Plasma membrane Affect shape and function Anchor protein to the
... 1. Impermeable barrier prevent diffusion of water soluble solute 2. Membrane protein mediate transport of specific molecule 3. Maintained by hydrophobic interaction ...
... 1. Impermeable barrier prevent diffusion of water soluble solute 2. Membrane protein mediate transport of specific molecule 3. Maintained by hydrophobic interaction ...
Amino Acid Biosynthesis Student Companion Ch 24 Self Test
... 1) What enzyme is responsible for the fixation of nitrogen? Describe it. 2) How many electrons are required to reduce nitrogen gas to ammonia? How many electrons are required in the biological reduction? 3) What are the ultimate biological molecules that act as acceptors of ammonia? What enzymes med ...
... 1) What enzyme is responsible for the fixation of nitrogen? Describe it. 2) How many electrons are required to reduce nitrogen gas to ammonia? How many electrons are required in the biological reduction? 3) What are the ultimate biological molecules that act as acceptors of ammonia? What enzymes med ...
CH 908: Mass Spectrometry Lecture 9 Electron Capture Dissociation
... Breuker, K.; McLafferty, F. W. Native electron capture dissociation for the structural characterization of noncovalent interactions in native cytochrome c Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 2003, 42, 4900-4904. ...
... Breuker, K.; McLafferty, F. W. Native electron capture dissociation for the structural characterization of noncovalent interactions in native cytochrome c Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 2003, 42, 4900-4904. ...
FT-IR Protein Structure Analyzer
... PROTA was introduced in 1998 as the first dedicated solution for structure elucidation of biologics and since has become the industry’s preferred choice. PROTA provides a fast, cost-effective and sensitive way to determine secondary structure of a protein or to follow structural changes due to pertu ...
... PROTA was introduced in 1998 as the first dedicated solution for structure elucidation of biologics and since has become the industry’s preferred choice. PROTA provides a fast, cost-effective and sensitive way to determine secondary structure of a protein or to follow structural changes due to pertu ...
AP Protein synthesis
... used to code for the protein are cut out. • introns – section that are cut out of the pre-mRNA • exons –sections that are left in the finalized mRNA ...
... used to code for the protein are cut out. • introns – section that are cut out of the pre-mRNA • exons –sections that are left in the finalized mRNA ...
Amino acids and proteins
... has an imidazole ring which often sits inside the active site of an enzyme and helps bonds to be broken or made. It can do this because it can exist in two states -uncharged, or positively charged. ...
... has an imidazole ring which often sits inside the active site of an enzyme and helps bonds to be broken or made. It can do this because it can exist in two states -uncharged, or positively charged. ...
Interactions, Tertiary Structures
... corkscrew shape with H bonds between amino acids three peptide chains woven like a rope ...
... corkscrew shape with H bonds between amino acids three peptide chains woven like a rope ...
Trimer Codon Mix 2 Antisense
... Trimer Codon Mix 2 omits the codon for cysteine and contains codons for the other 19 amino acids. This option is for those researchers who specifically want to exclude cysteine from their protein/peptide libraries. Such omission is often done to avoid complications resulting from intrachain and/or i ...
... Trimer Codon Mix 2 omits the codon for cysteine and contains codons for the other 19 amino acids. This option is for those researchers who specifically want to exclude cysteine from their protein/peptide libraries. Such omission is often done to avoid complications resulting from intrachain and/or i ...
Intro to Cell Biology Review
... for a late night snack. Your blood sugar goes back up. Which of the characteristics of living things is this an example of? ...
... for a late night snack. Your blood sugar goes back up. Which of the characteristics of living things is this an example of? ...
Amino Acid - forte elements
... of glucose and other amino acids. It also serves as an important energy source of cells of the immune system by providing fuel in the form of nitrogen and carbon. After surgery or traumatic injury, nitrogen is necessary for wound repair and organ function. About one-third of this nitrogen is derived ...
... of glucose and other amino acids. It also serves as an important energy source of cells of the immune system by providing fuel in the form of nitrogen and carbon. After surgery or traumatic injury, nitrogen is necessary for wound repair and organ function. About one-third of this nitrogen is derived ...
Or Is It? Section 1: Characteristics of Living Things (pg 4-7)
... All living things are made of one or more cells. o A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life ...
... All living things are made of one or more cells. o A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life ...
Amino Acids Are the Building Blocks Of Proteins
... a. Identify the following components: amino group, carboxyl group, the R group or sidechain, alpha carbon, carboxyl carbon, nitrogen. (See labeled diagram and parts list above.) b. Compare the two amino acids that have been built. Are they similar? How might two amino acids be different? Amino acids ...
... a. Identify the following components: amino group, carboxyl group, the R group or sidechain, alpha carbon, carboxyl carbon, nitrogen. (See labeled diagram and parts list above.) b. Compare the two amino acids that have been built. Are they similar? How might two amino acids be different? Amino acids ...
