Reproduction and Genetics: DNA Replication
... characteristics and give examples of each. They learned how to recognize whether an organism’s characteristics were inherited from parents or resulted from interactions with the environment. Students followed a characteristic through a given pedigree. Current Learning Students learn the components o ...
... characteristics and give examples of each. They learned how to recognize whether an organism’s characteristics were inherited from parents or resulted from interactions with the environment. Students followed a characteristic through a given pedigree. Current Learning Students learn the components o ...
RNAi, Penetrance and Expressivity Genetics 322, Fall 2008
... flower. They reasoned that extra copies of a purple pigment gene would produce extra pigment and help produce a darker colored flower. However, they were surprised to produce flowers that appeared variegated, spotty, or even completely white. What seemed to be happening was that the introduction of ...
... flower. They reasoned that extra copies of a purple pigment gene would produce extra pigment and help produce a darker colored flower. However, they were surprised to produce flowers that appeared variegated, spotty, or even completely white. What seemed to be happening was that the introduction of ...
If there is time OR when we get to Cell Unit…
... - What are the applications or uses of DNA Extraction? Identify & explain at least 2 uses for this lab. - Research a case (study or scenario) in which DNA was used. - MUST include a “Works Cited” page (last page of report) to cite your source!!! ...
... - What are the applications or uses of DNA Extraction? Identify & explain at least 2 uses for this lab. - Research a case (study or scenario) in which DNA was used. - MUST include a “Works Cited” page (last page of report) to cite your source!!! ...
Lect-7
... Discovered in E. coli by Larry Taylor (1963). Given the name Mu, for mutator because of its ability to cause mutations. It is known to cause mutations at high rate. The mutations proved to be insertions to Mu at random sites in the host genome disrupting the functioning of different genes. ...
... Discovered in E. coli by Larry Taylor (1963). Given the name Mu, for mutator because of its ability to cause mutations. It is known to cause mutations at high rate. The mutations proved to be insertions to Mu at random sites in the host genome disrupting the functioning of different genes. ...
- GenoSensor Corporation
... TAS2R38. The most common one, located at the 785 nucleotide position of the DNA template strand, is associated with a loss of function in the protein product. This particular snip is a transition mutation from the pyrimidine Cytosine to the pyrimidine Thymine as seen here: GCTGC to GTTGC. Tasters ha ...
... TAS2R38. The most common one, located at the 785 nucleotide position of the DNA template strand, is associated with a loss of function in the protein product. This particular snip is a transition mutation from the pyrimidine Cytosine to the pyrimidine Thymine as seen here: GCTGC to GTTGC. Tasters ha ...
Prometheus & Myriad
... Some myths on gene patents Patents and Costs – No evidence was found demonstrating that patents accelerated or inhibited test development for certain conditions (e.g. hearing loss). – Price for genetic tests did not appear to correlate with patent status. Some for-profit providers had the same co ...
... Some myths on gene patents Patents and Costs – No evidence was found demonstrating that patents accelerated or inhibited test development for certain conditions (e.g. hearing loss). – Price for genetic tests did not appear to correlate with patent status. Some for-profit providers had the same co ...
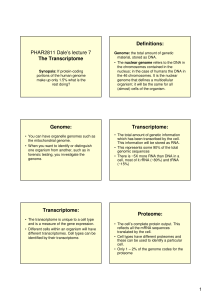
PHAR2811 Dale`s lecture 7 The Transcriptome Definitions: Genome
... • It was this enzyme that led scientists to the discovery of ribozymes; the RNA species capable of catalytic activity. ...
... • It was this enzyme that led scientists to the discovery of ribozymes; the RNA species capable of catalytic activity. ...
HH-Unit-1-PPQs - Dalkeith High School
... Genes and Proteins in Health and Disease 40. A substitution mutation results in a triplet of bases TTC being changed to TCC. The amino acid lysine is coded for by TTC and arginine by TCC. The effect of such a mutation on the resultant protein would be that A. arginine replaces lysine throughout the ...
... Genes and Proteins in Health and Disease 40. A substitution mutation results in a triplet of bases TTC being changed to TCC. The amino acid lysine is coded for by TTC and arginine by TCC. The effect of such a mutation on the resultant protein would be that A. arginine replaces lysine throughout the ...
Construction and stable transformation of Tetrahymena
... functional complementation. The model organism T. thermophila has 24.725 genes, 12.000 of them has no known biological function including some human homologs. In the future, one of main goals of Tetrahymena laboratories will be characterizing the unknown biological function of these genes in lifecyc ...
... functional complementation. The model organism T. thermophila has 24.725 genes, 12.000 of them has no known biological function including some human homologs. In the future, one of main goals of Tetrahymena laboratories will be characterizing the unknown biological function of these genes in lifecyc ...
Slides PPT
... Genome: the total amount of genetic material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) c ...
... Genome: the total amount of genetic material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) c ...
Questions - National Biology Competition
... A class can contain more than one phylum. A genus can contain more than one order. A family can contain more than one class. An order can contain more than one family. A genus can contain more than one family. ...
... A class can contain more than one phylum. A genus can contain more than one order. A family can contain more than one class. An order can contain more than one family. A genus can contain more than one family. ...
Biomolecules … another worksheet
... _______________________ 2. Animal fat, corn oil, cholesterol, chlorophyll, and bee’s wax, olive oil, whale blubber _______________________ 3. Meat, hair, skin, muscle, enzymes _______________________ 4. Information molecules like DNA & RNA, energy transfer molecules like ATP ...
