separated electrophoretically (at around 80 V), the gel is viewed under long wave UV light and a slit cut in the gel, just ahead of the desired band. A piece of DEAE paper is inserted in the slit. Another piece of DEAE paper can be inserted behind the desired band, to p ...
... After the DNA bands have been separated electrophoretically (at around 80 V), the gel is viewed under long wave UV light and a slit cut in the gel, just ahead of the desired band. A piece of DEAE paper is inserted in the slit. Another piece of DEAE paper can be inserted behind the desired band, to p ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review
... What is crossing over, and when does it occur during meiosis? Crossing over is the exchange of genetic information from two non-sister chromatids during prophase I of meiosis Distinguish between a chromosomal mutation and a gene mutation and give two examples of each type of mutation. Chromosomal mu ...
... What is crossing over, and when does it occur during meiosis? Crossing over is the exchange of genetic information from two non-sister chromatids during prophase I of meiosis Distinguish between a chromosomal mutation and a gene mutation and give two examples of each type of mutation. Chromosomal mu ...
Recombinant DNA Activity
... Steps to Recombination 1. Scientists must first identify the gene that codes for the production of the protein they want to manufacture. 2. Next scientists must isolate the desired gene. Restriction enzymes from bacterial cells are important in this step. Each restriction enzyme recognizes and cleav ...
... Steps to Recombination 1. Scientists must first identify the gene that codes for the production of the protein they want to manufacture. 2. Next scientists must isolate the desired gene. Restriction enzymes from bacterial cells are important in this step. Each restriction enzyme recognizes and cleav ...
High Frequency of Recombination (Hfr)
... • Untreated culture Do a serial dilution of the untreated wildtype E. coli culture: Fill 7 tubes with 4.5 ml of sterile saline. Transfer 0.5 ml of the undiluted culture to one of the tubes. This is a 10-1 dilution. Next make serial dilutions of 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-6 and 10-7. Always change pi ...
... • Untreated culture Do a serial dilution of the untreated wildtype E. coli culture: Fill 7 tubes with 4.5 ml of sterile saline. Transfer 0.5 ml of the undiluted culture to one of the tubes. This is a 10-1 dilution. Next make serial dilutions of 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-6 and 10-7. Always change pi ...
Biology EOC Review Pack
... 21) What are the main differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? (which one uses oxygen, which one makes more ATP?) a. Aerobic – b. Anaerobic – 22) What is alcoholic fermentation? What are the products? 23) What type of fermentation might be used in your own muscle cells when they do not ...
... 21) What are the main differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? (which one uses oxygen, which one makes more ATP?) a. Aerobic – b. Anaerobic – 22) What is alcoholic fermentation? What are the products? 23) What type of fermentation might be used in your own muscle cells when they do not ...
Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Detection of
... The lateral flow tests are becoming more and more popular for testing of wide range of analytes. The lateral flow tests offers many benefits (user-friendly format, short time to get test result, long-term stability, and relatively low price). A new promising application is the detection of genetic m ...
... The lateral flow tests are becoming more and more popular for testing of wide range of analytes. The lateral flow tests offers many benefits (user-friendly format, short time to get test result, long-term stability, and relatively low price). A new promising application is the detection of genetic m ...
Biochemistry 304 2014 Student Edition TRANSCRIPTION
... Voet, Voet & Pratt 2013 Fig 26.4 Lehninger (Nelson & Cox) 2005 Fig 26.3 ...
... Voet, Voet & Pratt 2013 Fig 26.4 Lehninger (Nelson & Cox) 2005 Fig 26.3 ...
En/Spm-Mu
... 1. Mu elements are known to transpose to any locus, especially genes, therefore it is very useful for creating tagged mutations. 2. Mutator’s frequent transposition activity (even to unlinked locus) is reminiscent of P element system of Drosophila. In Drosophila, P elements have been used as vectors ...
... 1. Mu elements are known to transpose to any locus, especially genes, therefore it is very useful for creating tagged mutations. 2. Mutator’s frequent transposition activity (even to unlinked locus) is reminiscent of P element system of Drosophila. In Drosophila, P elements have been used as vectors ...
