A1121 SD1 - Food Standards Australia New Zealand
... A. melleus is considered a safe strain for production of enzyme preparations used in food processing (Pariza and Johnson, 2001). Protease derived from A. melleus was marketed as a digestive aid in North America prior to 1994 (ETA, 2015). Further, protease derived from A. melleus is included on the A ...
... A. melleus is considered a safe strain for production of enzyme preparations used in food processing (Pariza and Johnson, 2001). Protease derived from A. melleus was marketed as a digestive aid in North America prior to 1994 (ETA, 2015). Further, protease derived from A. melleus is included on the A ...
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Related Enzymes in Cell
... fact that the cells lacked the corresponding enzymes. In support of this theory, Youmans, Millman & Youmans (1956) presented qualitative data on the oxidation of all the intermediates of the tricarboxylic acid cycle by acetone-dried cells of the organism. However, no correlation was made between the ...
... fact that the cells lacked the corresponding enzymes. In support of this theory, Youmans, Millman & Youmans (1956) presented qualitative data on the oxidation of all the intermediates of the tricarboxylic acid cycle by acetone-dried cells of the organism. However, no correlation was made between the ...
REVIEW Formation and Instability of o
... The identity of the degradation product is consistent with the scheme proposed by Stobaugh et al. (26). However, the degradation mechanism of Simons and Johnson does not account for the acceleration of isoindole degradation by increasing OPA concentration. Nakamura et al. (30) suggested that OPA des ...
... The identity of the degradation product is consistent with the scheme proposed by Stobaugh et al. (26). However, the degradation mechanism of Simons and Johnson does not account for the acceleration of isoindole degradation by increasing OPA concentration. Nakamura et al. (30) suggested that OPA des ...
Olanzapine Activates Hepatic Mammalian Target of Rapamycin
... OLZ-induced weight gain is not only an issue for patient compliance, but can also induce sequelae associated with weight gain/obesity such as glucose intolerance and/or insulin resistance. Interestingly, the changes induced by OLZ administration in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism may in fact prece ...
... OLZ-induced weight gain is not only an issue for patient compliance, but can also induce sequelae associated with weight gain/obesity such as glucose intolerance and/or insulin resistance. Interestingly, the changes induced by OLZ administration in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism may in fact prece ...
Transcriptome analysis of Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L
... units to form 16:0-ACP; and (c) elongation and desaturation of 16:0-ACP to form 18:0-ACP and 18:1-ACP, respectively [13]. Desaturation of 18:0-ACP to 18:1-ACP catalyzed by a stromal stearoyl-ACP desaturase is one of the key steps regulating unsaturated FA levels in the cell. In oilseeds, more than 9 ...
... units to form 16:0-ACP; and (c) elongation and desaturation of 16:0-ACP to form 18:0-ACP and 18:1-ACP, respectively [13]. Desaturation of 18:0-ACP to 18:1-ACP catalyzed by a stromal stearoyl-ACP desaturase is one of the key steps regulating unsaturated FA levels in the cell. In oilseeds, more than 9 ...
Sequence - BIOTEC - Biotechnology Center TU Dresden
... Species occupy local ecosystems Species are composed of organisms Organisms are composed of cells Cells are composed of molecules ...
... Species occupy local ecosystems Species are composed of organisms Organisms are composed of cells Cells are composed of molecules ...
Base Foreign Students 2015
... 7.After a serious viral infection a 3-year-old child has repeated vomiting, loss of consciousness, convulsions. Examination revealed hyperammoniemia. What may have caused changes of biochemical blood indices of this child? A.*Disorder of ammonia neutralization in ornithinic cycle. B.Activated proces ...
... 7.After a serious viral infection a 3-year-old child has repeated vomiting, loss of consciousness, convulsions. Examination revealed hyperammoniemia. What may have caused changes of biochemical blood indices of this child? A.*Disorder of ammonia neutralization in ornithinic cycle. B.Activated proces ...
by 3AB and 3ABC trans Complemented in Formation, and the
... Description of mutants. For the construction of mutants, we compared the primary amino acid sequences with the observed processing efficiency at the various cleavage sites in the polyprotein. Positions P1 and/or P3 at the 3A/3B and P1⬘ at the 3B/3C cleavage site were exchanged such that cleavage was ...
