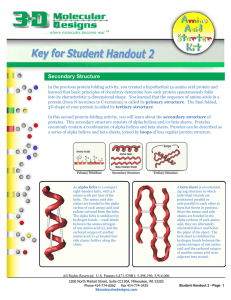
UNIT 2. Structure and function of proteins.
... ANALYSIS OF THE PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN: AMINO ACID SEQUENCE: • Chromatographic methods used to separate amino acids: Ion exchange chromatography: the charged molecules of interest (amino acids) are exchanged for another ion (salt ion) on a charged solid support (resins). Resins containing ne ...
... ANALYSIS OF THE PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN: AMINO ACID SEQUENCE: • Chromatographic methods used to separate amino acids: Ion exchange chromatography: the charged molecules of interest (amino acids) are exchanged for another ion (salt ion) on a charged solid support (resins). Resins containing ne ...
2.3. Three-Dimensional structure and function of proteins.
... ANALYSIS OF THE PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN: AMINO ACID SEQUENCE: • Chromatographic methods used to separate amino acids: Ion exchange chromatography: the charged molecules of interest (amino acids) are exchanged for another ion (salt ion) on a charged solid support (resins). Resins containing ne ...
... ANALYSIS OF THE PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN: AMINO ACID SEQUENCE: • Chromatographic methods used to separate amino acids: Ion exchange chromatography: the charged molecules of interest (amino acids) are exchanged for another ion (salt ion) on a charged solid support (resins). Resins containing ne ...
Davisco Whey Protein Processing
... Major whey protein fractions β-lactoglobulin ♦ Major whey protein (50% of total whey protein) ♦ 162 a.a., 2 disulfide bonds and one free cysteine, high in branched chain amino acids ♦ Often blamed for allergic reactions (not present in human milk) ♦ Undergoes pH dependent self association react ...
... Major whey protein fractions β-lactoglobulin ♦ Major whey protein (50% of total whey protein) ♦ 162 a.a., 2 disulfide bonds and one free cysteine, high in branched chain amino acids ♦ Often blamed for allergic reactions (not present in human milk) ♦ Undergoes pH dependent self association react ...
Proteomics methods for subcellular proteome analysis
... allowing peptide matching of MS data [13]. This allows accurate identification of proteins in the original sample, providing an inventory of the proteins that are present in the isolated organelle. For several compartments, such as the nucleus and the mitochondrion, biochemical enrichment is general ...
... allowing peptide matching of MS data [13]. This allows accurate identification of proteins in the original sample, providing an inventory of the proteins that are present in the isolated organelle. For several compartments, such as the nucleus and the mitochondrion, biochemical enrichment is general ...
essential amino acid
... synthesized de novo by the organism being considered, and therefore must be supplied in its diet. The nine amino acids humans cannot synthesize are phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, methionine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, and histidine. ...
... synthesized de novo by the organism being considered, and therefore must be supplied in its diet. The nine amino acids humans cannot synthesize are phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, methionine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, and histidine. ...
L11 Biochem alterations postharv storage - e
... 2. Cathepsin D Acid proteinase (optimum pH 4.0). It is relatively heat labile (inactivated by 70°C for 10 min). ...
... 2. Cathepsin D Acid proteinase (optimum pH 4.0). It is relatively heat labile (inactivated by 70°C for 10 min). ...
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Wheat is widely grown in Australia
... Wheat is widely grown in Australia, mainly for flour milling, with wheat not suitable for flour being used as stock feed. The protein, amino acid and energy content of wheat can vary widely. A protein range of 10 to 18.5 percent on an ‘as fed’ basis (11 to 21 percent on a dry matter basis) can o ...
... Wheat is widely grown in Australia, mainly for flour milling, with wheat not suitable for flour being used as stock feed. The protein, amino acid and energy content of wheat can vary widely. A protein range of 10 to 18.5 percent on an ‘as fed’ basis (11 to 21 percent on a dry matter basis) can o ...
Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: Read Section 2.1 – Atoms
... 24. Enzymes affect chemical reactions in living organisms by a. changing the direction of a reaction b. breaking down molecules into starch c. increasing the temperature range d. weakening bonds in all reactants 25. The specific reactants that an enzyme acts on are called a. catalysts ...
... 24. Enzymes affect chemical reactions in living organisms by a. changing the direction of a reaction b. breaking down molecules into starch c. increasing the temperature range d. weakening bonds in all reactants 25. The specific reactants that an enzyme acts on are called a. catalysts ...
Enzymes - Solon City Schools
... Think about it Tannic acid is used to form a scab on a burn. An egg becomes hard boiled when placed in hot water. What is similar about these two events? ...
... Think about it Tannic acid is used to form a scab on a burn. An egg becomes hard boiled when placed in hot water. What is similar about these two events? ...
CHEM 452.
... This course starts by exploring the chemical basis of biochemistry and molecular biology. It then examines the molecular components of cells to include proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. It examines the role of proteins as enzymes and the part they play in carbohydrate and lipid met ...
... This course starts by exploring the chemical basis of biochemistry and molecular biology. It then examines the molecular components of cells to include proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. It examines the role of proteins as enzymes and the part they play in carbohydrate and lipid met ...
