7. Making and storing fat and retrieving it to supply energy
... Most tissues can use fat to make ATP. Metabolism of fat always requires O2 and fatty acids are degraded to form CO2 in the mitochondria. CO2 is removed from the body by breathing, and it ultimately goes to the atmosphere. Two types of cells are notable in that they do not use fat as a fuel. Red bloo ...
... Most tissues can use fat to make ATP. Metabolism of fat always requires O2 and fatty acids are degraded to form CO2 in the mitochondria. CO2 is removed from the body by breathing, and it ultimately goes to the atmosphere. Two types of cells are notable in that they do not use fat as a fuel. Red bloo ...
A complete shikimate pathway in Toxoplasma gondii: an ancient
... the 54 kDa higher plant enzymes (Walker et al., 1996), but are now known also to exist in a number of divergent microbes such as Streptomyces and in the fungus N. crassa (Jensen et al., 2002). In plants, AroAII are feedbackinhibited by arogenate, a precursor of phenylalanine and tyrosine. Many bacte ...
... the 54 kDa higher plant enzymes (Walker et al., 1996), but are now known also to exist in a number of divergent microbes such as Streptomyces and in the fungus N. crassa (Jensen et al., 2002). In plants, AroAII are feedbackinhibited by arogenate, a precursor of phenylalanine and tyrosine. Many bacte ...
Extraction and distribution of free amino acids and
... and we suspect that this peak contained additional primary amines. Tryptophane is therefore not included in the results. Neither is ornithine and lysine, although they occurred in most samples, but their peaks were difftcult to quantify since they were present in low concentrations relative to other ...
... and we suspect that this peak contained additional primary amines. Tryptophane is therefore not included in the results. Neither is ornithine and lysine, although they occurred in most samples, but their peaks were difftcult to quantify since they were present in low concentrations relative to other ...
Pancreas
... groups (2-carbon structures) into acetyl CoA, which can then be used in metabolic reactions During the course of acetyl CoA production, energy is released and is used to convert NAD+ to NADH ...
... groups (2-carbon structures) into acetyl CoA, which can then be used in metabolic reactions During the course of acetyl CoA production, energy is released and is used to convert NAD+ to NADH ...
BCMB 3100 – Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics • Six Classes (IUBMB
... • Affinity labels resemble substrates, but contain reactive groups to interact covalently with the enzyme ...
... • Affinity labels resemble substrates, but contain reactive groups to interact covalently with the enzyme ...
aminoacids
... Proteins are made up of 20 different types of aminoacids Dietary proteins are digested to yield aminoacids These aminoacids are absorbed by the intestine and transferred to blood stream Aminoacids enter into different body cells from blood circulation In cells, aminoacids are then bonded together to ...
... Proteins are made up of 20 different types of aminoacids Dietary proteins are digested to yield aminoacids These aminoacids are absorbed by the intestine and transferred to blood stream Aminoacids enter into different body cells from blood circulation In cells, aminoacids are then bonded together to ...
Origin and Evolution of a New Gene Descended From alcohol
... presented as a paradox that challenges our understanding of the mechanisms underlying DNA sequence divergence. Here I show that Adh-qh is actually a new, functional gene recently descended from an Adh duplication. This descendant recruited -60new N-terminal amino acids, is considerably more basic th ...
... presented as a paradox that challenges our understanding of the mechanisms underlying DNA sequence divergence. Here I show that Adh-qh is actually a new, functional gene recently descended from an Adh duplication. This descendant recruited -60new N-terminal amino acids, is considerably more basic th ...
Differential diagnosis of (inherited) amino acid metabolism or
... acids can be metabolized into other amino acids, hormones, neurotransmitters, pigments, etc. The excess of amino acids can be degraded, mostly into organic acids. The first degradation step is usually the removal of nitrogen by transamination or deamination. Protein and amino acid metabolism is unde ...
... acids can be metabolized into other amino acids, hormones, neurotransmitters, pigments, etc. The excess of amino acids can be degraded, mostly into organic acids. The first degradation step is usually the removal of nitrogen by transamination or deamination. Protein and amino acid metabolism is unde ...
ppt
... – O2 substitutes for CO2 in the active site of the enzyme rubisco – The photosynthetic rate is reduced – Energetically less efficient – Early atmosphere contained little oxygen • Enzyme rubisco could not distinguish between O2 or CO2 and thus today this continues • Or free radical preventer? ...
... – O2 substitutes for CO2 in the active site of the enzyme rubisco – The photosynthetic rate is reduced – Energetically less efficient – Early atmosphere contained little oxygen • Enzyme rubisco could not distinguish between O2 or CO2 and thus today this continues • Or free radical preventer? ...