Grade 10 Biology Assessment 1 Cover Sheet 2016/17 File
... generation to the next? c. Select two examples of heritable characteristics: What part of the human chromosome does it get carried on and how is it passed from one generation to the next? (only father? Dominant or recessive?) 3. Select one example of a heritable disease: a. Name of the heritable dis ...
... generation to the next? c. Select two examples of heritable characteristics: What part of the human chromosome does it get carried on and how is it passed from one generation to the next? (only father? Dominant or recessive?) 3. Select one example of a heritable disease: a. Name of the heritable dis ...
221_exam_2_2004
... ____ What happens to ATP synthesis if the electron transport chain is stopped by addition of an inhibitor? A. ATP synthesis would stop due to a buildup of excess protons outside the ...
... ____ What happens to ATP synthesis if the electron transport chain is stopped by addition of an inhibitor? A. ATP synthesis would stop due to a buildup of excess protons outside the ...
Ant genetics DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) Cells have two sources of
... How do landscape features impact population structure and migration? What are the extinction/recolonization dynamics of the metapopulation? Did the population structure or connectivity change in the recent past? ...
... How do landscape features impact population structure and migration? What are the extinction/recolonization dynamics of the metapopulation? Did the population structure or connectivity change in the recent past? ...
slg mock midterm – for practice only
... b. Each strand of both daughter molecules contains a mixture of old and newly synthesized DNA. c. The two strands of the parental molecule separate, and each functions as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. d. DNA Polymerase III carries out synthesis by extending from the RNA pr ...
... b. Each strand of both daughter molecules contains a mixture of old and newly synthesized DNA. c. The two strands of the parental molecule separate, and each functions as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. d. DNA Polymerase III carries out synthesis by extending from the RNA pr ...
Unoshan_project
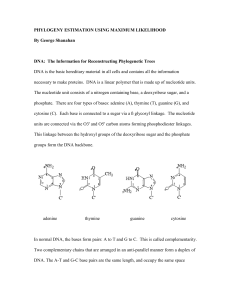
... their common ancestor. Its topology (form) and its length (sum of its branch lengths) characterize a phylogenetic tree. Each node of a tree is an estimation of the ancestor of the elements included in that node. Maximum Likelihood is a method for the inference of phylogeny. It evaluates a hypothesis ...
... their common ancestor. Its topology (form) and its length (sum of its branch lengths) characterize a phylogenetic tree. Each node of a tree is an estimation of the ancestor of the elements included in that node. Maximum Likelihood is a method for the inference of phylogeny. It evaluates a hypothesis ...
nov6_part1_Basics of molecular genetics
... • Mistakes during crossing over further increase the variability • Recombination (to a certain extent) is also possible during mitosis • Site-specific recombination is typical for viruses when they are integrating into the host cells • Transpositional recombination (caused by transposons) does not n ...
... • Mistakes during crossing over further increase the variability • Recombination (to a certain extent) is also possible during mitosis • Site-specific recombination is typical for viruses when they are integrating into the host cells • Transpositional recombination (caused by transposons) does not n ...
Setting the stage for passing on epigenetic information to the next
... study in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology how chromatin based epigenetic information is retained during the development of the sperm that eventually may be passed on to the next generation. In sperm, DNA is 10- to 20-fold more tightly packed than in nuclei of regular cells. The tight packaging ...
... study in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology how chromatin based epigenetic information is retained during the development of the sperm that eventually may be passed on to the next generation. In sperm, DNA is 10- to 20-fold more tightly packed than in nuclei of regular cells. The tight packaging ...
How DNA Evidence Works The Science of DNA Fingerprinting
... the line of duty. Even without a DNA match to conclusively identify a body, a profile is useful because it can provide important clues about the victim, such as his or her sex and race. • Studying the evolution of human populations - Scientists are trying to use samples extracted from skeletons and ...
... the line of duty. Even without a DNA match to conclusively identify a body, a profile is useful because it can provide important clues about the victim, such as his or her sex and race. • Studying the evolution of human populations - Scientists are trying to use samples extracted from skeletons and ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.