... Description of mutants. For the construction of mutants, we compared the primary amino acid sequences with the observed processing efficiency at the various cleavage sites in the polyprotein. Positions P1 and/or P3 at the 3A/3B and P1⬘ at the 3B/3C cleavage site were exchanged such that cleavage was ...
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition - UCSF Benioff Children`s Hospital
... 5. For fluid restriction, the "starter" TPN can run at a lower rate but the protein intake will be lower than target. 6. The admitting MD/NNP will also write the TPN order for the next bag, advancing as per ICN guidelines. An order to discontinue the "starter TPN" solution once the new TPN arrives w ...
... 5. For fluid restriction, the "starter" TPN can run at a lower rate but the protein intake will be lower than target. 6. The admitting MD/NNP will also write the TPN order for the next bag, advancing as per ICN guidelines. An order to discontinue the "starter TPN" solution once the new TPN arrives w ...
Coenzyme B 12-Dependent Ribonucleotide Reductase: Evidence
... in that, in contrast to most other enzymes that play key roles in primary metabolism, the reductases are not conserved with respect to quaternary structure and cofactor requirement. The ribonucleotide reductases have been classified on the basis of their cofactor requirement and quaternary structure ...
... in that, in contrast to most other enzymes that play key roles in primary metabolism, the reductases are not conserved with respect to quaternary structure and cofactor requirement. The ribonucleotide reductases have been classified on the basis of their cofactor requirement and quaternary structure ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... monophosphate pathway of phosphogluconate pathway and during the citrate shuttle ...
... monophosphate pathway of phosphogluconate pathway and during the citrate shuttle ...
Potato Bubbles: Intro to Enzymes Laboratory
... means that they ____________ _____ chemical reactions in our body. The way enzymes speed up reactions is by lowering the ______________________ _______________. Catalyzed reactions (reactions with an enzyme) happen much _________________ than uncatalyzed reactions (reactions without an enzyme). Dire ...
... means that they ____________ _____ chemical reactions in our body. The way enzymes speed up reactions is by lowering the ______________________ _______________. Catalyzed reactions (reactions with an enzyme) happen much _________________ than uncatalyzed reactions (reactions without an enzyme). Dire ...
̶ Targets like an antibody ̶ Performs like a small molecule ̶
... Identification of phage Bicycle binders – binders were selected from chemically scaffolded “naïve” phage libraries(2) and then optimized using target-specific bespoke phage libraries. Binding affinity of Bicycles – determined by fluorescence polarization (FP) using either fluorescein-labelled Bicycl ...
... Identification of phage Bicycle binders – binders were selected from chemically scaffolded “naïve” phage libraries(2) and then optimized using target-specific bespoke phage libraries. Binding affinity of Bicycles – determined by fluorescence polarization (FP) using either fluorescein-labelled Bicycl ...
Development of Software Package for Determining Protein
... contour) red represents the negative, and the blue represent the positive ...
... contour) red represents the negative, and the blue represent the positive ...
Antibiotics By - Sudan University of Science and technology
... Definition of Antibiotic A substance of biological, semisyntheticor synthetic origin of low molecular weight (on-protein) produced by a fungus or bacterium as secondary metabolites that inhibits or stop growth of other microorganisms in vitro and in vivo selectively, when it used in low concent ...
... Definition of Antibiotic A substance of biological, semisyntheticor synthetic origin of low molecular weight (on-protein) produced by a fungus or bacterium as secondary metabolites that inhibits or stop growth of other microorganisms in vitro and in vivo selectively, when it used in low concent ...
Regulation of secondary metabolism in fungi
... intermediate in the aflatoxin pathway. These workers found that whereas ammonium salts support both growth and production, nitrate utilization yields only growth. Kachholz and Demain (27) working with an averufin—(another intermediate) producing mutant showed that nitrate represses averufin producti ...