II. Beta oxidation of fatty acid
... A. RNA polymerase II has 3’-5’ exonuclease activity and can proofread its work B. DNA polymerase II has 3’-5’ exonuclease activity and can proofread its work C. mRNA half-life is short and mRNA is not passed on to the cell’s progeny D. Ribosomes can bypass errors in mRNA transcript and continue with ...
... A. RNA polymerase II has 3’-5’ exonuclease activity and can proofread its work B. DNA polymerase II has 3’-5’ exonuclease activity and can proofread its work C. mRNA half-life is short and mRNA is not passed on to the cell’s progeny D. Ribosomes can bypass errors in mRNA transcript and continue with ...
Protein Structure Prediction and Structural Genomics
... produced by de novo methods is much lower than that of comparative models based on alignments with more than 30% sequence identity, but the basic topology of a protein or domain can in some cases be predicted reasonably well (Fig. 1, D and E). For roughly 40% of proteins shorter than 150 amino acids ...
... produced by de novo methods is much lower than that of comparative models based on alignments with more than 30% sequence identity, but the basic topology of a protein or domain can in some cases be predicted reasonably well (Fig. 1, D and E). For roughly 40% of proteins shorter than 150 amino acids ...
... between the OH group and the 3’OH on the adenine of the CCA acceptor stem. However, when this charged tRNA is incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain on the ribosome it terminates elongation of the chain. Based on your knowledge of peptide bond formation in the ribosome, how does H2N this co ...
9) Banned Substances - Mondovi School District
... Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (hCG) Insulin-like growth hormone (IGF-1) Leutenizin hormone (LH) All the respective releasing factors of the above-mentioned substances are also banned: Erythropoietin (EPO), darbypoetin, sermorelin DISCOURAGED – Schools may not provide or allow in connection to school ...
... Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (hCG) Insulin-like growth hormone (IGF-1) Leutenizin hormone (LH) All the respective releasing factors of the above-mentioned substances are also banned: Erythropoietin (EPO), darbypoetin, sermorelin DISCOURAGED – Schools may not provide or allow in connection to school ...
Biological effects of GH
... – Coupled with zinc within the beta cells – Very short life • Around 5 to 15 min after synthesis • Metabolized by kidneys and liver ...
... – Coupled with zinc within the beta cells – Very short life • Around 5 to 15 min after synthesis • Metabolized by kidneys and liver ...
Identification of two novel mutations associated
... 461 amino acid residues [3,4]. The human PS gene (PROS1) resides on chromosome 3 (3p11.1-q11.2) and contains 15 exons coding for 636 amino acid residues [5-7]. The human genome also contains a pseudogene for protein S (PROSP or PROS2) also located on chromosome 3 (3p21-cen) [5-7]. Hereditary deficie ...
... 461 amino acid residues [3,4]. The human PS gene (PROS1) resides on chromosome 3 (3p11.1-q11.2) and contains 15 exons coding for 636 amino acid residues [5-7]. The human genome also contains a pseudogene for protein S (PROSP or PROS2) also located on chromosome 3 (3p21-cen) [5-7]. Hereditary deficie ...
Heat shock response in hyperthermophilic microorganisms
... and J Baross, unpublished results]. The densest protein band produced in both organisms during heat-shock, as seen by pulse labeling with 35S-labeled amino acids, had a mass of approximately 60 kDa and was shown to be a chaperonin [see below]. In ES4, other proteins of various masses were also produ ...
... and J Baross, unpublished results]. The densest protein band produced in both organisms during heat-shock, as seen by pulse labeling with 35S-labeled amino acids, had a mass of approximately 60 kDa and was shown to be a chaperonin [see below]. In ES4, other proteins of various masses were also produ ...
Identification of Pseudomonas proteins coordinately
... Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) are microorganisms with a potential to enhance crop yields. They can contribute to plant growth by biofertilization, by secretion of growth hormones or by the production of antibiotics that control pathogenic fungi and competing bacteria (Bloemberg & Lugt ...
... Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) are microorganisms with a potential to enhance crop yields. They can contribute to plant growth by biofertilization, by secretion of growth hormones or by the production of antibiotics that control pathogenic fungi and competing bacteria (Bloemberg & Lugt ...
Regulation of cellular homoeostasis by reversible lysine acetylation
... activity in yeast, where the reduction in calories caused an increase in available NAD+, which is required for sirtuin function [11]. The ability of SIRT1 homologues to increase lifespan in various organisms led to the search for novel chemical activators. One of the best known is resveratrol, an an ...
... activity in yeast, where the reduction in calories caused an increase in available NAD+, which is required for sirtuin function [11]. The ability of SIRT1 homologues to increase lifespan in various organisms led to the search for novel chemical activators. One of the best known is resveratrol, an an ...
Presentation453.12
... Electrophoresis under native conditions in either agarose (a mixture of a polysaccharide derived from algae) or acrylamide can be used not only to separate nucleic acids based on their size but also based on their conformation Double stranded DNA - can be separated according to their size under nati ...
... Electrophoresis under native conditions in either agarose (a mixture of a polysaccharide derived from algae) or acrylamide can be used not only to separate nucleic acids based on their size but also based on their conformation Double stranded DNA - can be separated according to their size under nati ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.