BIF CH4 5th proofs.qxd
... Because homology implies a common ancestor, it can also imply a common function or structure for two homologous proteins, which can be a useful pointer to function if one of the proteins is known only from its sequence. The operation of natural selection tends to result in the acceptance of mutation ...
... Because homology implies a common ancestor, it can also imply a common function or structure for two homologous proteins, which can be a useful pointer to function if one of the proteins is known only from its sequence. The operation of natural selection tends to result in the acceptance of mutation ...
C63
... fiber content due to the lack of a hull and consequently contain a slightly increased fat content. Covered barley varieties produced in Alaska appear to have a slightly lower available energy content than those produced in the Lower 48. The available energy content of hulless barleys reported here ...
... fiber content due to the lack of a hull and consequently contain a slightly increased fat content. Covered barley varieties produced in Alaska appear to have a slightly lower available energy content than those produced in the Lower 48. The available energy content of hulless barleys reported here ...
Engineering of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase reaction and
... doughs for baked products which comprises incorporation of the CGTase into the dough to increase the volume of the baked product [17]. 2.3. CGTase properties limiting its industrial application Like most starch-degrading enzymes, the CGTase from Bacillus macerans, which is used for the commercial pr ...
... doughs for baked products which comprises incorporation of the CGTase into the dough to increase the volume of the baked product [17]. 2.3. CGTase properties limiting its industrial application Like most starch-degrading enzymes, the CGTase from Bacillus macerans, which is used for the commercial pr ...
The Ovine Lens Cytoskeleton - Lincoln University Research Archive
... cell polarity, and organelle localization in a large variety of cell types (reviewed by Karsenti et al., 2006; Murray & Wolkoff, 2003). Tubulin itself is formed from dimers of !- and "tubulin, each of which are approximately 55 kDa (Padgaonkar et al., 1999). Very little work appears to have been com ...
... cell polarity, and organelle localization in a large variety of cell types (reviewed by Karsenti et al., 2006; Murray & Wolkoff, 2003). Tubulin itself is formed from dimers of !- and "tubulin, each of which are approximately 55 kDa (Padgaonkar et al., 1999). Very little work appears to have been com ...
Regulation of metabolic pathways at the cellular level
... Interconversion of enzymes • Enzyme is activated / inhibited by other enzyme • Reversible ATP-dependent phosphorylation and dephosphorylation (Ser, Thr, Tyr) • Proteinkinases and phosphatases • Phosphorylation can activate or inhibit • Fast switching between active and inactive form of the enzyme ...
... Interconversion of enzymes • Enzyme is activated / inhibited by other enzyme • Reversible ATP-dependent phosphorylation and dephosphorylation (Ser, Thr, Tyr) • Proteinkinases and phosphatases • Phosphorylation can activate or inhibit • Fast switching between active and inactive form of the enzyme ...
Protein composition and function of red and white skeletal - AJP-Cell
... fast isoforms of contractile proteins, whereas red muscle has greater abundance of contractile protein slow isoforms and higher oxidative enzyme content (16, 38, 51). The larger oxidative capacity in red muscle is due, at least in part, to a two- to threefold greater mitochondrial content compared w ...
... fast isoforms of contractile proteins, whereas red muscle has greater abundance of contractile protein slow isoforms and higher oxidative enzyme content (16, 38, 51). The larger oxidative capacity in red muscle is due, at least in part, to a two- to threefold greater mitochondrial content compared w ...
Enzyme inhibitor
... process for inhibitors with sub-nanomolar dissociation constants. In these cases, it is usually more practical to [I] + Ki − [I] treat the tight-binding inhibitor as an irreversible inhibitor Dividing by [I]+Kᵢ (see below); however, it can still be possible to estimate Kᵢ' kinetically if Kᵢ is measu ...
... process for inhibitors with sub-nanomolar dissociation constants. In these cases, it is usually more practical to [I] + Ki − [I] treat the tight-binding inhibitor as an irreversible inhibitor Dividing by [I]+Kᵢ (see below); however, it can still be possible to estimate Kᵢ' kinetically if Kᵢ is measu ...
Tasks for 1stMidtermExam. Introduction. Metabolic Regulation
... A) Green and yellow vegetables (pumpkin, sweet pepper). B) lemon, eggplant, eggs C) melon, pumpkin, milk D) pear, lemon, rose hips ...