... intermediate in the aflatoxin pathway. These workers found that whereas ammonium salts support both growth and production, nitrate utilization yields only growth. Kachholz and Demain (27) working with an averufin—(another intermediate) producing mutant showed that nitrate represses averufin producti ...
1 Organic Chemistry V : Enzyme Mechanisms and Natural Product
... kcat (yeast OMP-decarboxylase) = 39 s-1 In this case the reaction rate is increased by the enzyme by a factor of ≈ 1017 ! ...
... kcat (yeast OMP-decarboxylase) = 39 s-1 In this case the reaction rate is increased by the enzyme by a factor of ≈ 1017 ! ...
Amino Acids
... bone and chondroblasts of cartilage) and secreted into extracellular matrix. • After enzymatic modification, mature collagen monomers aggregate & become cross-linked to form collagen fibrils ...
... bone and chondroblasts of cartilage) and secreted into extracellular matrix. • After enzymatic modification, mature collagen monomers aggregate & become cross-linked to form collagen fibrils ...
Print this article - Journals at the University of Arizona
... It is essential to ensure that the pretreatment procedures used do not add significant amounts of carbon contamination. The extraneous carbon resulting from the extra steps involved in separating single amino acids using chromatographic technique comes from 2 sources: 1) from the stationary phase: 1 ...
... It is essential to ensure that the pretreatment procedures used do not add significant amounts of carbon contamination. The extraneous carbon resulting from the extra steps involved in separating single amino acids using chromatographic technique comes from 2 sources: 1) from the stationary phase: 1 ...
mammalian hibernation: biochemical adaptation
... of ATP production needed to support their shivering is supplied by aerobic sugar oxidation in muscle using the massive stores of honey that the colony laid down from summer foraging. Hence, honeybees use a social solution to winter warmth. Another futile form of ATP turnover that supports thermogene ...
... of ATP production needed to support their shivering is supplied by aerobic sugar oxidation in muscle using the massive stores of honey that the colony laid down from summer foraging. Hence, honeybees use a social solution to winter warmth. Another futile form of ATP turnover that supports thermogene ...
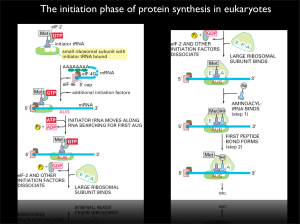
The initiation phase of protein synthesis in eukaryotes
... uORF1, ∼50% of the 40S ribosomes remain attached to the mRNA and resume scanning. Under nonstarvation conditions, the 40S subunit quickly rebinds the TC and reinitiates at uORF4 because the ...
... uORF1, ∼50% of the 40S ribosomes remain attached to the mRNA and resume scanning. Under nonstarvation conditions, the 40S subunit quickly rebinds the TC and reinitiates at uORF4 because the ...
cell biology and membrane biochemistry
... Receptor Guanylate cyclase, cytokine receptor super family. ...
... Receptor Guanylate cyclase, cytokine receptor super family. ...
Anatomy of the red cell membrane skeleton: unanswered questions
... specialized functional domains at the “head” end for spectrin dimer-tetramer association and for ankyrin-1 binding, and domains at the “tail” end for binding to protein 4.1R, protein 4.2, short filaments of actin and other proteins. The details of spectrin structure are shown in Figure 3. On average ...
... specialized functional domains at the “head” end for spectrin dimer-tetramer association and for ankyrin-1 binding, and domains at the “tail” end for binding to protein 4.1R, protein 4.2, short filaments of actin and other proteins. The details of spectrin structure are shown in Figure 3. On average ...
The Metabolic Significance of the Citric Acid Cycle in
... various branches of the cycle. It was possible for them to determine the extent to which decarboxylations in the cycle were responsible for the production of respiratory carbon dioxide. Their methods have the advantage of requiring the isolation of amino acids rather than of minute quantities of tra ...
... various branches of the cycle. It was possible for them to determine the extent to which decarboxylations in the cycle were responsible for the production of respiratory carbon dioxide. Their methods have the advantage of requiring the isolation of amino acids rather than of minute quantities of tra ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.