... _______________________ 2. Animal fat, corn oil, cholesterol, chlorophyll, and bee’s wax, olive oil, whale blubber _______________________ 3. Meat, hair, skin, muscle, enzymes _______________________ 4. Information molecules like DNA & RNA, energy transfer molecules like ATP ...
10.3 Theory of Natural Selection
... • There is a struggle for survival due to overpopulation and limited resources. • Darwin proposed that adaptations arose over many generations. • Natural selection is when individuals that have inherited beneficial adaptations produce more offspring ...
... • There is a struggle for survival due to overpopulation and limited resources. • Darwin proposed that adaptations arose over many generations. • Natural selection is when individuals that have inherited beneficial adaptations produce more offspring ...
Classification of Microorganisms
... • This technique involves the sequencing fragments from 6 to 7 genes (often housekeeping genes) from an organism and comparing these with the same gene set from different strains of the same organism • Can distinguish between closely related strains • While rRNA gene sequence analysis is capable of ...
... • This technique involves the sequencing fragments from 6 to 7 genes (often housekeeping genes) from an organism and comparing these with the same gene set from different strains of the same organism • Can distinguish between closely related strains • While rRNA gene sequence analysis is capable of ...
Notes
... A) 4 of these make up 96% of living matter 1) C, O, H & N B) The remaining 4% primarily include P, S, Ca, K, Na, Cl, & Mg C) trace elements are ones only required in small quantities 1) Fe, Cu & Zn are examples D. Atom – smallest unit of an element that still has the properties of the element E. Mol ...
... A) 4 of these make up 96% of living matter 1) C, O, H & N B) The remaining 4% primarily include P, S, Ca, K, Na, Cl, & Mg C) trace elements are ones only required in small quantities 1) Fe, Cu & Zn are examples D. Atom – smallest unit of an element that still has the properties of the element E. Mol ...
MCA Test Prep Answers Part 1
... a) Give 1 example of a problem that may be understood better as genetic technology continues to advance. Genetic diseases b) Explain how this problem may be solved with advancing technology. We can use genetic technology to identify what genes are affected in various genetic diseases and perhaps som ...
... a) Give 1 example of a problem that may be understood better as genetic technology continues to advance. Genetic diseases b) Explain how this problem may be solved with advancing technology. We can use genetic technology to identify what genes are affected in various genetic diseases and perhaps som ...
Synthetic Biology presentation Linköping
... of biology easier and more reliable.” Wikipedia – Synthetic Biology ...
... of biology easier and more reliable.” Wikipedia – Synthetic Biology ...
Advancing Science with DNA Sequence
... Metagenomic data are noisy • Definition of high quality genome sequence: an example of “finished” JGI genomes - each base is covered by at least two Sanger reads in each direction with a quality of at least Q20 • Definition of “ high quality” metagenome? Too many variables: species composition/abu ...
... Metagenomic data are noisy • Definition of high quality genome sequence: an example of “finished” JGI genomes - each base is covered by at least two Sanger reads in each direction with a quality of at least Q20 • Definition of “ high quality” metagenome? Too many variables: species composition/abu ...
Selective Breeding
... • Undesirable traits from both parents may appear in the offspring • Disease can accumulate in the population – deaf dalmatians, boxers with heart disease, labs with hip problems, etc. ...
... • Undesirable traits from both parents may appear in the offspring • Disease can accumulate in the population – deaf dalmatians, boxers with heart disease, labs with hip problems, etc. ...
Biology 2.3 2.4 - Sleeping Dog Studios
... A fatty acid is a long chain of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms bonded to them. ...
... A fatty acid is a long chain of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms bonded to them. ...
Monitoring viral DNA release with capillary electrophoresis
... To label DNA released from virus particles, we used a DNAintercalating fluorescent dye, YOYO-1, which increases its quantum yield approximately 100–1000 fold upon intercalating with double-stranded DNA (dsDNA).12 YOYO-1 has been used successfully by staining sea-water viral samples to identify and e ...
... To label DNA released from virus particles, we used a DNAintercalating fluorescent dye, YOYO-1, which increases its quantum yield approximately 100–1000 fold upon intercalating with double-stranded DNA (dsDNA).12 YOYO-1 has been used successfully by staining sea-water viral samples to identify and e ...
Discovery through RNA-Seq
... • Overall, using “mate pair” information, more power, but sometimes experimental artifacts can effect results ...
... • Overall, using “mate pair” information, more power, but sometimes experimental artifacts can effect results ...
Screening for Recombinants
... Introduction Now that you’ve transformed your DNA and allowed the colonies to grow overnight, you need to determine if they contain the insert of interest. You can either screen them by colony PCR or the more traditional plasmid miniprep followed by restriction digestion. Colony PCR is the most rapi ...
... Introduction Now that you’ve transformed your DNA and allowed the colonies to grow overnight, you need to determine if they contain the insert of interest. You can either screen them by colony PCR or the more traditional plasmid miniprep followed by restriction digestion. Colony PCR is the most rapi ...
File
... Students may have a pre-existing negative view of genetic technologies. There is a large amount of technical vocabulary associated with genetic engineering – present this in context and recap at regular points in the teaching sequence. Understanding genetic engineering requires a basic understanding ...
... Students may have a pre-existing negative view of genetic technologies. There is a large amount of technical vocabulary associated with genetic engineering – present this in context and recap at regular points in the teaching sequence. Understanding genetic engineering requires a basic understanding ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.