Genetics ppt 1
... together mRNA, a tRNA with the first amino acid, and the two ribosomal subunits • First, a small ribosomal subunit binds with mRNA and a special initiator tRNA • Then the small subunit moves along the mRNA until it reaches the start codon (AUG) • Proteins called initiation factors bring in the large ...
... together mRNA, a tRNA with the first amino acid, and the two ribosomal subunits • First, a small ribosomal subunit binds with mRNA and a special initiator tRNA • Then the small subunit moves along the mRNA until it reaches the start codon (AUG) • Proteins called initiation factors bring in the large ...
Human Primary Cell cDNA
... While the single-strand cDNA product is relatively less stable than doublestrand cDNA, it is still significantly more stable than RNA. ...
... While the single-strand cDNA product is relatively less stable than doublestrand cDNA, it is still significantly more stable than RNA. ...
Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations
... anemia, the homozygous individuals have a certain recessive allele at the locus that causes sickle-cell disease, resulting in distorted red blood cells in low-oxygen conditions. These sickled cells cause serious damage to vital organs by clumping together. Heterozygous individuals for the sickle-cel ...
... anemia, the homozygous individuals have a certain recessive allele at the locus that causes sickle-cell disease, resulting in distorted red blood cells in low-oxygen conditions. These sickled cells cause serious damage to vital organs by clumping together. Heterozygous individuals for the sickle-cel ...
The Chemical Basis of Life Atoms, Molecules, Ions, and Bonds
... • Fatty acids vary in structure by the number of carbons and by the placement of single and double covalent bonds between the carbons, as follows: • A saturated fatty acid has a single covalent bond between each pair of carbon atoms, and each carbon has two hydrogens bonded to it (three hydrogens bo ...
... • Fatty acids vary in structure by the number of carbons and by the placement of single and double covalent bonds between the carbons, as follows: • A saturated fatty acid has a single covalent bond between each pair of carbon atoms, and each carbon has two hydrogens bonded to it (three hydrogens bo ...
Powerpoint file - revised
... Therefore, transcriptional initiation is usually the major control point. Most prokaryotic genes are regulated in units called operons (Jacob and Monod, 1960) Operon: a coordinated unit of gene expression consisting of one or more related genes and the operator and promoter sequences that regulate t ...
... Therefore, transcriptional initiation is usually the major control point. Most prokaryotic genes are regulated in units called operons (Jacob and Monod, 1960) Operon: a coordinated unit of gene expression consisting of one or more related genes and the operator and promoter sequences that regulate t ...
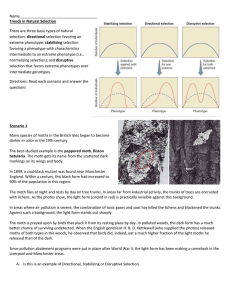
Name Trends in Natural Selection There are three basic types of
... C. With the advent of modern medical technologies and procedures, how might those babies at the “upper end and lower ends” (those with lighter and heavier birth weights) may have a higher survival rate when compared to those earlier in human history? ...
... C. With the advent of modern medical technologies and procedures, how might those babies at the “upper end and lower ends” (those with lighter and heavier birth weights) may have a higher survival rate when compared to those earlier in human history? ...
Chapter 2 The chemistry of life
... • Homotropic enzymes – show a sigmoidal relationship between V and [S] • Cooperativity – enzymes show increased affinity for S with ...
... • Homotropic enzymes – show a sigmoidal relationship between V and [S] • Cooperativity – enzymes show increased affinity for S with ...
Mark Scheme - A-level Biology Tutor
... (ii) DNA does not absorb UV strongly at these wavelengths; maximum absorption over this range of wavelengths is about 10%; most of the, energy / UV, passes through the DNA without affecting it; only if energy is absorbed can the DNA be, damaged / chemically changed; chemical change / damage to DNA, ...
... (ii) DNA does not absorb UV strongly at these wavelengths; maximum absorption over this range of wavelengths is about 10%; most of the, energy / UV, passes through the DNA without affecting it; only if energy is absorbed can the DNA be, damaged / chemically changed; chemical change / damage to DNA, ...