Definition of a RACK1 Interaction Network in Drosophila
... showed that Receptor for Activated protein C Kinase 1 (RACK1) is an essential host factor for the replication of fly and human viruses (Majzoub et al. 2014). More specifically, we demonstrated that RACK1, a component of the 40S subunit of the ribosome, is required for translation driven by the 5’ in ...
... showed that Receptor for Activated protein C Kinase 1 (RACK1) is an essential host factor for the replication of fly and human viruses (Majzoub et al. 2014). More specifically, we demonstrated that RACK1, a component of the 40S subunit of the ribosome, is required for translation driven by the 5’ in ...
Amino Acids are the Building Blocks of Proteins
... a. Identify the following components: amino group, carboxyl group, the R group or sidechain, alpha carbon, carboxyl carbon, nitrogen. (See labeled diagram and parts list above.) b. Compare the two amino acids that have been built. Are they similar? How might two amino acids be different? Amino acids ...
... a. Identify the following components: amino group, carboxyl group, the R group or sidechain, alpha carbon, carboxyl carbon, nitrogen. (See labeled diagram and parts list above.) b. Compare the two amino acids that have been built. Are they similar? How might two amino acids be different? Amino acids ...
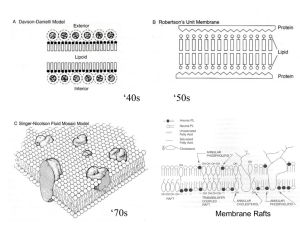
lecture 11
... 4 reviews on domain formation in model membranes and physical properties that underlie raft formation 2 reviews to describe techniques used for studying rafts (FRET) – and uncertainty for detecting rafts in cell membranes Raft Function in Cells: 4 on signal transduction(IgE receptor signaling, Growt ...
... 4 reviews on domain formation in model membranes and physical properties that underlie raft formation 2 reviews to describe techniques used for studying rafts (FRET) – and uncertainty for detecting rafts in cell membranes Raft Function in Cells: 4 on signal transduction(IgE receptor signaling, Growt ...
Class: Protein functional Annotation and Family Classification
... When an experiment yields a sequence (or a set of sequences), we need to find out as much as we can about this protein and its possible function from available data Especially important for poorly characterized or uncharacterized (“hypothetical”) proteins More challenging for large sets of sequences ...
... When an experiment yields a sequence (or a set of sequences), we need to find out as much as we can about this protein and its possible function from available data Especially important for poorly characterized or uncharacterized (“hypothetical”) proteins More challenging for large sets of sequences ...
Interactions between Human Two-pore Channels and Nonaspanin
... Two pore channels, a family consisting of TPC1, TPC2, TPC3, are cation-selective ion channels. Structurally, they contain two six transmembrane domains and form a dimer in the membrane (6). TPCs are found in plants and mammalian cells, and humans express two TPC isoforms TPC1 and TPC2, which locali ...
... Two pore channels, a family consisting of TPC1, TPC2, TPC3, are cation-selective ion channels. Structurally, they contain two six transmembrane domains and form a dimer in the membrane (6). TPCs are found in plants and mammalian cells, and humans express two TPC isoforms TPC1 and TPC2, which locali ...
You Asked for it…..
... Remember, genes are made of DNA and are in the nucleus Genes (DNA) contain the instruction for making a protein In transcription, DNA is used to make mRNA in the nucleus mRNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome In translation, tRNA then brings amino acids in the proper order to make the ...
... Remember, genes are made of DNA and are in the nucleus Genes (DNA) contain the instruction for making a protein In transcription, DNA is used to make mRNA in the nucleus mRNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome In translation, tRNA then brings amino acids in the proper order to make the ...
Computational Biology Lecture #1: Introduction
... • “Using only the solid lines in [earlier figure] we found no such parameter sets despite extensive efforts.. Thus the solid connections cannot suffice to explain even the most basic behavior of the segment polarity network… • “There must be active repression of en cells anterior to wg-expressing st ...
... • “Using only the solid lines in [earlier figure] we found no such parameter sets despite extensive efforts.. Thus the solid connections cannot suffice to explain even the most basic behavior of the segment polarity network… • “There must be active repression of en cells anterior to wg-expressing st ...
NOTE: The provided figures may be useful and beneficial. Use them
... 7. The polypeptide chain that makes up a tight junction weaves back & forth through the membrane 4 times, with 2 extra-cellular loops, and 1 loop plus short C-terminal and N-terminal tails in the cytoplasm. Looking at Figure 5.17, what would you predict about the amino acid sequence of each region n ...
... 7. The polypeptide chain that makes up a tight junction weaves back & forth through the membrane 4 times, with 2 extra-cellular loops, and 1 loop plus short C-terminal and N-terminal tails in the cytoplasm. Looking at Figure 5.17, what would you predict about the amino acid sequence of each region n ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.