... A) Green and yellow vegetables (pumpkin, sweet pepper). B) lemon, eggplant, eggs C) melon, pumpkin, milk D) pear, lemon, rose hips ...
Regulation of Cytochrome bd Expression in Mycobacterium
... spread from person to person through the air. The bacilli are released by a patient with active disease and inhaled by a healthy person. As soon as the bacilli reach the pulmonary alveoli they are phagocytized by macrophages (Figure 1). As a protective mechanism, the macrophages start producing lyso ...
... spread from person to person through the air. The bacilli are released by a patient with active disease and inhaled by a healthy person. As soon as the bacilli reach the pulmonary alveoli they are phagocytized by macrophages (Figure 1). As a protective mechanism, the macrophages start producing lyso ...
Folic Acid and Its Receptors - OPUS
... Unlike humans, most forms of bacteria, as well as plants and fungi, have a very unique folic acid property: the ability to create folate on their own. Folate cannot cross cell walls by diffusion or active transport, into or out of the cell. Cell walls are made of peptidoglycan, crosslinked sugars an ...
... Unlike humans, most forms of bacteria, as well as plants and fungi, have a very unique folic acid property: the ability to create folate on their own. Folate cannot cross cell walls by diffusion or active transport, into or out of the cell. Cell walls are made of peptidoglycan, crosslinked sugars an ...
Lipoteichoic Acid Synthesis and Function in Gram
... both as free membrane lipids and as LTA anchors such as β-glycosyl(1–6)-β-glucosyl(1–3)diacylglycerol (Glc2 -DAG) in S. aureus and B. subtilis or α-galactosyl(1–2)-α-glucosyl(1–3)-DAG in L. monocytogenes (34, 59, 60, 66, 69, 123, 128). However, glycolipids with mono-, tri-, or tetrasaccharides are a ...
... both as free membrane lipids and as LTA anchors such as β-glycosyl(1–6)-β-glucosyl(1–3)diacylglycerol (Glc2 -DAG) in S. aureus and B. subtilis or α-galactosyl(1–2)-α-glucosyl(1–3)-DAG in L. monocytogenes (34, 59, 60, 66, 69, 123, 128). However, glycolipids with mono-, tri-, or tetrasaccharides are a ...
Biochemistry 7/e
... the reaction proceeding through a phosphorolytic step is that: 1. The glucose is removed from glycogen in an activated state, i.e. phosphorylated and this occurs without ATP consumption. 2. The concentration of Pi in the cell is high enough to drive the equilibrium of the reaction the favorable dire ...
... the reaction proceeding through a phosphorolytic step is that: 1. The glucose is removed from glycogen in an activated state, i.e. phosphorylated and this occurs without ATP consumption. 2. The concentration of Pi in the cell is high enough to drive the equilibrium of the reaction the favorable dire ...
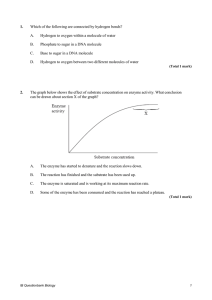
1. Which of the following are connected by hydrogen bonds? A
... PanI is a gene in cod fish that codes for an integral membrane protein called pantophysin. Two alleles of the gene, PanIA and PanIB, code for versions of pantophysin, that differ by four amino acids in one region of the protein. Samples of cod fish were collected from 23 locations in the north Atlan ...
... PanI is a gene in cod fish that codes for an integral membrane protein called pantophysin. Two alleles of the gene, PanIA and PanIB, code for versions of pantophysin, that differ by four amino acids in one region of the protein. Samples of cod fish were collected from 23 locations in the north Atlan ...
Human Physiology - Maryville University
... can be hydrolyzed to glycerol & fatty acids These can be modified to run thru Kreb's Proteins can be broken down to amino acids Which can be deaminated & run thru Kreb's These pathways can be used to interconvert ...
... can be hydrolyzed to glycerol & fatty acids These can be modified to run thru Kreb's Proteins can be broken down to amino acids Which can be deaminated & run thru Kreb's These pathways can be used to interconvert ...
Basic Science for Clinicians
... However, the molecular signaling role of AMP is dramatically extended by activation of the AMPK pathway. Because many more proteins are regulated by AMPK than contain specialized AMP-binding sites, the ability of AMP to signal energy compromise is greatly enhanced. AMPK is a protein kinase that has ...
... However, the molecular signaling role of AMP is dramatically extended by activation of the AMPK pathway. Because many more proteins are regulated by AMPK than contain specialized AMP-binding sites, the ability of AMP to signal energy compromise is greatly enhanced. AMPK is a protein kinase that has ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.