File
... (1) These catalysts must have a specific shape. (3) Body temperature must be above 40°C. (2) These catalysts must be able to reproduce. (4) Body pH must be above 10. 3. The term “substrate” is most commonly used to describe (1) a chemical or material in the cell (2) the building blocks that make up ...
... (1) These catalysts must have a specific shape. (3) Body temperature must be above 40°C. (2) These catalysts must be able to reproduce. (4) Body pH must be above 10. 3. The term “substrate” is most commonly used to describe (1) a chemical or material in the cell (2) the building blocks that make up ...
doc Midterm with answers
... B) fibrous proteins can often contain several types of secondary structure, whereas globular proteins usually consist largely of a single type of secondary structure. C) globular proteins are insoluble in water, and fibrous proteins are usually soluble. D) globular proteins are more likely than fibr ...
... B) fibrous proteins can often contain several types of secondary structure, whereas globular proteins usually consist largely of a single type of secondary structure. C) globular proteins are insoluble in water, and fibrous proteins are usually soluble. D) globular proteins are more likely than fibr ...
Lctures Clinical genetics – 4
... unstable a premutation (at risk of fragile X associated disorders), or full mutation 200 or > (usually affected by the syndrome). As gc repeats are difficult to amplify or detect by pcr so Southern blottB, x –inactivation of repeat expansions cause methylation of FMR1 promotor thus restriction enzym ...
... unstable a premutation (at risk of fragile X associated disorders), or full mutation 200 or > (usually affected by the syndrome). As gc repeats are difficult to amplify or detect by pcr so Southern blottB, x –inactivation of repeat expansions cause methylation of FMR1 promotor thus restriction enzym ...
Enzymes
... • Enzymes in blood work best at a pH of 7 (neutral) • Enzymes in stomach work best at a pH of 2 (acid) • Enzymes in intestine work best at a pH of 8 (base) ...
... • Enzymes in blood work best at a pH of 7 (neutral) • Enzymes in stomach work best at a pH of 2 (acid) • Enzymes in intestine work best at a pH of 8 (base) ...
Functional constraints and frequency of deleterious mutations in
... in the genome and to quantify the fraction of deleterious mutations is to search for segments of the genome having lower between-species levels of divergence than the average for the genome or than a linked putatively neutral sequence (14). Previous attempts to quantify the fraction of conserved nuc ...
... in the genome and to quantify the fraction of deleterious mutations is to search for segments of the genome having lower between-species levels of divergence than the average for the genome or than a linked putatively neutral sequence (14). Previous attempts to quantify the fraction of conserved nuc ...
SUMMARY Evidence 1s summarized showing that thymine methyls
... more easily providing the right sequence combination occurs (21). DenaturabiHty 1s especially relevent to proteins that interact with and melt DNA. For example, RNA polymerase denatures 12 bp in the promoter from the middle of the -10 region through the transcription start site during open complex f ...
... more easily providing the right sequence combination occurs (21). DenaturabiHty 1s especially relevent to proteins that interact with and melt DNA. For example, RNA polymerase denatures 12 bp in the promoter from the middle of the -10 region through the transcription start site during open complex f ...
Genomic DNA Extraction From Buccal Epithelial Cells
... gently scrape the inside of both cheeks. Scrape well so that you get lots of cells. However, this procedure should be non-invasive so don’t draw blood. 3. Transfer the cells that you have removed from the toothpick/pipette tip to the Chelex tube. Vigorously twirl the toothpick/tip in the Chelex resi ...
... gently scrape the inside of both cheeks. Scrape well so that you get lots of cells. However, this procedure should be non-invasive so don’t draw blood. 3. Transfer the cells that you have removed from the toothpick/pipette tip to the Chelex tube. Vigorously twirl the toothpick/tip in the Chelex resi ...
the genetics of viruses and bacteria
... The genome of viruses may consist of double-stranded DNA, single-stranded DNA, doublestranded RNA, or single-stranded RNA, depending on the kind of virus. ° A virus is called a DNA virus or an RNA virus, according to the kind of nucleic acid that makes up its genome. ° The viral genome is usually or ...
... The genome of viruses may consist of double-stranded DNA, single-stranded DNA, doublestranded RNA, or single-stranded RNA, depending on the kind of virus. ° A virus is called a DNA virus or an RNA virus, according to the kind of nucleic acid that makes up its genome. ° The viral genome is usually or ...
lac
... the lac repressor, then it should bind to the lac operator in an inducer sensitive manner (i.e. the addition of inducer should prevent the repressor from binding to the operator). Experiment: Cohn and colleagues used a nitrocellulose filter binding assay. They mixed 32P-labeled lacO DNA with the pro ...
... the lac repressor, then it should bind to the lac operator in an inducer sensitive manner (i.e. the addition of inducer should prevent the repressor from binding to the operator). Experiment: Cohn and colleagues used a nitrocellulose filter binding assay. They mixed 32P-labeled lacO DNA with the pro ...
Mar. 31 Presentation Phage Display
... Easy to amplify selected phages in E. coli Selection process easy and already in use in various forms. Can create Phage library variation by inducing mutations, using error prone PCR, etc. ...
... Easy to amplify selected phages in E. coli Selection process easy and already in use in various forms. Can create Phage library variation by inducing mutations, using error prone PCR, etc. ...
II. Beta oxidation of fatty acid
... _B__57. This DNA form is seen in physiologic conditions where the cell is well hydrated: A. A form B. B form C. Z form D. D form _C__58. Regions of the DNA strand that are easily denatured are rich in this base pair: A. GC B. AT C. AU D. CT _D__59. This is the primary function of nucleic acids: A. s ...
... _B__57. This DNA form is seen in physiologic conditions where the cell is well hydrated: A. A form B. B form C. Z form D. D form _C__58. Regions of the DNA strand that are easily denatured are rich in this base pair: A. GC B. AT C. AU D. CT _D__59. This is the primary function of nucleic acids: A. s ...
Molecular Cell Biology - Biomedical Informatics
... three nucleotides in the anticodon regions of tRNA molecules. At the other end of each type of tRNA molecule, a specific amino acid is held in a high-energy linkage, and when matching occurs, this amino acid is added to the end of the growing polypeptide chain. Thus translation of the mRNA nucleotid ...
... three nucleotides in the anticodon regions of tRNA molecules. At the other end of each type of tRNA molecule, a specific amino acid is held in a high-energy linkage, and when matching occurs, this amino acid is added to the end of the growing polypeptide chain. Thus translation of the mRNA nucleotid ...
CHAPTER 19 DNA Mutation and Repair
... Chemical Mutagens Mutagenic Effects of 5BU 1. Chemical mutagens may be naturally occurring, or synthetic. They form different groups based on their mechanism of action: a. Base analogs depend upon replication, which incorpocates a base with alternate states (tautomers) that allow it to base pair in ...
... Chemical Mutagens Mutagenic Effects of 5BU 1. Chemical mutagens may be naturally occurring, or synthetic. They form different groups based on their mechanism of action: a. Base analogs depend upon replication, which incorpocates a base with alternate states (tautomers) that allow it to base pair in ...
Eukaryotic DNA Replication
... followed by its electrophoretic path (solid line). The dashed line shows the path for a linear DNA. ...
... followed by its electrophoretic path (solid line). The dashed line shows the path for a linear DNA. ...
PDF
... morphogenetic inactivity of cell nuclei. This would seem paradoxical if the nuclei are supposed to be the sole site for RNA synthesis. This paradox might be resolved, however, if the 'early' RNA synthesis were partly or entirely independent of the cell nuclei. We attempted to clarify this point by m ...
... morphogenetic inactivity of cell nuclei. This would seem paradoxical if the nuclei are supposed to be the sole site for RNA synthesis. This paradox might be resolved, however, if the 'early' RNA synthesis were partly or entirely independent of the cell nuclei. We attempted to clarify this point by m ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.